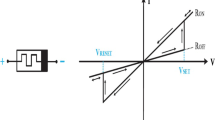
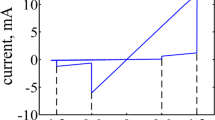
Abstract
Memristor is one of the most promising emerging technologies to solve the von Neumann bottleneck problem due to its non-volatile and binary characteristics. This paper studies the design method of high-efficiency logic circuit based on memristor. First, a multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO) logic circuit design scheme based on IMPLY and AND logic is proposed, which can derive multiple new efficient logic operation methods and complete complex logic with fewer steps and memristors. Second, in order to perform rapid interactive operations between different rows, an alternating crossbar array structure is designed which can quickly complete cross-row logic operations. Finally, a high-efficient full adder (FA) based on MIMO logic and alternating crossbar array is proposed. To accomplish 32-bit add operation, the proposed FA needs 160 memristors and only 41 steps. Compared with the state of art FA, our work has faster execution speed and fewer memristors.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article, as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Chua, L.O.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
Chua, L.O., Kang, S.M.: Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 64(2), 209–223 (1976)
Ho, Y., Huang, G.M., Li, P.: Dynamical properties and design analysis for nonvolatile memristor memories. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 58(4), 724–736 (2011)
Zangeneh, M., Joshi, A.: Design and optimization of nonvolatile multibit 1T1R resistive RAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 22(8), 1815–1828 (2014)
Wang, X., Li, S., Liu, H., Zeng, Z.: A compact scheme of reading and writing for memristor-based multi-valued memory. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aid. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 37, 1505–1509 (2017)
Zhou, C., Wang, C., Sun, Y., Yao, W., Lin, H.: Cluster output synchronizationfor memristive neural networks. Inf. Sci. 589, 459–477 (2022)
Zhou, C., Wang, C., Yao, W., Lin, H.: Observer-based synchronization of memristive neural networks under DoSattacks and actuator saturation and its application to image encryption. Appl. Math. Computat. 425, 127080 (2022)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Cui, L., Sun, Y., Xu, C., Yu, F.: Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption. IEEE. Trans. Ind. Inform. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3155599
Lin, H., Wang, C., Xu, C., Zhang, X., Iu, H.: A memristive synapse control method to generate diversified multi-structure chaotic attractors. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aid. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAD.2022.3186516
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, J., Zhang, X., Sun, Y., Iu, H.: Memristor-coupled asymmetric neural networks: bionic modeling, chaotic dynamics analysis and encryption application. Chaos Solitons Fract. 166, 112905 (2023)
Zhao, Q., Wang, C., Zhang, X.: A universal emulator for memristor, memcapacitor, and meminductor and its chaotic circuit. Chaos 29(1), 013141 (2019)
Chen, M., Sun, M., Bao, H., Hu, Y., Bao, B.: Flux-charge analysis of two-memristor-based Chua’s circuit: dimensionality decreasing model for detecting extreme multistability. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(3), 2197–2206 (2020)
Haj-Ali, A., Ben-Hur, R., Wald, N., Ronen, R., Kvatinsky, S.: Not in name alone: a memristive memory processing unit for real in-memory processing. IEEE Micro. 38(5), 13–21 (2018)
Kvatinsky, S.: Real processing-in-memory with memristive memory processing unit (mmpu). In: 2019 IEEE 30th International Conference on Application-specific Systems, Architectures and Processors (ASAP), vol. 2160-052X, pp. 142–148 (2019)
Yang, R., Huang, H.M., Hong, Q.H., Yin, X.B., Tan, Z.H., Shi, T., Zhou, Y.X., Miao, X.S., Wang, X.P., Mi, S.B., Jia, C.L.: Synaptic suppression triplet STDP learning rule realized in second order memristors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 28(5), 1704455 (2018)
Ali, K.A., Rizk, M., Baghdadi, A., Diguet, J., Jomaah, J., Onizawa, N., Hanyu, T.: Memristive computational memory using memristor overwrite logic (mol). IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 28, 1–13 (2020)
Kvatinsky, S., Wald, N., Satat, G., Kolodny, A., Weiser, U.C., Friedman, E.G.: Mrl-memristor ratioed logic. In: 2012 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, pp. 1–6 (2012)
Papandroulidakis, G., Serb, A., Khiat, A., Merrett, G.V., Prodromakis, T.: Practical Implementation of Memristor-Based Threshold Logic Gates. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 66(8), 3041–3051 (2019)
Gale, E., de Lacy Costello, B., Adamatzky, A.: Boolean logic gates from a single memristor via low-level sequential logic. In: Unconventional Computation and Natural Computation, USA, NY, New York: Springer, pp. 79-89, (2013)
Xu, N., Fang, L., Kim, K.M., Hwang, C.S.: Time-efficient stateful dual-bit-memristor logic. physica status solidi (RRL)—Rapid Research Letters, (2019)
Kvatinsky, S., Belousov, D., Liman, S., Satat, G., Weiser, U.C.: Magic-memristor-aided logic. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 61(11), 895–899 (2014)
Borghetti, J., Snider, G.S., Kuekes, P.J., Yang, J.J., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: ‘Memristive’ switches enable ‘stateful’ logic operations via material implication. Nature 464(7290), 873–876 (2010)
Yang, Y., Mathew, J., Pontarelli, S., Ottavi, M., Pradhan, D.K.: Complementary resistive switch-based arithmetic logic implementations using material implication. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 15(1), 94–108 (2016)
Kim, K.M., Xu, N., Shao, X., Yoon, K.J., Kim, H., Williams, R., Hwang, C.S.: Single-cell stateful logic using a dual-bit memristor. physica status solidi (RRL)—Rapid Research Letters, (2018)
Guckert, L., Swartzlander, E.E.: Optimized memristor-based multipliers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 64(2), 373–385 (2017)
Kvatinsky, S., Satat, G., Wald, N., Friedman, E.G., Kolodny, A., Weiser, U.C.: Memristor-based material implication (imply) logic: design principles and methodologies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 22(10), 2054–2066 (2014)
Rohani, S.G., Taherinejad, N., Radakovits, D.: A semiparallel full-adder in imply logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 28(1), 297–301 (2020)
Shin, S., Kim, K., Kang, S.: Reconfigurable stateful nor gate for large-scale logic-array integrations. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 58(7), 442–446 (2011)
Huang, P., Kang, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, S., Han, R., Zhou, Z., Chen, Z., Ma, W., Li, M., Liu, L.: Reconfigurable nonvolatile logic operations in resistance switching crossbar array for large-scale circuits advanced materials, (2019)
Siemon, A., Drabinski, R., Schultis, M.J., Hu, X., Friedman, J.S.: Stateful three-input logic with memristive switches. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 14618 (2019)
Rohani, S.G., TaheriNejad, N.: An improved algorithm for imply logic based memristive full-adder. In: 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), pp. 1–4 (2017)
Radakovits, D., Taherinejad, N., Cai, M., Delaroche, T., Mirabbasi, S.: A memristive multiplier using semi-serial IMPLY-based adder. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 99, 1–12 (2020)
Fu, H., Hong, Q., Wang, C., Sun, J., Li, Y.: Solving non-homogeneous linear ordinary differential equations using memristor-capacitor circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(11), 4495–4507 (2021)
Ebong, I.E., Mazumder, P.: Self-controlled writing and erasing in a memristor crossbar memory. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 10(6), 1454–1463 (2011)
Talati, N., Ali, A. H., Ben Hur, R., Wald, N., Ronen, R., Gaillardon, P., Kvatinsky, S.: Practical challenges in delivering the promises of real processing-in-memory machines. In: 2018 Design, Automation Test in Europe Conference Exhibition (DATE), pp. 1628–1633, (2018)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62171182), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ3014) and the Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing, Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (CSTB 2022NSCQ-M SX0770).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Sun, J., Wang, C. et al. An efficient memristive alternating crossbar array and the design of full adder. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 20331–20345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08887-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08887-9