Abstract
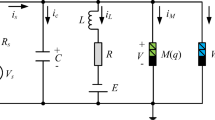
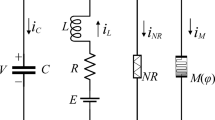
The ion exchange in neurons can trigger time-varying magnetic fields. According to the superposition field principle, each neuron is exposed to the integrated magnetic field generated by the other neurons. This paper considers the effect of magnetic field coupling between two neurons on neuron dynamics. The magnetic flux of the memristor describes the impact of the magnetic field. According to the different coupling types of neurons, the excitatory coupling between excitatory neurons. The inhibitory magnetic coupling between excitatory and inhibitory neurons is also considered. And then, the excitatory and inhibitory magnetic field coupling is studied under different external excitation currents. The excitatory magnetic field coupling can promote the firing of neurons. When the intensity of inhibitory magnetic field coupling is large enough, the neuronal firing mode is static. The firing mode of neurons can be changed by adjusting the coupling intensity. Therefore, magnetic field coupling can provide new insights into the mechanism of information interaction between neurons. Finally, the excitability and inhibition of magnetic field coupling are improved by comparing magnetic field coupling with synaptic coupling. These results indicate that magnetic field coupling has the same function as a synapse to some extent and has the characteristics of radiation propagation.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Komendantov, A.O., Venkadesh, S., Rees, C.L., Wheeler, D.W., Hamilton, D.J., Ascoli, G.A.: Quantitative firing pattern phenotyping of hippocampal neuron types. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–17 (2019)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1569–1578 (2017)
Chua, L.: Memristor—the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
Ma, M., Yang, Y., Qiu, Z., Peng, Y., Sun, Y., Li, Z., Wang, M.: A locally active discrete memristor model and its application in a hyperchaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 66, 1–15 (2022)
Ma, X., Mou, J., Xiong, L., Banerjee, S., Cao, Y., Wang, J.: A novel chaotic circuit with coexistence of multiple attractors and state transition based on two memristors. Chaos Solitons Fract. 152, 111363 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Hong, Q., Sun, Y.: A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., Zeng, Z.: A novel no-equilibrium hr neuron model with hidden homogeneous extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fract. 145, 110761 (2021)
Varshney, V., Sabarathinam, S., Prasad, A., Thamilmaran, K.: Infinite number of hidden attractors in memristor-based autonomous duffing oscillator. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 28(01), 1850013 (2018)
Deng, Q., Wang, C., Yang, L.: Four-wing hidden attractors with one stable equilibrium point. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 30(06), 2050086 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Cui, L., Sun, Y., Xu, C., Yu, F.: Brain-like initial-boosted hyperchaos and application in biomedical image encryption. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2022.3155599
Zhou, L., Wang, C., Zhou, L.: Generating hyperchaotic multi-wing attractor in a 4d memristive circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(4), 2653–2663 (2016)
Zhou, L., Wang, C., Zhou, L.: A novel no-equilibrium hyperchaotic multiwing system via introducing memristor. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 46(1), 84–98 (2018)
Yan, D., Wang, L., Duan, S., Chen, J., Chen, J.: Chaotic attractors generated by a memristor-based chaotic system and Julia fractal. Chaos Solitons Fract. 146, 110773 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., Xu, C., Hong, Q., Yao, W., Sun, Y.: An extremely simple multiwing chaotic system: Dynamics analysis, encryption application, and hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(12), 12708–12719 (2021)
Yu, F., Kong, X., Chen, H., Yu, Q., Cai, S., Huang, Y., Du, S.: A 6d fractional-order memristive Hopfield neural network and its application in image encryption. Front. Phys. 109, 66 (2022)
Yang, Y., Wang, L., Duan, S., Luo, L.: Dynamical analysis and image encryption application of a novel memristive hyperchaotic system. Opt. Laser Technol. 133, 106553 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Chen, C., Sun, Y., Zhou, C., Xu, C., Hong, Q.: Neural bursting and synchronization emulated by neural networks and circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 68(8), 3397–3410 (2021)
Xu, C., Wang, C., Jiang, J., Sun, J., Lin, H.: Memristive circuit implementation of context-dependent emotional learning network and its application in multi-task. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 66, 1 (2021)
Yang, L., Wang, C.: Emotion model of associative memory possessing variable learning rates with time delay. Neurocomputing 460, 117–125 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Deng, Q., Xu, C., Deng, Z., Zhou, C.: Review on chaotic dynamics of memristive neuron and neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 959–973 (2021)
Xie, W., Wang, C., Lin, H.: A fractional-order multistable locally active memristor and its chaotic system with transient transition, state jump. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(4), 4523–4541 (2021)
Chen, J., Li, C., Huang, T., Yang, X.: Global stabilization of memristor-based fractional-order neural networks with delay via outputfeedback control. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 31(05), 1750031 (2017)
Jahanshahi, H., Yousefpour, A., Munoz-Pacheco, J.M., Kacar, S., Pham, V.-T., Alsaadi, F.E.: A new fractional-order hyperchaotic memristor oscillator: Dynamic analysis, robust adaptive synchronization, and its application to voice encryption. Appl. Math. Comput. 383, 125310 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, Y., Yao, W.: Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(4), 3667–3683 (2020)
Li, C., Li, H., Xie, W., Du, J.: A s-type bistable locally active memristor model and its analog implementation in an oscillator circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 106(1), 1041–1058 (2021)
Dong, Y., Wang, G., Iu, H.H.-C., Chen, G., Chen, L.: Coexisting hidden and self-excited attractors in a locally active memristor-based circuit. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 30(10), 103123 (2020)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., Ma, J., Song, X.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–1490 (2016)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Bao, H., Liu, W., Chen, M.: Hidden extreme multistability and dimensionality reduction analysis for an improved non-autonomous memristive Fitzhugh–Nagumo circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(3), 1879–1894 (2019)
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W., Bao, B.: Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(2), 502–511 (2019)
Ma, J., Zhang, G., Hayat, T., Ren, G.: Model electrical activity of neuron under electric field. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(2), 1585–1598 (2019)
Yan, B., Panahi, S., He, S., Jafari, S.: Further dynamical analysis of modified Fitzhugh–Nagumo model under the electric field. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(1), 521–529 (2020)
Wu, F., Ma, J., Zhang, G.: A new neuron model under electromagnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 347, 590–599 (2019)
Lu, L., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., Ge, M., Yang, L., Zhan, X.: Energy dependence on modes of electric activities of neuron driven by different external mixed signals under electromagnetic induction. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62(3), 427–440 (2019)
Hindmarsh, J., Rose, R.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
Gambuzza, L.V., Di Patti, F., Gallo, L., Lepri, S., Romance, M., Criado, R., Frasca, M., Latora, V., Boccaletti, S.: Stability of synchronization in simplicial complexes. Nat. Commun. 12(1), 1–13 (2021)
Wang, G., Xu, Y., Ge, M., Lu, L., Jia, Y.: Mode transition and energy dependence of Fitzhugh–Nagumo neural model driven by high-low frequency electromagnetic radiation. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 120, 153209 (2020)
FitzHugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1(6), 445–466 (1961)
Yang, Y., Ma, J., Xu, Y., Jia, Y.: Energy dependence on discharge mode of Izhikevich neuron driven by external stimulus under electromagnetic induction. Cognit. Neurodyn. 15(2), 265–277 (2021)
Izhikevich, E.: Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(6), 1569–1572 (2003)
Wan, Q., Yan, Z., Li, F., Liu, J., Chen, S.: Multistable dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic radiation and dual bias currents. Nonlinear Dyn. 66, 1–17 (2022)
Wan, Q., Yan, Z., Li, F., Chen, S., Liu, J.: Complex dynamics in a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic induction and electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 32(7), 073107 (2022)
Lin, H., Wang, C.: Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 369, 124840 (2020)
Yu, F., Zhang, Z., Shen, H., Huang, Y., Cai, S., Jin, J., Du, S.: Design and fpga implementation of a pseudo-random number generator based on a Hopfield neural network under electromagnetic radiation. Front. Phys. 9, 302 (2021)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yao, W., Tan, Y.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 90, 105390 (2020)
Qu, L., Du, L., Hu, H., Cao, Z., Deng, Z.: Pattern control of external electromagnetic stimulation to neuronal networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(4), 2739–2757 (2020)
Zandi-Mehran, N., Jafari, S., Hashemi Golpayegani, S.M.R., Nazarimehr, F., Perc, M.: Different synaptic connections evoke different firing patterns in neurons subject to an electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(2), 1809–1824 (2020)
Alcamí, P., Pereda, A. E.: Beyond plasticity: the dynamic impact of electrical synapses on neural circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20(5), 253–271 (2019)
Xu, K., Maidana, J.P., Orio, P.: Diversity of neuronal activity is provided by hybrid synapses. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(3), 2693–2710 (2021)
Li, Y., Gu, H., Jia, B., Ding, X.: The nonlinear mechanism for the same responses of neuronal bursting to opposite self-feedback modulations of autapse. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64(7), 1459–1471 (2021)
Uzuntarla, M.: Firing dynamics in hybrid coupled populations of bistable neurons. Neurocomputing 367, 328–336 (2019)
Ma, J., Mi, L., Zhou, P., Xu, Y., Hayat, T.: Phase synchronization between two neurons induced by coupling of electromagnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 307, 321–28 (2017)
Guo, S., Xu, Y., Wang, C., Jin, W., Hobiny, A., Ma, J.: Collective response, synapse coupling and field coupling in neuronal network. Chaos Solitons Fract. 105, 120–127 (2017)
Zhao, Y., Sun, X., Liu, Y., Kurths, J.: Phase synchronization dynamics of coupled neurons with coupling phase in the electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(3), 1315–1324 (2018)
Zhou, Q., Wei, D.Q.: Collective dynamics of neuronal network under synapse and field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(1), 753–765 (2021)
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ma, J., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Collective responses in electrical activities of neurons under field coupling. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–10 (2018)
Ozer, M., Uzuntarla, M., Agaoglu, S.N.: Effect of the sub-threshold periodic current forcing on the regularity and the synchronization of neuronal spiking activity. Phys. Lett. A 360(1), 135–140 (2006)
Rakshit, S., Bera, B.K., Ghosh, D., Sinha, S.: Emergence of synchronization and regularity in firing patterns in timevarying neural hypernetworks. Phys. Rev. E 97, 052304 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61971185) and Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ4218).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, Z., Wang, C., Deng, Q. et al. Regulating memristive neuronal dynamical properties via excitatory or inhibitory magnetic field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn 110, 3823–3835 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07813-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07813-9