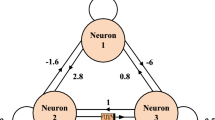
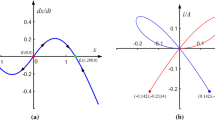
Abstract
Neural networks with changeable synaptic weights usually exhibit more complex and diverse dynamics than those with fixed synaptic weights. It was proved that the tri-neuron resistive-cyclic Hopfield neural network (RC-HNN) cannot show chaos. To this end, we first consider a RC-HNN with bipolar pulse current to generate double-scroll chaotic attractors. On this basis, we then construct a tri-neuron memristive-cyclic Hopfield neural network (MC-HNN) by replacing the resistive weights with memristive ones, and spatial multi-scroll chaotic behaviors and spatial initial-offset coexisting behaviors are revealed therein using phase portrait, Poincaré map and basin of attraction. The results manifest that by setting the parameters related to the internal states of three memristors, the MC-HNN can not only generate spatial multi-scroll chaotic attractors (MSCAs) with different scroll numbers, but also produce spatial initial-offset coexisting attractors (IOCAs) with different attractor numbers. Besides, an FPGA hardware platform is developed and the spatial MSCAs and spatial IOCAs are displayed experimentally to confirm the numerical simulations.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hopfield, J.J.: Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of 2-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81(10), 3088–3092 (1984)
Aram, Z., Jafari, S., Ma, J., Sprott, J.C., Zendehrouh, S., Pham, V.T.: Using chaotic artificial neural networks to model memory in the brain. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 44, 449–459 (2017)
Hu, S.G., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., et al.: Associative memory realized by a reconfigurable memristive Hopfield neural network. Nat. Commun. 6(7), 7522 (2015)
Chen, C., Chen, J., Bao, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3385–3399 (2019)
Li, C., Yang, Y., Yang, X., Zi, X., Xiao, F.: A tristable locally active memristor and its application in Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 108(2), 1697–1717 (2022)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Hong, Q., Sun, Y.: A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020)
Balasubramonian, M., Rajamani, V.: Design and real-time implementation of SHEPWM in single-phase inverter using generalized Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(11), 6327–6336 (2014)
Yu, F., Zhang, Z., Shen, H., Huang, Y., Cai, S., Du, S.: FPGA implementation and image encryption application of a new PRNG based on a memristive Hopfield neural network with a special activation gradient. Chin. Phys. B 31(2), 020505 (2022)
Njitacke, Z.T., Isaac, S.D., Nestor, T., Kengne, J.: Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3D Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Comput. Appl. 33(12), 6733–6752 (2021)
Xu, S., Wang, X., Ye, X.: A new fractional-order chaos system of Hopfield neural network and its application in image encryption. Chaos Solitons Fractals 157, 111889 (2022)
Njitacke, Z.T., Matze, C.L., Tsotsop, M.F.: Remerging feigenbaum trees, coexisting behaviors and bursting oscillations in a novel 3D generalized Hopfield neural network. Neural. Process. Lett. 52(1), 267–289 (2020)
Bao, H., Hua, M., Ma, J., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Offset-control plane coexisting behaviors in two-memristor-based Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 70(10), 10526–10535 (2023)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Chen, C., Sun, Y., Zhou, C., Xu, C., Hong, Q.: Neural bursting and synchronization emulated by neural networks and circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 68(8), 3397–3410 (2021)
Chua, L., Sbitnev, V., Kim, H.: Hodgkin–Huxley axon is made of memristors. Int. J. Bifur. Chaos 22(3), 1230011 (2012)
Lehtonen, E., Poikonen, J.H., Laiho, M., Kanerva, P.: Large-scale memristive associative memories. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 22(3), 562–574 (2014)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, J., Iu, H.H.C.: Memristor-coupled asymmetric neural networks: bionic modeling, chaotic dynamics analysis and encryption application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166, 112905 (2023)
Ding, S., Wang, N., Bao, H., Chen, B., Xu, Q.: Memristor synapse-coupled piecewise-linear simplified Hopfield neural network: dynamics analysis and circuit implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166, 112899 (2023)
Cai, F., Kumar, S., Van Vaerenbergh, T., et al.: Power-efficient combinatorial optimization using intrinsic noise in memristor Hopfield neural networks. Nat. Electron. 3(7), 409–418 (2020)
Hu, X., Liu, C., Liu, L., Ni, J., Yao, Y.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network under electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(3), 1541–1554 (2018)
Yu, F., Shen, H., Zhang, Z., Huang, Y., Cai, S., Du, S.: Dynamics analysis, hardware implementation and engineering applications of novel multi-style attractors in a neural network under electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 152, 111350 (2021)
Wan, Q., Yan, Z., Li, F., Chen, S., Liu, J.: Complex dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. Chaos 32(7), 073107 (2022)
Chen, C., Min, F., Zhang, Y., Bao, B.: Memristive electromagnetic induction effects on Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(3), 2559–2576 (2021)
Leng, Y., Yu, D., Hu, Y., Yu, S., Ye, Z.: Dynamic behaviors of hyperbolic-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network considering synaptic crosstalk. Chaos 30(3), 033108 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Cui, L., Sun, Y., Zhang, X., Yao, W.: Hyperchaotic memristive ring neural network and application in medical image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. 110(1), 841–855 (2022)
Lai, Q., Lai, C., Kuate, P.D.K., Li, C., He, S.: Chaos in a simplest cyclic memristive neural network. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 32(3), 2250042 (2022)
Chen, C., Min, F.: ReLU-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231(16), 2979–2992 (2022)
Dong, T., Gong, X., Huang, T.: Zero-Hopf bifurcation of a memristive synaptic Hopfield neural network with time delay. Neural Netw. 149, 146–156 (2022)
Njitacke, Z.T., Kengne, J.: Complex dynamics of a 4D Hopfield neural networks (HNNs) with a nonlinear synaptic weight: Coexistence of multiple attractors and remerging Feigenbaum trees. AEÜ-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 93, 242–252 (2018)
Doubla, I.S., Ramakrishnan, B., Tabekoueng, Z.N., Kengne, J., Rajagopal, K.: Infinitely many coexisting hidden attractors in a new hyperbolic-type memristor based HNN. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 231, 2371–2385 (2022)
Parastesh, F., Jafari, S., Azarnoush, H., Hatef, B., Namazi, H., Dudkowski, D.: Chimera in a network of memristor-based Hopfield neural network. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 2023–2033 (2019)
Yu, F., Kong, X., Mokbel, A.A.M., Yao, W., Cai, S.: Complex dynamics, hardware implementation and image encryption application of multiscroll memeristive Hopfield neural network with a novel local active memeristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 70(1), 326–330 (2022)
Bao, H., Chen, Z., Cai, J., Xu, Q., Bao, B.: Memristive cyclic three-neuron-based neural network with chaos and global coexisting attractors. Sci. China Tech. Sci. 65(11), 2582–2592 (2022)
Wang, N., Zhang, G., Kuznetsov, N.V., Li, H.: Generating grid chaotic sea from system without equilibrium point. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 107, 106194 (2022)
Bao, H., Ding, R., Chen, B., Xu, Q., Bao, B.: Two-dimensional non-autonomous neuron model with parameter-controlled multi-scroll chaotic attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 169, 113228 (2023)
Yu, F., Shen, H., Yu, Q., Kong, X., Sharma, P.K., Cai, S.: Privacy protection of medical data based on multi-scroll memristive Hopfield neural network. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 10(2), 845–858 (2023)
Bao, B., Wang, Z., Hua, Z., Chen, M., Bao, H.: Regime transition and multi-scroll hyperchaos in a discrete neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 13499–13512 (2023)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Xu, C., Zhang, X., Iu, H.H.C.: A memristive synapse control method to generate diversified multi-structure chaotic attractors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst.. Integr. Circuits Syst. 42(3), 942–955 (2023)
Lai, Q., Wan, Z., Kuate, P.D.K.: Generating grid multi-scroll attractors in memristive neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 70(3), 1324–1336 (2023)
Wan, Q., Li, F., Chen, S., Yang, Q.: Symmetric multi-scroll attractors in magnetized Hopfield neural network under pulse controlled memristor and pulse current stimulation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 169, 113259 (2023)
Wan, Q., Chen, S., Yang, Q., Liu, J., Sun, K.: Grid multi-scroll attractors in memristive Hopfield neural network under pulse current stimulation and multi-piecewise memristor. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(19), 18505–18521 (2023)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., Hong, Q., Xu, C., Sun, Y.: A triple-memristor Hopfield neural network with space multi-structure attractors and space initial-offset behaviors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst.. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAD.2023.3287760
Ma, J.: Biophysical neurons, energy, and synapse controllability: a review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 24(2), 109–129 (2023)
Xie, Y., Yao, Z., Ma, J.: Phase synchronization and energy balance between neurons. Front. Inform. Technol. Electron. Eng. 23(9), 1407–1420 (2022)
Yang, X.: 3-D cellular neural networks with cyclic connections cannot exhibit chaos. Int. J. Bifur. Chaos 18(4), 1227–1230 (2008)
Yang, X., Huan, Y.: Complex dynamics in simple Hopfield neural networks. Chaos 16(3), 033114 (2006)
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W.: Bipolar pulse-induced coexisting firing patterns in two-dimensional Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model. Int. J. Bifuration Chaos 29(1), 1950006 (2019)
Lai, Q., Wan, Z., Zhang, H., Chen, G.: Design and analysis of multiscroll memristive Hopfield neural network with adjustable memductance and application to image encryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3146570
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., Zeng, Z., He, S.: Initial offset boosting coexisting attractors in memristive multi-double-scroll Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(2), 2821–2841 (2020)
Yu, X., Bao, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Energy balance via memristor synapse in Morris–Lecar two-neuron network with FPGA implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 171, 113442 (2023)
Ding, S., Wang, N., Bao, H., Chen, B., Wu, H., Xu, Q.: Memristor synapse-coupled piecewise-linear simplified Hopfield neural network: dynamics analysis and circuit implementation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 166, 112899 (2023)
Bao, H., Hua, Z., Li, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Memristor-based hyperchaotic maps and application in auxiliary classifier generative adversarial nets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 18(8), 5297–5306 (2022)
Cao, W., Cai, H., Hua, Z.: n-Dimensional chaotic map with application in secure communication. Chaos Solitons Fractals 163, 112519 (2022)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China under Grant No. 62201094, Grant No. 62271088, Grant No. 52277001, and Grant No. 12172066, the Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial Education Department, China, under Grant No. 22KJB510001, and the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, China, under Grant No. KYCX23_3175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, H., Chen, Z., Chen, M. et al. Memristive-cyclic Hopfield neural network: spatial multi-scroll chaotic attractors and spatial initial-offset coexisting behaviors. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 22535–22550 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08993-8