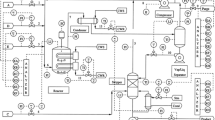
Abstract
Process data are generally subjected to noise during the measuring, transmission and processing procedures, which may lead to the deterioration and even failure of the process supervision and control. Although Kalman filters are widely used to estimate the true states of linear or linearized systems, their applications are limited to state–space models that can be mathematical or empirical. Neural networks are satisfactory solutions to model unknown nonlinear dynamic systems. However, there is no valid confidence evaluation about the model prediction of neural networks. In this paper, Gaussian process regression (GPR) complementarily advantages dynamic data reconciliation (DDR) to form a novel data-driven filtering scheme named GPR–DDR. DDR is served as an alternative filter, which is suitable for a broader class of process models compared with Kalman filters, while GPR is employed to predict system outputs with their associate uncertainty, which makes parameters of the DDR needless to online tune and adaptive for varying inputs. The effectiveness of GPR–DDR is demonstrated by its implementations on a classical mathematical example and a dynamic chemical process. The simulation results show that the proposed method can further improve the output response and is robust to changes of the noise level.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Kalman, R.E.: A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 82, 35–45 (1960)
Kalman, R.E., Bucy, R.S.: New results in linear filtering and prediction theory. J. Basic Eng. 83, 95–108 (1961)
Julier S.J., Uhlmann J.K.: New extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. In: Signal processing, sensor fusion, and target recognition, pp. 182–193 (1997)
Nørgaard, M., Poulsen, N.K., Ravn, O.: New developments in state estimation for nonlinear systems. Automatica 36, 1627–1638 (2000)
Jiang, T., Wang, J., He, Y., Wang, Y.: Design of the modified fractional central difference Kalman filters under stochastic colored noises. ISA Trans. 127, 487–500 (2022)
Arasaratnam, I., Haykin, S.: Cubature Kalman filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 54, 1254–1269 (2009)
Yang, C., Gao, Z., Miao, Y., Kan, T.: Study on initial value problem for fractional-order cubature Kalman filters of nonlinear continuous-time fractional-order systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 2387–2403 (2021)
Bai, S., Thibault, J., McLean, D.D.: Dynamic data reconciliation: alternative to Kalman filter. J. Process Control 16, 485–498 (2006)
Bai, S.H., McLean, D.D., Thibault, J.: Enhancing controller performance via dynamic data reconciliation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 83, 515–526 (2005)
Bai, S., McLean, D.D., Thibault, J.: Simultaneous measurement bias correction and dynamic data reconciliation. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 85, 111–117 (2007)
Zhang, Z., Chen, J.: Dynamic data reconciliation for enhancing performance of minimum variance control in univariate and multivariate systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 10990–11002 (2016)
Zhang, Z., Chen, J.: Enhancing performance of generalized minimum variance control via dynamic data reconciliation. J. Franklin Inst. 356, 8829–8854 (2019)
Yang, G., Zhang, Z., Zhao, S., Zhu, W., Chen, C.: Dynamic data reconciliation to decrease the effect of measurement noise on controller performance assessment. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 15, 714–722 (2020)
Ren, M., Zhang, W., Chen, J., Shi, P., Yan, G.: Performance assessment for non-Gaussian systems by minimum entropy control and dynamic data reconciliation. J. Franklin Inst. 359, 3930–3950 (2022)
Zhu, W., Zhang, Z., Armaou, A., Hu, G., Zhao, S., Huang, S.: Dynamic data reconciliation to improve the result of controller performance assessment based on GMVC. ISA Trans. 117, 288–302 (2021)
Zhu, W., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Zhao, S., Huang, S.: Dynamic data reconciliation to enhance the performance of feedforward/feedback control systems with measurement noise. J. Process Control 108, 12–24 (2021)
Xia, T., Zhang, Z., Hong, Z., Huang, S.: Design of fractional order PID controller based on minimum variance control and application of dynamic data reconciliation for improving control performance. ISA Trans. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2022.06.041
Hu, G., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., Armaou, A., Yan, Z.: Elman neural networks combined with extended Kalman filters for data-driven dynamic data reconciliation in nonlinear dynamic process systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 60, 15219–15235 (2021)
Jiang, B., Liu, Y., Geng, H., Wang, Y., Zeng, H., Ding, J.: A holistic feature selection method for enhanced short-term load forecasting of power system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3219499
Song, F., Li, Y., Cheng, W., Dong, L., Li, M., Li, J.: An improved Kalman filter based on long short-memory recurrent neural network for nonlinear radar target tracking. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 8280428 (2022)
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Li, W., Cheng, W., Zhu, Q.: State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries using gated recurrent unit recurrent neural network and adaptive Kalman filter. J. Energy Stor. 55, 105396 (2022)
Revach, G., Shlezinger, N., Ni, X., Escoriza, A.L., Van Sloun, R.J., Eldar, Y.C.: KalmanNet: neural network aided Kalman filtering for partially known dynamics. IEEE Trans. Sign. Process. 70, 1532–1547 (2022)
Neal, R.M.: Bayesian Learning for Neural Networks. Springer Science & Business Media, New York (2012)
Williams, C.K., Rasmussen, C.E.: Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2006)
Burke, J., King, S.: Edge tracing using Gaussian process regression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 138–148 (2021)
Deringer, V.L., Bartók, A.P., Bernstein, N., Wilkins, D.M., Ceriotti, M., Csányi, G.: Gaussian process regression for materials and molecules. Chem. Rev. 121, 10073–10141 (2021)
Gs, V., Vs, H.: Prediction of bus passenger traffic using Gaussian process regression. J. Sign. Process. Syst. 95(2–3), 281–292 (2023)
Liu, D., Tang, M., Fu, J.: Robust adaptive trajectory tracking for wheeled mobile robots based on Gaussian process regression. Syst. Control Lett. 163, 105210 (2022)
da Silva Lima, G., Bessa, W.M.: Sliding mode control with Gaussian process regression for underactuated mechanical systems. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 20, 963–969 (2022)
Deng, Z., Hu, X., Lin, X., Che, Y., Xu, L., Guo, W.: Data-driven state of charge estimation for lithium-ion battery packs based on Gaussian process regression. Energy 205, 118000 (2020)
Wang, J., Deng, Z., Yu, T., Yoshida, A., Xu, L., Guan, G., Abudula, A.: State of health estimation based on modified Gaussian process regression for lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Stor. 51, 104512 (2022)
Bernardo, D., Hagras, H., Tsang, E.: A genetic type-2 fuzzy logic based system for the generation of summarised linguistic predictive models for financial applications. Soft. Comput. 17, 2185–2201 (2013)
Cacciola M., Pellicanò D., Megali G., Lay-Ekuakille A., Versaci M., Morabito F.: Aspects about air pollution prediction on urban environment. In: Proceedings of the 4th IMEKO TC19 symposium on environmental instrumentation and measurements, pp. 15–20 (2013)
Yang, S., Zhang, J.: An adaptive human–machine control system based on multiple fuzzy predictive models of operator functional state. Biomed. Sign. Process. Control 8, 302–310 (2013)
Zhang, C., Xie, K., He, Y., Wang, Q., Wu, M.: An improved stability criterion for digital filters with generalized overflow arithmetic and time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67, 2099–2103 (2019)
Chen Z.: Gaussian process regression methods and extensions for stock market prediction. Ph.D. Thesis: University of Leiceste (2017)
Renson, L., Sieber, J., Barton, D.A., Shaw, A., Neild, S.: Numerical continuation in nonlinear experiments using local Gaussian process regression. Nonlinear Dyn. 98, 2811–2826 (2019)
Chen, Z., Wang, B.: How priors of initial hyperparameters affect Gaussian process regression models. Neurocomputing 275, 1702–1710 (2018)
Liu, K., Li, Y., Hu, X., Lucu, M., Widanage, W.D.: Gaussian process regression with automatic relevance determination kernel for calendar aging prediction of lithium-Ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 16, 3767–3777 (2020)
Cheng, M., Jiao, L., Yan, P., Feng, L., Qiu, T., Wang, X., Zhang, B.: Prediction of surface residual stress in end milling with Gaussian process regression. Measurement 178, 109333 (2021)
Pham, D.T., Karaboga, D.: Training Elman and Jordan networks for system identification using genetic algorithms. Artif. Intell. Eng. 13, 107–117 (1999)
Schmidt, A.D., Ray, W.H.: The dynamic behavior of continuous polymerization reactors—I: isothermal solution polymerization in a CSTR. Chem. Eng. Sci. 36, 1401–1410 (1981)
Shi W.: Development of data-based modeling, data reconciliation, controller design and performance assessment using correntropy information. Ph.D. Thesis: Chung Yuan Christian University (2012)
Hu, G., Xu, L., Zhang, Z.: Correntropy based Elman neural network for dynamic data reconciliation with gross errors. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 140, 104568 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62071363) and the Key R&D program of Shaanxi Province (2021LLRH-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, G., Xu, L. & Zhang, Z. Gaussian process regression combined with dynamic data reconciliation for improving the performance of nonlinear dynamic systems. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 15145–15163 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08624-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08624-2