Abstract
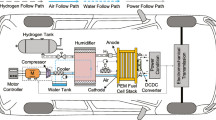
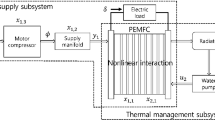
The oxygen excess ratio (OER) significantly affects the output efficiency and durability of the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC), which is unmeasurable and difficult to control reliably. This paper comprehensively considers various practical limitations of the automotive PEMFC air feeding subsystem, including time-varying load, unavailable variables, actuator saturation, performance constraints and limited communication resources, to specially address the event-triggered estimation and control problems for OER. First, a switching threshold event-triggered mechanism (STETM)-based extended state observer (termed STET-ESO) is developed to exactly estimate the unmeasured cathode pressure and OER, in which an adaptive observer bandwidth ensures a dynamic balance between disturbance rejection and noise immunity. Similarly, another STET-ESO is constructed to simultaneously approximate the lumped disturbance and the derivative of OER tracking error. Then, a prescribed performance sliding mode function and an auxiliary system are designed to deal with the tracking error constraints and input saturation, respectively. Further, a switching threshold event-triggered anti-saturation prescribed performance sliding mode controller is proposed to guarantee superior OER regulation under uncertainties, disturbances and constraints; moreover, the chattering and jump phenomena of control signal can be greatly attenuated. It is worth mentioning that different STETMs embed in the sensor-to-controller and controller-to-actuator channels can not only save communication resources, but also better compromise estimation/control performance and communication frequency; besides, the unexpected Zeno behavior can be strictly excluded. Finally, the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed scheme in different operating scenarios are verified by comparative simulations.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Shahiri, M., Ranjbar, A., Karami, M.R., Ghader, R.: Robust control of nonlinear PEMFC against uncertainty using fractional complex order control. Nonlinear Dyn. 80(4), 1785–1800 (2014)
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Chai, T.: Observer-based discrete adaptive neural network control for automotive PEMFC air-feed subsystem. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70(4), 3149–3163 (2021)
Kim, B.M., Yoo, S.J.: Decentralized event-triggered adaptive control for interconnected nonlinear dynamics of constrained air supply and thermal management systems of PEMFCs. Nonlinear Dyn. 103, 791–808 (2021)
Zhao, D., Xia, L., Dang, H., Wu, Z., Li, H.: Design and control of air supply system for PEMFC UAV based on dynamic decoupling strategy. Energy Convers. Manag. 253, 115159 (2022)
Sun, L., Jin, Y., Pan, L., Shen, J., Lee, K.Y.: Efficiency analysis and control of a grid-connected PEM fuel cell in distributed generation. Energy Convers. Manag. 195, 587–596 (2019)
Li, X., Wang, Y., Yang, D., Chen, Z.: Adaptive energy management strategy for fuel cell/battery hybrid vehicles using Pontryagin’s minimal principle. J. Power Sources 440, 227105 (2019)
Wang, Y., Diaz, D.F.R., Chen, K., Wang, Z., Adroher, X.C.: Materials, technological status, and fundamentals of PEM fuel cells—a review. Mater. Today 32, 178–203 (2020)
Wu, L., Mehrdad, F.G.: A novel fuzzy reset method for pressure control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell in the presence of uncertainty. Int. J. Energy Res. 46(2), 1951–1961 (2021)
Abbaker, A.M.O., Wang, H., Tian, Y.: Adaptive integral type-terminal sliding mode control for PEMFC air supply system using time delay estimation algorithm. Asian J. Control 24(1), 217–226 (2022)
Zhao, D., Xu, L., Huangfu, Y., Dou, M., Liu, J.: Semi-physical modeling and control of a centrifugal compressor for the air feeding of a PEM fuel cell. Energy Convers. Manag. 154, 380–386 (2017)
Yang, Z., Du, Q., Jia, Z., Yang, C., Jiao, K.: Effects of operating conditions on water and heat management by a transient multi-dimensional PEMFC system model. Energy 183, 462–476 (2019)
Pukrushpan, J.T., Stefanopoulou, A.G., Peng, H.: Control of fuel cell power systems: principles. Modeling analysis and feedback design. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Talj, R., Ortega, R., Astolfi, A.: Passivity and robust PI control of the air supply system of a PEM fuel cell model. Automatica 47(12), 2554–2561 (2011)
Chen, J., Liu, Z., Wang, F., Quan, O., Su, H.: Optimal oxygen excess ratio control for PEM fuel cells. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 26(5), 1711–1721 (2018)
Gruber, J.K., Bordons, C., Oliva, A.: Nonlinear MPC for the airflow in a PEM fuel cell using a Volterra series model. Control Eng. Pract. 20(2), 205–217 (2012)
Ziogou, C., Papadopoulou, S., Georgiadis, M.C., Voutetakis, S.: On-line nonlinear model predictive control of a PEM fuel cell system. J. Process Contr. 23(4), 483–492 (2013)
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Xu, J.: Observer-based adaptive neural network control for PEMFC air-feed subsystem. Appl. Soft Comput. 113, 108003 (2021)
Kim, B.M., Choi, Y.H., Yoo, S.J.: Adaptive control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell air supply systems with asymmetric oxygen excess ratio constraints. IEEE Access 8, 5537–5549 (2020)
Zhang, H., Wang, Y., Wang, D., Wang, Y.: Adaptive robust control of oxygen excess ratio for PEMFC system based on type-2 fuzzy logic system. Inform. Sci. 511, 1–17 (2020)
Yang, D., Pan, R., Wang, Y., Chen, Z.: Modeling and control of PEMFC air supply system based on TS fuzzy theory and predictive control. Energy 188, 116078 (2019)
Baroud, Z., Benmiloud, M., Benalia, A., Ocampo-Martinez, C.: Novel hybrid fuzzy-PID control scheme for air supply in PEM fuel-cell-based systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42(15), 10435–10447 (2017)
Kunusch, C., Puleston, P.F., Mayosky, M.A., Riera, J.: Sliding mode strategy for PEM fuel cells stacks breathing control using a super-twisting algorithm. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(1), 167–174 (2008)
Matraji, I., Laghrouche, S., Jemei, S., Wack, M.: Robust control of the PEM fuel cell air-feed system via sub-optimal second order sliding mode. Appl. Energy 104, 945–957 (2013)
Pilloni, A., Pisano, A., Usai, E.: Observer-based air excess ratio control of a PEM fuel cell system via high-order sliding mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(8), 5236–5246 (2015)
Deng, H., Li, Q., Cui, Y., Zhu, Y., Chen, W.: Nonlinear controller design based on cascade adaptive sliding mode control for PEM fuel cell air supply systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 44(35), 19357–19369 (2019)
Abbaker, A.M.O., Wang, H., Tian, Y.: Robust model-free adaptive interval type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control for PEMFC system using disturbance observer. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22(7), 2188–2203 (2020)
Esfandiari, K., Abdollahi, F., Talebi, H.A.: Adaptive control of uncertain nonaffine nonlinear systems with input saturation using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn Syst. 26(10), 2311–2322 (2014)
Wu, Y., Huang, R., Wang, Y., Wang, J.: Adaptive tracking control of robot manipulators with input saturation and time-varying output constraints. Asian J. Control 23(3), 1476–1489 (2021)
Liang, K., Lin, X., Chen, Y., Li, J., Ding, F.: Adaptive sliding mode output feedback control for dynamic positioning ships with input saturation. Ocean Eng. 206, 107245 (2020)
Rakhtala, S.M., Noei, A.R., Ghaderi, R., Usai, E.: Design of finite-time high-order sliding mode state observer: A practical insight to PEM fuel cell system. J. Process Contr. 24(1), 203–224 (2014)
Liu, J., Gao, Y., Su, X., Wack, M., Wu, L.: Disturbance-observer-based control for air management of PEM fuel cell systems via sliding mode technique. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 27(3), 1129–1138 (2018)
Yuan, H., Dai, H., Ming, P., Zhan, J., Wei, X.: A fuzzy extend state observer-based cascade decoupling controller of air supply for vehicular fuel cell system. Energy Convers. Manage. 236, 114080 (2021)
Zhang, C., Yang, G.: Event-triggered global finite-time control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 65(3), 1340–1347 (2019)
Lu, Q., Shi, P., Wu, L., Lim, C.C.: Event-triggered estimation and model predictive control for linear systems with actuator fault. IET Control Theory Appl. 14(16), 2406–2412 (2020)
Xing, L., Wen, C., Liu, Z., Su, H., Cai, J.: Event-triggered adaptive control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 62(4), 2071–2076 (2016)
Talj, R.J., Hissel, D., Ortega, R., Becherif, M., Hilairet, M.: Experimental validation of a PEM fuel-cell reduced-order model and a moto-compressor higher order sliding-mode control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(6), 1906–1913 (2009)
Huang, Y., Wang, J., Shi, D., Shi, L.: Toward event-triggered extended state observer. IEEE Trans. Autom. Contr. 63(6), 1842–1849 (2017)
Huang, S., Wang, J., Xiong, L., Liu, J., Li, P., Wang, Z.: Distributed predefined-time fractional-order sliding mode control for power system with prescribed tracking performance. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 37(3), 2233–2246 (2022)
Xu, G., Xia, Y., Zhai, D., Ma, D.: Adaptive prescribed performance terminal sliding mode attitude control for quadrotor under input saturation. IET Control Theory Appl. 14(17), 2473–2480 (2020)
Zhang, R., Xu, B., Zhao, W.: Finite-time prescribed performance control of MEMS gyroscopes. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(4), 2223–2234 (2020)
Yang, Y., Ge, C., Wang, H., Li, X., Hua, C.: Adaptive neural network based prescribed performance control for teleoperation system under input saturation. J. Frankl. Inst. 352(5), 1850–1866 (2015)
Shao, K., Zheng, J., Wang, H., Xu, F., Liang, B.: Recursive sliding mode control with adaptive disturbance observer for a linear motor positioner. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 146, 107014 (2021)
Ma, B., Luo, G., Wang, Y.: Observer-based event-triggered control of steer-by-wire systems with prespecified tracking accuracy. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 161, 107857 (2021)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number [51675091]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhang, Z., Li, H. et al. Switching threshold event-triggered estimation and control for unmeasured oxygen excess ratio of automotive PEMFC air feeding system with input and prescribed performance constraints. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 14027–14054 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08559-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08559-8