Abstract
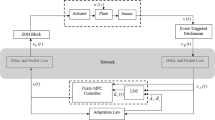
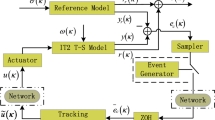
This article focuses on the issue of adaptive memory-event-triggered control for a class of interval type-2 Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy system (IT-2 TSFS) subjected to network-induced delays. Firstly, the IT-2 TSFS is established to effectively describe the nonlinearities and parameter uncertainties. Secondly, in order to decrease the burden of network transmission, a novel adaptive memory-event-triggered mechanism (AMETM) is presented by employing a buffer in event-triggered module. The historical information stored in the buffer is used to select the “necessary” control signal. Furthermore, the proposed AMETM can adaptively adjust the threshold to balance the data releasing rate and control performance. Then, the stability analysis is carried out by utilizing the discontinuous looped Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional. The properties of fuzzy membership functions are used to derive the improved stability conditions, which ensure the \(H_{\infty }\) performance. Finally, the numerical example is represented to verify the advantages of the control method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Li, H., Zhang, Z., Yan, H., et al.: Adaptive event-triggered fuzzy control for uncertain active suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(12), 4388–4397 (2018)
Mo, Y., Chabukswar, R., Sinopoli, B.: Detecting integrity attacks on SCADA systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 22(4), 1396–1407 (2013)
Peng, C., Zhang, J., Yan, H.: Adaptive event-triggering \({H} _ {\infty } \) load frequency control for network-based power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(2), 1685–1694 (2017)
Gupta, R.A., Chow, M.Y.: Networked control system: overview and research trends. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 57(7), 2527–2535 (2009)
Zhang, D., Shi, P., Wang, Q.G., et al.: Analysis and synthesis of networked control systems: a survey of recent advances and challenges. ISA Trans. 66, 376–392 (2017)
Liu, B., Liu, Y.: Mixed event-triggered mechanism modeling and controlling for networked control systems with time-varying delays and uncertainties. Asian J. Control 22(2), 803–817 (2020)
Lang, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, B.: Event-triggered network-based synchronization of delayed neural networks. Neurocomputing 190, 155–164 (2016)
Xue, W., Mao, W.: Asymptotic stability and finite-time stability of networked control systems: analysis and synthesis. Asian J. Control 15(5), 1376–1384 (2013)
Li, K., Hua, C.C., You, X., et al.: Output feedback-based consensus control for nonlinear time delay multiagent systems. Automatica 111(1), 108669 (2020)
Hua, C.C., Li, K., Guan, X.P.: Semi-global/global output consensus for nonlinear multiagent systems with time delays. Automatica 103, 480–489 (2019)
Hua, C.C., Guan, X.P.: Smooth dynamic output feedback control for multiple time-delay systems with nonlinear uncertainties. Automatica 68, 1–8 (2016)
Hu, S., Yue, D., Peng, C., et al.: Event-triggered controller design of nonlinear discrete-time networked control systems in T-S fuzzy model. Appl. Soft Comput. 30, 400–411 (2015)
Ge, C., Park, J.H., Hua, C., et al.: Dissipativity analysis for T-S fuzzy system under memory sampled-data control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 51(2), 961–969 (2019)
Cai, X., Wang, J., Zhong, S., et al.: Fuzzy quantized sampled-data control for extended dissipative analysis of T-S fuzzy system and its application to WPGSs. J. Frankl. Inst. 358(2), 1350–1375 (2021)
Hao, L.Y., Zhang, H., Li, T.S., et al.: Fault tolerant control for dynamic positioning of unmanned marine vehicles based on T-S fuzzy model with unknown membership functions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 70(1), 146–157 (2021)
Liu, J., Yin, T., Cao, J., et al.: Security control for T-S fuzzy systems with adaptive event-triggered mechanism and multiple cyber-attacks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 51(10), 6544–6554 (2020)
Zhao, Y., Wang, J., Yan, F., et al.: Adaptive sliding mode fault-tolerant control for type-2 fuzzy systems with distributed delays. Inf. Sci. 473, 227–238 (2019)
Du, Z., Kao, Y., Karimi, H.R., et al.: Interval type-2 fuzzy sampled-data \( H_ {\infty } \) control for nonlinear unreliable networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(7), 1434–1448 (2019)
Zheng, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., et al.: Robust \({H_{\infty }}\) amic output feedback control for interval type-2 T-S fuzzy multiple time-varying delays systems with external disturbance. J. Frankl. Inst. 357(6), 3193–3218 (2020)
Lian, Z., Shi, P., Lim, C.C.: Hybrid-triggered interval type-2 fuzzy control for networked systems under attacks. Inf. Sci. 567, 332–347 (2021)
Yang, Y., Niu, Y., Reza, Karimi H.: Dynamic learning control design for interval type-2 fuzzy singularly perturbed systems: a component-based event-triggering protocol. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 32(5), 2518–2535 (2022)
Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Ren, J.: A novel adaptive event-triggering scheme for network descriptor systems with time-delay. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 30(18), 7947–7961 (2020)
Shi, P., Wang, H., Lim, C.C.: Network-based event-triggered control for singular systems with quantizations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(2), 1230–1238 (2015)
Peng, C., Han, Q.L., Yue, D.: To transmit or not to transmit: a discrete event-triggered communication scheme for networked Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 164–170 (2012)
Lei, T., Meng, W., Zhao, K., et al.: Adaptive asymptotic tracking control of constrained multi-input multi-output nonlinear systems via event-triggered strategy. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 31(5), 1479–1496 (2021)
Zhang, J., Peng, C., Du, D., et al.: Adaptive event-triggered communication scheme for networked control systems with randomly occurring nonlinearities and uncertainties. Neurocomputing 174, 475–482 (2016)
Peng, C., Yang, M., Zhang, J., et al.: Network-based \(H_{\infty }\) control for T-S fuzzy systems with an adaptive event-triggered communication scheme. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 329, 61–76 (2017)
Begnini, M., Bertol, D.W., Martins, N.A.: A robust adaptive fuzzy variable structure tracking control for the wheeled mobile robot: simulation and experimental results. Control. Eng. Pract. 64, 27–43 (2017)
Ding, Z.: Adaptive consensus output regulation of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown high-frequency gain. Automatica 51, 348–355 (2015)
Zhang, Z.M., He, Y., Wu, M., et al.: Exponential synchronization of chaotic neural networks with time-varying delay via intermittent output feedback approach. Appl. Math. Comput. 314, 121–132 (2017)
Du, Z., Kao, Y., Park, J.H., et al.: Fuzzy event-triggered control for nonlinear networked control systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 359(6), 2593–2607 (2022)
Li, Z., Yan, H., Zhang, H., et al.: Aperiodic sampled-data-based control for interval type-2 fuzzy systems via refined adaptive event-triggered communication scheme. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 29(2), 310–321 (2020)
Yan, H., Hu, C., Zhang, H., et al.: \( H_ {\infty } \) output tracking control for networked systems with adaptively adjusted event-triggered scheme. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(10), 2050–2058 (2018)
Yang, H., Wang, X., Park, J.H.: Sampled-data-based dissipative stabilization of IT-2 TSFSs via fuzzy adaptive event-triggered protocol. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3105058
Peng, C., Zhang, J.: Event-triggered output-feedback \(H_{\infty }\) control for networked control systems with time-varying sampling. IET Control Theory Appl. 9(9), 1384–1391 (2015)
Peng, C., Han, Q.L.: A novel event-triggered transmission scheme and \({{\cal{L} }} _ 2 \) control co-design for sampled-data control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(10), 2620–2626 (2013)
Tian, E., Peng, C.: Memory-based event-triggering \(H_{\infty }\) load frequency control for power systems under deception attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(11), 4610–4618 (2020)
Chen, G., Chen, Y., Zeng, H.B.: Event-triggered \(H_{\infty }\) filter design for sampled-data systems with quantization. ISA Trans. 101, 170–176 (2020)
Yue, D., Tian, E., Han, Q.L.: A delay system method for designing event-triggered controllers of networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(2), 475–481 (2012)
Li, M., Zhao, J., Xia, J., et al.: Non-fragile extended dissipative control for event-triggered networked stochastic systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 51(4), 746–758 (2020)
Park, P.G., Ko, J.W., Jeong, C.: Reciprocally convex approach to stability of systems with time-varying delays. Automatica 47(1), 235–238 (2011)
Sababheh, M., Choi, D.: A complete refinement of Young’s inequality. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 440(1), 379–393 (2016)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflicts of interests/competing interests
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, C., Liu, C., Liu, Y. et al. Interval type-2 fuzzy control for nonlinear system via adaptive memory-event-triggered mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 1301–1314 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07880-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07880-y