Abstract
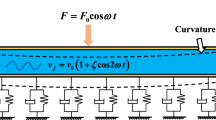
The nanoscale fluid–solid dynamic interaction with movable boundary is common in the adhesion of nanoelectromechanical systems, which presents complex size-dependent inertia and stiffness nonlinearities affecting the resonance response, frequency band and bifurcation topology greatly. The size-dependent nonlinear primary resonance of fluid-conveying functionally graded nanotubes with movable boundary under the internal pulsatile nanoflow and external forced excitation is studied. The size dependency of the nanosolid behavior is modeled by nonlocal strain gradient theory coupled with surface elasticity, while that of nanofluid is characterized by slip flow model. A proposed comprehensive geometrically nonlinear model encompasses two parts: First, Zhang-Fu’s refined beam model is modified to reflect nonlinear curvature effect. Subsequently, the inertial nonlinearity caused by the movable boundary is introduced based on the assumption of “non-extensible beam.” A two-step perturbation-incremental harmonic balance method is developed to obtain the amplitude–frequency bifurcation curves. Results provide the bifurcation sets under three stiffness conditions. Parametric analysis reveals the combined resonance mechanism and discusses the influences of nonlocal stress, strain gradient effect, surface effect, slip flow effect and material gradient index on the results. It is found that the size-dependent nonlinear inertia not only plays the role of softening nonlinear behaviors but also changes the bifurcation topology.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Lloyd, D.J.: Particle reinforced aluminium and magnesium matrix composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 39(1), 1–23 (1994)
Liu, H., Li, B., Liu, Y.: The inconsistency of nonlocal effect on carbon nanotube conveying fluid and a proposed solution based on local/nonlocal model. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids 78, 103837 (2019)
Naderi, A., Fakher, M., Hosseini-Hashemi, S.: On the local/nonlocal piezoelectric nanobeams: vibration, buckling, and energy harvesting. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 151, 107432 (2021)
Lyu, Z., Yang, Y., Liu, H.: High-accuracy hull iteration method for uncertainty propagation in fluid-conveying carbon nanotube system under multi-physical fields. Appl. Math. Model. 79, 362–380 (2020)
Caporale, A., Darban, H., Luciano, R.: Nonlocal strain and stress gradient elasticity of Timoshenko nano-beams with loading discontinuities. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 173, 103620 (2022)
Behdad, S., Fakher, M., Hosseini-Hashemi, S.: Dynamic stability and vibration of two-phase local/nonlocal VFGP nanobeams incorporating surface effects and different boundary conditions. Mech. Mater. 153, 103633 (2021)
Ghane, M., Saidi, A.R., Bahaadini, R.: Vibration of fluid-conveying nanotubes subjected to magnetic field based on the thin-walled Timoshenko beam theory. Appl. Math. Model. 80, 65–83 (2020)
Sadeghi-Goughari, M., Jeon, S., Kwon, H.J.: Fluid structure interaction of cantilever micro and nanotubes conveying magnetic fluid with small size effects under a transverse magnetic field. J. Fluid Struct. 94, 102951 (2020)
Darban, H., Fabbrocino, F., Luciano, R.: Size-dependent linear elastic fracture of nanobeams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 157, 103381 (2020)
Qing, H., Wei, L.: Linear and nonlinear free vibration analysis of functionally graded porous nanobeam using stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 109, 106300 (2022)
Ghaffari, S.S., Ceballes, S., Abdelkefi, A.: Nonlinear dynamical responses of forced carbon nanotube-based mass sensors under the influence of thermal loadings. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(2), 1013–1035 (2020)
Zheng, S., Chen, D., Wang, H.: Size dependent nonlinear free vibration of axially functionally graded tapered microbeams using finite element method. Thin Wall Struct. 139, 46–52 (2019)
Ansari, R., Gholami, R.: Size-dependent nonlinear vibrations of first-order shear deformable magneto-electro-thermo elastic nanoplates based on the nonlocal elasticity theory. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 8(04), 1650053 (2016)
Malikan, M., Eremeyev, V.A.: On the geometrically nonlinear vibration of a piezo-flexomagnetic nanotube. Math. Method Appl. Sci. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6758
Ebrahimi, F., Hosseini, S.H.S.: Nonlinear vibration and dynamic instability analysis nanobeams under thermo-magneto-mechanical loads: a parametric excitation study. Eng. Comput. 37(1), 395–408 (2021)
Ghadiri, M., Hosseini, S.H.S.: Parametric excitation of Euler–Bernoulli nanobeams under thermo-magneto-mechanical loads: nonlinear vibration and dynamic instability. Compos. B Eng. 173, 106928 (2019)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farajpour, A.: Nonlinear mechanics of nanoscale tubes via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 129, 84–95 (2018)
Ansari, R., Gholami, R., Rouhi, H.: Size-dependent nonlinear forced vibration analysis of magneto-electro-thermo-elastic Timoshenko nanobeams based upon the nonlocal elasticity theory. Compos. Struct. 126, 216–226 (2015)
Rajasekaran, S., Khaniki, H.B.: Size-dependent forced vibration of non-uniform bi-directional functionally graded beams embedded in variable elastic environment carrying a moving harmonic mass. Appl. Math. Model. 72, 129–154 (2019)
Wang, J., Zhu, Y., Zhang, B., Shen, H., Liu, J.: Nonlocal and strain gradient effects on nonlinear forced vibration of axially moving nanobeams under internal resonance conditions. Appl. Math. Mech. 41(2), 261–278 (2020)
Pourkiaee, S.M., Khadem, S.E., Shahgholi, M., Bab, S.: Nonlinear modal interactions and bifurcations of a piezoelectric nanoresonator with three-to-one internal resonances incorporating surface effects and van der Waals dissipation forces. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(3), 1785–1816 (2017)
Krysko, V.A., Jr., Awrejcewicz, J., Dobriyan, V., Papkova, I.V., Krysko, V.A.: Size-dependent parameter cancels chaotic vibrations of flexible shallow nano-shells. J. Sound Vib. 446, 374–386 (2019)
Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M., Nikkhah-Bahrami, M., Yazdi, M.R.H.: On nonlinear stability of fluid-conveying imperfect micropipes. Int. J. Eng. Sci 120, 254–271 (2017)
Esfahanian, V., Dehdashti, E., Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M.: Fluid-structure interaction in microchannel using Lattice Boltzmann method and size-dependent beam element. Adv. Appl. Math. Mech. 6(3), 345–358 (2014)
Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M., Nikkhah-Bahrami, M., Yazdi, M.R.H.: On nonlinear vibrations of micropipes conveying fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 117, 20–33 (2017)
Jin, Q., Ren, Y.: Dynamic instability mechanism of post-buckled FG nanotubes transporting pulsatile flow: size-dependence and local/global dynamics. Appl. Math. Model. 111, 139–159 (2022)
Hosseini, S.H.S., Ghadiri, M.: Nonlinear dynamics of fluid conveying double-walled nanotubes incorporating surface effect: a bifurcation analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 92, 594–611 (2021)
Mahmoudpour, E., Esmaeili, M.: Nonlinear free and forced vibration of carbon nanotubes conveying magnetic nanoflow and subjected to a longitudinal magnetic field using stress-driven nonlocal integral model. Thin Wall Struct. 166, 108134 (2021)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farajpour, A., Farokhi, H.: Effect of flow pulsations on chaos in nanotubes using nonlocal strain gradient theory. Commun Nonlinear Sci. 83, 105090 (2020)
Farajpour, A., Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H.: Chaotic motion analysis of fluid-conveying viscoelastic nanotubes. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids 74, 281–296 (2019)
Pirmoradian, M., Torkan, E., Abdali, N., Hashemian, M., Toghraie, D.: Thermo-mechanical stability of single-layered graphene sheets embedded in an elastic medium under action of a moving nanoparticle. Mech. Mater. 141, 103248 (2020)
Hashemian, M., Falsafioon, M., Pirmoradian, M., Toghraie, D.: Nonlocal dynamic stability analysis of a Timoshenko nanobeam subjected to a sequence of moving nanoparticles considering surface effects. Mech. Mater. 148, 103452 (2020)
Lotfan, S., Fathi, R., Ettefagh, M.M.: Size-dependent nonlinear vibration analysis of carbon nanotubes conveying multiphase flow. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 115, 723–735 (2016)
Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M., Dehdashti, E., Yazdi, M.R.H., Nikkhah-Bahrami, M.: Nonlinear thermo-resonant behavior of fluid-conveying FG pipes. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 144, 103141 (2019)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farajpour, A.: A review on the mechanics of functionally graded nanoscale and microscale structures. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 137, 8–36 (2019)
Witvrouw, A., Mehta, A.: The use of functionally graded poly-SiGe layers for MEMS applications. In: Materials Science Forum, vol. 492–493, pp. 255–260 (2005). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.492-493.255
Tong, G., Liu, Y., Cheng, Q., Dai, J.: Stability analysis of cantilever functionally graded material nanotube under thermo-magnetic coupling effect. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids 80, 103929 (2020)
Wang, Y.Q., Wan, Y.H., Zu, J.W.: Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of functionally graded sandwich thin nanoshells conveying fluid incorporating surface stress influence. Thin Wall Struct. 135, 537–547 (2019)
Jin, Q., Ren, Y.: Nonlinear size-dependent bending and forced vibration of internal flow-inducing pre-and post-buckled FG nanotubes. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 104, 106044 (2022)
Ramini, A., Alcheikh, N., Ilyas, S., Younis, M.I.: Efficient primary and parametric resonance excitation of bistable resonators. AIP Adv. 6(9), 095307 (2016)
Dai, H.L., Abdelkefi, A., Wang, L.: Piezoelectric energy harvesting from concurrent vortex-induced vibrations and base excitations. Nonlinear Dyn. 77(3), 967–981 (2014)
Demšić, M., Uroš, M., Lazarević, A.J., Lazarević, D.: Resonance regions due to interaction of forced and parametric vibration of a parabolic cable. J. Sound Vib. 447, 78–104 (2019)
Yang, H., Xiao, F.: Instability analyses of a top-tensioned riser under combined vortex and multi-frequency parametric excitations. Ocean Eng. 81, 12–28 (2014)
Wang, D., Bai, C., Zhang, H.: Nonlinear vibrations of fluid-conveying FG cylindrical shells with piezoelectric actuator layer and subjected to external and piezoelectric parametric excitations. Compos. Struct. 248, 112437 (2020)
Mao, X.Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Dynamics of a super-critically axially moving beam with parametric and forced resonance. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(2), 1475–1487 (2017)
Dai, H.L., Wang, L., Qian, Q., Ni, Q.: Vortex-induced vibrations of pipes conveying pulsating fluid. Ocean Eng. 77, 12–22 (2014)
Tang, Y.Q., Zhang, D.B., Gao, J.M.: Parametric and internal resonance of axially accelerating viscoelastic beams with the recognition of longitudinally varying tensions. Nonlinear Dyn. 83(1), 401–418 (2016)
Sahoo, B., Panda, L.N., Pohit, G.: Combination, principal parametric and internal resonances of an accelerating beam under two frequency parametric excitation. Int. J. NonLin Mech. 78, 35–44 (2016)
Mao, X.Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Forced vibration of axially moving beam with internal resonance in the supercritical regime. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 131, 81–94 (2017)
Li, L., Zhang, Q., Wang, W., Han, J.: Nonlinear coupled vibration of electrostatically actuated clamped–clamped microbeams under higher-order modes excitation. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(3), 1593–1606 (2017)
Jin, Q., Ren, Y.: Nonlinear size-dependent dynamic instability and local bifurcation of FG nanotubes transporting oscillatory fluids. Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 521513 (2022)
Mittal, K.L.: Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives. John Wiley & Sons, New York (2015)
Lorenzoni, M., Llobet, J., Perez-Murano, F.: Study of buckling behavior at the nanoscale through capillary adhesion force. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112(19), 193102 (2018)
Formica, G., Arena, A., Lacarbonara, W., Dankowicz, H.: Coupling FEM with parameter continuation for analysis of bifurcations of periodic responses in nonlinear structures. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 8(2), 021013 (2013)
Balasubramanian, P., Franchini, G., Ferrari, G., Painter, B., Karazis, K., Amabili, M.: Nonlinear vibrations of beams with bilinear hysteresis at supports: interpretation of experimental results. J. Sound Vib. 499, 115998 (2021)
Lacarbonara, W.: Nonlinear Structural Mechanics: Theory, Dynamical Phenomena and Modeling. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2013)
Chen, W., Dai, H., Jia, Q., Wang, L.: Geometrically exact equation of motion for large-amplitude oscillation of cantilevered pipe conveying fluid. Nonlinear Dyn. 98(3), 2097–2114 (2019)
Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M.: Nonlinear geometrically exact dynamics of fluid-conveying cantilevered hard magnetic soft pipe with uniform and nonuniform magnetizations. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.14618 (2022)
Bolotin, V.V.: The dynamic stability of elastic systems. Am. J. Phys. 33(9), 752–753 (1965)
Fu, Y., Zhong, J., Shao, X., Chen, Y.: Thermal postbuckling analysis of functionally graded tubes based on a refined beam model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 96, 58–64 (2015)
Zuo, D., Ma, G., Cao, Y., Zhou, C., Luo, J.: The large amplitude response of functionally graded non-uniform and imperfect nanotube. Wave Random Complex (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/17455030.2021.2014602
Hu, X., Jin, Q., Fu, X.: Parametric resonance of shear deformable nanotubes: a novel higher-order model incorporating nonlinearity from both curvature and inertia. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solids 96, 104693 (2022)
Dehrouyeh-Semnani, A.M., Zafari-Koloukhi, H., Dehdashti, E., Nikkhah-Bahrami, M.: A parametric study on nonlinear flow-induced dynamics of a fluid-conveying cantilevered pipe in post-flutter region from macro to micro scale. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 85, 207–225 (2016)
Lim, C.W., Zhang, G., Reddy, J.: A higher-order nonlocal elasticity and strain gradient theory and its applications in wave propagation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 78, 298–313 (2015)
Bahaadini, R., Saidi, A.R., Hosseini, M.: On dynamics of nanotubes conveying nanoflow. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 123, 181–196 (2018)
Mahinzare, M., Mohammadi, K., Ghadiri, M.: A nonlocal strain gradient theory for vibration and flutter instability analysis in rotary SWCNT with conveying viscous fluid. Wave Random Complex 31(2), 305–330 (2021)
Lu, L., Guo, X., Zhao, J.: On the mechanics of Kirchhoff and Mindlin plates incorporating surface energy. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 124, 24–40 (2018)
Jin, Q., Ren, Y., Jiang, H., Li, L.: A higher-order size-dependent beam model for nonlinear mechanics of fluid-conveying FG nanotubes incorporating surface energy. Compos. Struct. 269, 114022 (2021)
Bahaadini, R., Hosseini, M.: Effects of nonlocal elasticity and slip condition on vibration and stability analysis of viscoelastic cantilever carbon nanotubes conveying fluid. Comput. Mater. Sci. 114, 151–159 (2016)
Beskok, A., Karniadakis, G.E.: Report: a model for flows in channels, pipes, and ducts at micro and nano scales. Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 3(1), 43–77 (1999)
Rashidi, V., Mirdamadi, H.R., Shirani, E.: A novel model for vibrations of nanotubes conveying nanoflow. Comput. Mater. Sci. 51(1), 347–352 (2012)
Farajpour, A., Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H.: A nonlinear viscoelastic model for NSGT nanotubes conveying fluid incorporating slip boundary conditions. J. Vib. Control 25(12), 1883–1894 (2019)
Farajpour, A., Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H., Hussain, S.: Nonlinear mechanics of nanotubes conveying fluid. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 133, 132–143 (2018)
Atluri, S.: Nonlinear vibrations of a hinged beam including nonlinear inertia effects. J. Appl. Mech. 40(1), 121–126 (1973)
Shen, H.S., Li, C., Reddy, J.N.: Large amplitude vibration of FG-CNTRC laminated cylindrical shells with negative Poisson’s ratio. Comput. Method Appl. Mech. 360, 112727 (2020)
Ren, Y., Li, L., Jin, Q., Nie, L., Peng, F.: Vibration and snap-through of fluid-conveying graphene reinforced composite pipes under low-velocity impact. AIAA J. 59(12), 5091–5105 (2021)
Barretta, R., de Sciarra, F.M.: Constitutive boundary conditions for nonlocal strain gradient elastic nano-beams. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 130, 187–198 (2018)
Li, L., Hu, Y., Li, X.: Longitudinal vibration of size-dependent rods via nonlocal strain gradient theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 115, 135–144 (2016)
Dai, H.L., Abdelkefi, A., Wang, L.: Modeling and nonlinear dynamics of fluid-conveying risers under hybrid excitations. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 81, 1–14 (2014)
Huang, J.L., Zhu, W.D.: Nonlinear dynamics of a high-dimensional model of a rotating Euler–Bernoulli beam under the gravity load. J. Appl. Mech.-T ASME. 81(10), 101007 (2014)
Xu, M.R., Xu, S.P., Guo, H.Y.: Determination of natural frequencies of fluid-conveying pipes using homotopy perturbation method. Comput. Math. Appl. 60(3), 520–527 (2010)
Jin, Q.D., Yuan, F.G., Ren, Y.R.: Resonance interaction of flow-conveying nanotubes under forced vibration. Acta Mech. (2022) (in press)
Aghamohammadi, M., Sorokin, V., Mace, B.: Dynamic analysis of the response of Duffing-type oscillators subject to interacting parametric and external excitations. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 99–120 (2022)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52172356) and Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX20210384).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QJ involved in theoretical modeling and computation, writing, discussion and analysis. YR took part in providing guidance, investigation, validation. FY took part in supervision, revising.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Q., Ren, Y. & Yuan, FG. Combined resonance of pulsatile flow-transporting FG nanotubes under forced excitation with movable boundary. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 6157–6178 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-08148-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-08148-1