Abstract
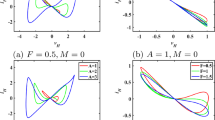
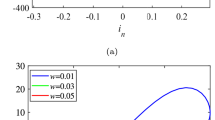
Reconstruction techniques can capture the attractor data of dissipative chaotic systems, which will lead to a threat to the security of the cryptosystem. Since conservative chaotic systems do not form chaotic attractors, they can avoid the defects of the dissipative system and resist attacks. This paper aims to construct a new type of active charge-controlled memristor based on a triangular wave and apply it to build a non-Hamiltonian globally conservative circuit, the characteristic roots of which are all on the imaginary axis. The system is critically stable and presents extremely high sensitivity to the initial values, exhibiting heterogeneous multistability and homogeneous multistability with local amplitude modulation. This special multistability is of great significance to engineering applications. In addition, as the hardware accuracy is limited and only a few conservative systems have been implemented digitally, the DSP platform is employed herein for the physical implementation of the proposed system. In the end, we applied the novel system to a plaintext-related image encryption algorithm. The results show that the system not only merely can resist the risk of data reconstruction, but also has excellent random characteristics, and is suitable for encryption. Therefore, this research makes major contributions to enriching the types of charge-controlled memristors and providing a conservative chaotic system in engineering.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chua, L.O.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–19 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337
Chua, L.: Resistance switching memories are memristors. Appl. Phys. a-Mater. Sci. Process. 102(4), 765–83 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-011-6264-9
Itoh, M., Chua, L.O.: Memristor oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 18(11), 3183–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127408022354
Bao, H., Wang, N., Bao, B.C., Chen, M., Jin, P.P., Wang, G.Y.: Initial condition-dependent dynamics and transient period in memristor-based hypogenetic jerk system with four line equilibria. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 57, 264–75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.10.001
Bao, B.C., Bao, H., Wang, N., Chen, M., Xu, Q.: Hidden extreme multistability in memristive hyperchaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 94, 102–11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2016.11.016
Yuan, F., Jin, Y., Li, Y.X.: Self-reproducing chaos and bursting oscillation analysis in a meminductor-based conservative system. Chaos 30(5), 053127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0008313
Bao, H., Hua, Z., Li, H., Chen, M., Bao, B.: Memristor-based hyperchaotic maps and application in auxiliary classifier generative adversarial nets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 18(8), 5297–306 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/tii.2021.3119387
Corinto, F., Ascoli, A.: Memristive diode bridge with LCR filter. Electron. Lett. 48(14), 824–5 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1049/el.2012.1480
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., Williams, R.S.: The missing memristor found (vol 453, pg 80, 2008). Nature 459(7250), 80–3 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08166
Njitacke, Z.T., Feudjio, C., Signing, V.F., Koumetio, B.N., Tsafack, N., Awrejcewicz, J.: Circuit and microcontroller validation of the extreme multistable dynamics of a memristive Jerk system: application to image encryption. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137(5), 619 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02821-5
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., Zeng, Z.: Multi-scroll hidden attractor in memristive HR neuron model under electromagnetic radiation and its applications. Chaos 31(1), 011101 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0035595
Pecora, L.M., Moniz, L., Nichols, J., Carroll, T.L.: A unified approach to attractor reconstruction. Chaos 17(1), 013110 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2430294
Jie, M.S., Yan, D.W., Du, X.Y., Duan, S.K., Wang, L.D.: A novel conservative system with hidden flows evolved from the simplest memristive circuit. Chaos 32(3), 033111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0066676
Wang, Z., Qi, G.Y.: Modeling and analysis of a three-terminal-memristor-based conservative chaotic system. Entropy 23(1), 71 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/e23010071
Jafari, S., Sprott, J.C., Dehghan, S.: Categories of conservative flows. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(2), 1950021 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127419500214
Li, C., Sprott, J.C.: Coexisting hidden attractors in a 4-D simplified Lorenz system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24(3), 1450034 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218127414500345
Deng, Y., Li, Y.X.: A memristive conservative chaotic circuit consisting of a memristor and a capacitor. Chaos 30(1), 013120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5128384
Du, C.H., Liu, L.C., Zhang, Z.P., Yu, S.X.: A memristive conservative chaotic circuit with two different offset boosting behaviors. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 147, 154146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aeue.2022.154146
Dong, E., Yuan, M., Du, S., Chen, Z.: A new class of Hamiltonian conservative chaotic systems with multistability and design of pseudo-random number generator. Appl. Math. Model. 73, 40–71 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.03.037
Yu, S.M.: Circuit implementation for generating three-dimensional multi-scroll chaotic attractors via triangular wave series. Acta Phys. Sin. 54(4), 1500–9 (2005). (http://wulixb.iphy.ac.cn/CN/Y2005/V54/I4/1500)
Adhikari, S.P., Sah, M.P., Kim, H., Chua, L.O.: Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Tran. Circuits Syst. I-Regular Papers 60(11), 3008–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/tcsi.2013.2256171
Qi, G.Y., Hu, J.B., Wang, Z.: Modeling of a Hamiltonian conservative chaotic system and its mechanism routes from periodic to quasiperiodic, chaos and strong chaos. Appl. Math. Model. 78, 350–65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2019.08.023
Zhang, Y., Tang, Y.J.: A plaintext-related image encryption algorithm based on chaos. Multimed. Tools Appl. 77(6), 6647–69 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4577-1
Zhang, Y.: A new unified image encryption algorithm based on a lifting transformation and chaos. Inf. Sci. 547, 307–27 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.07.058
Zhang, Y., Chen, A., Tang, Y., Dang, J., Wang, G.: Plaintext-related image encryption algorithm based on perceptron-like network. Inf. Sci. 526, 180–202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.03.054
Funding
The work was supported by the national natural science foundation of China under Grant no. 61865002; Department of Guizhou Education Provincial “Golden Class” in 2022, digital signal processing (bilingual).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, C., Liu, L., Zhang, Z. et al. A conservative system based on a triangular wave memristor and its application in image encryption. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 15515–15529 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08653-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08653-x