Abstract
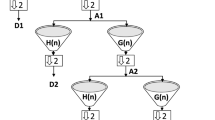
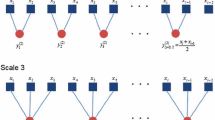
Recently, coded permutation entropy has been proposed, which enhances the noise immunity by quadratic partitioning on the basis of permutation entropy. However, coded permutation entropy and permutation entropy only consider the order of amplitude values and ignore some information related to amplitude. To overcome these defects, this paper applies the concept of quadratic partitioning to dispersion entropy (DE), takes advantage of the fact that DE can effectively measure amplitude information, and proposes coded DE (CDE), which increases the number of patterns and improves the divisibility by further coding the dispersion patterns in DE. Moreover, to reduce the computational consumption of CDE, we simplify the division criterion in quadratic partitioning while guaranteeing that no effective information is lost and propose simplified CDE (SCDE). Several simulation experiments demonstrate the advantages of SCDE and CDE over DE, permutation entropy, and coded permutation entropy in detecting the nonlinear dynamic changes within chaotic and synthetic signals. In addition, real-world experiments on electroencephalogram signals, bearing signals, and ship signals show that SCDE has better performance in medical diagnosis, fault diagnosis and signal classification, and the accuracy of SCDE-based classification methods is higher than that of other entropy-based methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DE:
-
Dispersion entropy
- PE:
-
Permutation entropy
- CPE:
-
Coded permutation entropy
- CDE:
-
Coded dispersion entropy
- SCDE:
-
Simplified coded permutation entropy
- LZC:
-
Lempel–Ziv complexity
- RPE:
-
Reverse permutation entropy
- RDE:
-
Reverse dispersion entropy
- NCDF:
-
Normal cumulative distribution function
- FRDE:
-
Fluctuation-based reverse dispersion entropy
- FuzzDE:
-
Fuzzy dispersion entropy
- STD:
-
Standard deviation
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- KNN:
-
K-nearest neighbor
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalogram
References
Bai, Y., Liang, Z., Li, X.: A permutation Lempel-Ziv complexity measure for EEG analysis. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 19, 102–114 (2015)
Li, Y., Geng, B., Jiao, S.: Dispersion entropy-based Lempel-Ziv complexity: A new metric for signal analysis. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 161, 112400 (2022)
Lin, H., Scs, Y.: Analysis of a nonlinear system exhibiting chaotic, noisy chaotic, and random behaviors. J. Appl. Mech. 63(2), 509–516 (1996)
Simiu E. Chaotic Transitions in Deterministic and Stochastic Dynamical Systems: Applications of the Melnikov Method in Engineering, Physics, and Neuroscience. Princeton University Press, 2002.
Yao, W., Dai, J., Perc, M.: Permutation-based time irreversibility in epileptic electroencephalograms. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 907–919 (2020)
Gao, Z., Dang, W., Wang, X.: Complex networks and deep learning for EEG signal analysis. Cogn Neurodyn 15, 369–388 (2021)
Enders, W.: Applied Econometric Time Series. Wiley, New York (1994)
Azami, H., Rostaghi, M., Abásolo, D., Escudero, J.: Refined composite multiscale dispersion entropy and its application to biomedical signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 64(12), 2872–2879 (2017)
Tenreiro, M., Lopes, A.: Entropy analysis of human death uncertainty. Nonlinear Dyn 104, 3897–3911 (2021)
Lempel, A., Ziv, J.: On the complexity of finite sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22(1), 75–81 (1976)
Yeh, C., Shi, W.: Generalized multiscale Lempel-Ziv complexity of cyclic alternating pattern during sleep. Nonlinear Dyn 93, 1899–1910 (2018)
Babloyantz, A., Destexhe, A.: Is the normal heart a periodic oscillator? Biol. Cybern. 58, 203–211 (1988)
Grassberger, P., Procaccia, I.: Characterization of strange attractors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 346 (1983)
Li, Y., Li, Y., Chen, X., Yu, J.: A novel feature extraction method for ship-radiated noise based on variational mode decomposition and multi-scale permutation entropy. Entropy 19, 342 (2017)
Bandt, C., Pompe, B.: Permutation entropy: a natural complexity measure for time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(17), 174102 (2002)
Zanin, M., Zunino, L., Rosso, O.: Permutation entropy and its main biomedical and econophysics applications: a review. Entropy, 14(8) (2012)
Fadlallah, B., Chen, B., Keil, A., Príncipe, J.: Weighted-permutation entropy: a complexity measure for time series incorporating amplitude information. Phys. Rev. E 87, 022911 (2013)
Xia, J., Shang, P., Wang, J., Shi, W.: Permutation and weighted-permutation entropy analysis for the complexity of nonlinear time series. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 31, 60–68 (2016)
Bandt, C.: A new kind of permutation entropy used to classify sleep stages from invisible EEG microstructure. Entropy 19, 197 (2017)
Kang, H., Zhang, X., Zhang, G.: Coded permutation entropy: a measure for dynamical changes based on the secondary partitioning of amplitude information. Entropy 22(2), 187 (2020)
Mao, X., Shang, P., Xu, M.: Measuring time series based on multiscale dispersion Lempel-Ziv complexity and dispersion entropy plane. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 137, 109868 (2020)
Rostaghi, M., Khatibi, M., Ashory, M., Azami, H.: Fuzzy dispersion entropy: a nonlinear measure for signal analysis. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(9), 3785–3796 (2022)
Zheng, J., Pan, H.: Use of generalized refined composite multiscale fractional dispersion entropy to diagnose the faults of rolling bearing. Nonlinear Dyn. 101, 1417–1440 (2021)
Rostaghi, M,, Azami, H.: Dispersion entropy: a measure for time-series analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett., 610–614 (2016).
Azami, H., Fernandez, A., Escudero, J.: Multivariate multiscale dispersion entropy of biomedical times series. Entropy 21(9), 913 (2017)
Li, Y., Gao, X., Wang, L.: Reverse dispersion entropy: a new complexity measure for sensor signal. Sensors 19(23), 5203 (2019)
Jiao, S., Geng, B., Li, Y.: Fluctuation-based reverse dispersion entropy and its applications to signal classification. Appl. Acoust. 175(4), 107857 (2021)
Azami, H., Sanei, S., Rajji, T.: Ensemble entropy: a low bias approach for data analysis. Knowl.-Based Syst. 256, 109876 (2022)
Ocampo, S.: A new special function and its application in probability. Int. J. Math. Math. Sci. 2018(12), 5146794 (2018)
Dobson, A.: Introduction to Statistical Modelling. Chapman and Hall, New York (1983)
Wu, G., Baleanu, D.: Chaos synchronization of the discrete fractional logistic map. Signal Process. 102(9), 96–99 (2014)
Li, Y., Liu, F., Wang, S.: Multi-scale symbolic lempel-ziv: an effective feature extraction approach for fault diagnosis of railway vehicle systems. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inf. 17(1), 199–208 (2021)
Chen, F., Baleanu, D.: Chaos synchronization of fractional chaotic maps based on the stability condition. Physica Stat. Mech. Appl. 460, 374–383 (2016)
[Online]. https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40521823/article/details/103862255. Accessed 30 Oct 2022
[Online]. http://csegroups.case.edu/bearingdatacenter/pages/ download-data-file. Accessed 30 Oct 2022
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2022JM-337).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Geng, B. & Tang, B. Simplified coded dispersion entropy: a nonlinear metric for signal analysis. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 9327–9344 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08339-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08339-4