Abstract
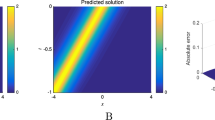
In this work, we extend the generalized conditional symmetry enhanced physics-informed neural network (gsPINN) to study the partial differential equations (PDEs) with Robin initial/boundary conditions. The gsPINN incorporates the inherent physical laws, i.e., generalized conditional symmetry of PDEs, into the loss function of PINN and thus learns higher accuracy numerical solutions than PINN with fewer training points and simpler architecture of network. More specifically, we compare the performances of PINN and gsPINN to solve the KdV-like PDEs and show that gsPINN outperforms PINN in terms of the accuracy of learned solutions. Moreover, for the problem of PDEs together with what form of initial/boundary conditions are admitted by the known generalized conditional symmetry, we use the gsPINN method to learn the undetermined functions in Robin initial/boundary conditions and demonstrate the superiorities and robustness of gsPINN over PINN. Our results provide an alternative way for utilizing the deep neural network to study the problems of generalized conditional symmetry of PDEs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Han, J., Jentzen, A., Epriya, W.N.: Solving high-dimensional partial differential equations using deep learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 115(34), 8505–8510 (2018)
Raissi, M., Perdikaris, P., Karniadakis, G.E.: Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 378, 686–707 (2019)
Bai, Y., Chaolu, T., Bilige, S.: The application of improved physics-informed neural network (IPINN) method in finance. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 3655–3667 (2022)
Fang, Y., Wu, G.Z., Wang, Y.Y., Dai, C.Q.: Data-driven femtosecond optical soliton excitations and parameters discovery of the high-order NLSE using the PINN. Nonlinear Dyn. 105, 603–616 (2021)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C.: Bilinear residual network method for solving the exactly explicit solutions of nonlinear evolution equations. Nonlinear Dyn. 108, 521–531 (2022)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Albishari, M., Zheng, F.C., Lan, Z.Z.: Generalized lump solutions, classical lump solutions and rogue waves of the (2+1)-dimensional Caudrey-Dodd-Gibbon-Kotera-Sawada-like equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 403, 126201 (2021)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Gan, J.Y., Li, Q., Lan, Z.Z.: Novel trial functions and rogue waves of generalized breaking soliton equation via bilinear neural network method. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 154, 111692 (2022)
Zhang, R.F., Bilige, S.: Bilinear neural network method to obtain the exact analytical solutions of nonlinear partial differential equations and its application to p-gBKP equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3041–3048 (2019)
Zhang, R.F., Li, M.C., Cherraf, A., Vadyala, S.R.: The interference wave and the bright and dark soliton for two integro-differential equation by using BNNM. Nonlinear Dyn. 5, 79 (2023)
Stein, M.: Large sample properties of simulations using Latin hypercube sampling. Technometrics 29, 143–151 (1987)
Wu, C., Zhu, M., Tan, Q., Karthac, Y., Lu, L.: A comprehensive study of non-adaptive and residual-based adaptive sampling for physics-informed neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 403, 115671 (2023)
Dwivedi, V., Srinivasan, B.: Physics informed extreme learning machine (PIELM)-A rapid method for the numerical solution of partial differential equations. Neurocomputing 391, 96–118 (2020)
Meng, X., Li, Z., Zhang, D., Karniadakis, G.E.: PPINN: Parareal physics-informed neural network for time-dependent PDEs. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 370, 113250 (2020)
Zhu, W., Khademi, W., Charalampidis, E.G., Kevrekidis, P.G.: Neural networks enforcing physical symmetries in nonlinear dynamical lattices: the case example of the Ablowitz-Ladik model. Physica D 434, 133264 (2022)
Jagtap, A.D., Kawaguchi, K., Karniadakis, G.E.: Locally adaptive activation functions with slope recovery for deep and physics-informed neural networks. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 476, 20200334 (2020)
Cai, W., Li, X., Liu, L.: A phase shift deep neural network for high frequency approximation and wave problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 42(5), A3285–A3312 (2020)
Yu, J., Lu, L., Meng, X.H., Karniadakis, G.E.: Gradient-enhanced physics-informed neural networks for forward and inverse PDE problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 393, 114823 (2022)
Lin, N., Chen, Y.: A two-stage physics-informed neural network method based on conserved quantities and applications in localized wave solutions. J. Comput. Phys. 457, 111053 (2022)
Zhang, Z.Y., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., Li, J.Y.: Generalized conditional symmetry enhanced physics-informed neural networks and application to the forward and inverse problems of nonlinear diffusion equations. Chaos Soliton. Fract. 168, 113169 (2023)
Zhang, Z.Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, L.S., Guo, L.L.: Enforcing continuous symmetries in physics-informed neural network for solving forward and inverse problems of partial differential equations. arXiv:2206.09299, (2022)
Wang, S., Teng, Y., Perdikaris, P.: Understanding and mitigating gradient pathologies in physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 43(5), A3055–A3081 (2021)
Li, J.H., Chen, J.C., Li, B.: Gradient-optimized physics-informed neural networks (GOPINNs): a deep learning method for solving the complex modified KdV equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 781–792 (2022)
Yang, L., Meng, X.H., Karniadakis, G.E.: B-PINNs: Bayesian physics-informed neural networks for forward and inverse PDE problems with noisy data. J. Comput. Phys. 425, 109913 (2021)
Gao, H., Zahr, M.J., Wang, J.X.: Physics-informed graph neural Galerkin networks: a unified framework for solving PDE-governed forward and inverse problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 390, 114502 (2022)
Yuan, L., Ni, Y.Q., Deng, X.Y., Hao, S.: A-PINN: auxiliary physics informed neural networks for forward and inverse problems of nonlinear integro-differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 462, 111260 (2022)
Pang, G., Lu, L., Karniadakis, G.E.: fPINNs: fractional physics-informed neural networks. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 41, A2603–A2626 (2019)
Wang, S., Zhang, H., Jiang, X.: Fractional physics-informed neural networks for time-fractional phase field models. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 2715–2739 (2022)
Kharazmi, E., Zhang, Z.Q., Karniadakis, G.E.: hp-VPINNs: variational physics-informed neural networks with domain decomposition. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 374, 113547 (2021)
Basarab-Horwath, P., Zhdanov, R.Z.: Initial-value problems for evolutionary partial differential equations and higher-order conditional symmetries. J. Math. Phys. 42, 376–389 (2001)
Kumar, S., Mohan, B.: A generalized nonlinear fifth-order KdV-type equation with multiple soliton solutions: Painlevé analysis and Hirota Bilinear technique. Phys. Scripta. 97(12), 125214 (2022)
Kumar, S., Mohan, B.: A novel and efficient method for obtaining Hirota’s bilinear form for the nonlinear evolution equation in (n+1) dimensions. Partial Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 5, 100274 (2022)
Kumar, S., Mohan, B., Kumar, R.: Lump, soliton, and interaction solutions to a generalized two-mode higher-order nonlinear evolution equation in plasma physics. Nonlinear Dyn. 110, 693–704 (2022)
Wazwaz, A.M., Albalawi, W., El-Tantawy, S.A.: Optical envelope soliton solutions for coupled nonlinear Schrödinger equations applicable to high birefringence fibers. Optik 255, 168673 (2022)
Kumar, S., Kumar, A., Mohan, B.: Evolutionary dynamics of solitary wave profiles and abundant analytical solutions to a (3+1)-dimensional burgers system in ocean physics and hydrodynamics. J. Ocean Eng. Sci. 8, 1–14 (2021)
Olver, P.J.: Applications of Lie Groups to Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1993)
Zhdanov, R.Z.: Conditional Lie-Bäcklund symmetry and reduction of evolution equations. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 28(13), 3841–3850 (1995)
Zhang, Z.Y., Chen, Y.F.: Classical and nonclassical symmetries analysis for initial value problems. Phys. Lett. A 374(9), 1117–1120 (2010)
Goard, J.: Finding symmetries by incorporating initial conditions as side conditions. Eur. J. Appl. Math. 19, 701–715 (2008)
Baydin, A.G., Pearlmutter, B.A., Radul, A.A., Siskind, J.M.: Automatic differentiation in machine learning: a survey. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 18(153), 1–43 (2018)
Liu, D.C., Nocedal, J.: On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Math. Program. 45(1), 503–528 (1989)
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv: 1412.6980 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The paper is supported by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 1222014), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11671014) and the Cross Research Project for Minzu University of China (No. 2021JCXK04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Cai, SJ., Li, JY. et al. Enforcing generalized conditional symmetry in physics-informed neural network for solving the KdV-like equation with Robin initial/boundary conditions. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 10381–10392 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08361-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08361-6