Abstract
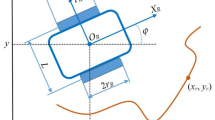
This paper studies the formation control of a nonlinear multi-agent system based on a broad learning system under actuator fault and input saturation. Firstly, the multi-agent tracking error is proposed based on graph theory. Besides, fault tolerance should be considered when actuator fault exists. Meanwhile, the broad learning system is put forward to approximate the unknown nonlinear function in the multi-agent system. Then, an input saturation auxiliary system is introduced to reduce the adverse effects of input saturation constraints. At the same time, the disturbance observer technology is used to estimate the actuator failure as a lumped uncertainty. At last, dynamic surface control is introduced to realize formation control with actuator fault and input saturation. Obviously, it is difficult to design a controller with unknown nonlinear function, input saturation, and actuator fault existing in the multi-agent system. The Lyapunov method can prove the stability of the formation control. The simulation results verify the effectiveness of the controller.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
References
Yu, D., Chen, C.L.P., Xu, H.: Fuzzy swarm control based on sliding-mode strategy with self-organized omnidirectional mobile robots system. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 35, 1–13 (2021)
Hua, Y., Dong, X., Li, Q., Ren, Z.: Distributed fault-tolerant time-varying formation control for high-order linear multi-agent systems with actuator failures. ISA Trans. 71, 40–50 (2017)
Yu, D., Chen, C.L.P.: Smooth transition in communication for swarm control with formation change. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 16(11), 6962–6971 (2020)
Liu, Y.-J., Zeng, Q., Tong, S., Chen, C.L.P., Liu, L.: Adaptive neural network control for active suspension systems with time-varying vertical displacement and speed constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(12), 9458–9466 (2019)
Yu, D., Chen, C.L.P., Xu, H.: Intelligent decision making and bionic movement control of self-organized swarm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(7), 6369–6378 (2021)
Hua, Y., Dong, X., Li, Q., Ren, Z.: Distributed fault-tolerant time-varying formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with actuator failures and directed topologies. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Expr. Briefs 65(6), 774–778 (2018)
Liu, L., Wang, Z., Yao, X., Zhang, H.: Echo state networks based data-driven adaptive fault tolerant control with its application to electromechanical system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 23(3), 1372–1382 (2018)
Yu, Z., Qu, Y., Zhang, Y.: Distributed fault-tolerant cooperative control for multi-UAVs under actuator fault and input saturation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 27(6), 2417–2429 (2019)
Shen, Q., Yue, C., Goh, C.H., Wang, D.: Active fault-tolerant control system design for spacecraft attitude maneuvers with actuator saturation and faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(5), 3763–3772 (2019)
Liu, L., Wang, Z., Zhang, H.: Data-based adaptive fault estimation and fault-tolerant control for MIMO model-free systems using generalized fuzzy hyperbolic model. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(6), 3191–3205 (2018)
Zhang, L., Yang, G.-H.: Adaptive fuzzy prescribed performance control of nonlinear systems with hysteretic actuator nonlinearity and faults. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 48(12), 2349–2358 (2018)
Hou, Z.-G., Cheng, L., Tan, M.: Decentralized robust adaptive control for the multiagent system consensus problem using neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Part B (Cybern.) 39(3), 636–647 (2009)
Yu, D., Chen, C.L.P.: Automatic leader-follower persistent formation generation with minimum agent-movement in various switching topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(4), 1569–1581 (2020)
Shi, Q., Li, T., Li, J., Chen, C.P., Xiao, Y., Shan, Q.: Adaptive leader-following formation control with collision avoidance for a class of second-order nonlinear multi-agent systems. Neurocomputing 350, 282–290 (2019)
Yu, D., Chen, C.L.P., Ren, C.-E., Sui, S.: Swarm control for self-organized system with fixed and switching topology. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 50(10), 4481–4494 (2020)
Li, X., Song, S., Wu, J.: Exponential stability of nonlinear systems with delayed impulses and applications. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64(10), 4024–4034 (2019)
Liu, Y.-J., Li, Y.-X.: Adaptive fuzzy output-feedback control of uncertain SISO nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 61(4), 749–761 (2010)
Zhang, J., Xiang, Z.: Event-triggered adaptive neural network sensor failure compensation for switched interconnected nonlinear systems with unknown control coefficients. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 59, 1–12 (2021)
Xu, H., Yu, D., Sui, S., Zhao, Y.-P., Chen, C.L.P., Wang, Z.: Nonsingular practical fixed-time adaptive output feedback control of MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2, 1–13 (2022)
Wen, G.-X., Liu, Y.-J.: Adaptive fuzzy-neural tracking control for uncertain nonlinear discrete-time systems in the NARMAX form. Nonlinear Dyn. 66(4), 745–753 (2011)
Zhang, J., Li, S., Ahn, C.K., Xiang, Z.: Adaptive fuzzy decentralized dynamic surface control for switched large-scale nonlinear systems with full-state constraints. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 3, 1–12 (2021)
Liu, Y., Huang, P., Zhang, F., Zhao, Y.: Distributed formation control using artificial potentials and neural network for constrained multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 28(2), 697–704 (2020)
Li, C., Tong, S., Wang, W.: Fuzzy adaptive high-gain-based observer backstepping control for SISO nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 181(11), 2405–2421 (2011)
Li, Y., Ren, C., Tong, S.: Adaptive fuzzy backstepping output feedback control of nonlinear uncertain time-delay systems based on high-gain filters. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(3), 781–792 (2012)
Wen, G., Chen, C.L.P., Feng, J., Zhou, N.: Optimized multi-agent formation control based on an identifier-actor-critic reinforcement learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(5), 2719–2731 (2018)
Chen, C.L.P., Ren, C.-E., Du, T.: Fuzzy observed-based adaptive consensus tracking control for second-order multiagent systems with heterogeneous nonlinear dynamics. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 24(4), 906–915 (2016)
Ren, C.-E., Chen, L., Chen, C.L.P.: Adaptive fuzzy leader-following consensus control for stochastic multiagent systems with heterogeneous nonlinear dynamics. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 25(1), 181–190 (2017)
Li, Y., Ren, C., Tong, S.: Adaptive fuzzy backstepping output feedback control for a class of MIMO time-delay nonlinear systems based on high-gain observer. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 1175–1191 (2011)
Zhang, Y., Wang, D., Peng, Z., Li, T.: Distributed containment maneuvering of uncertain multiagent systems in MIMO strict-feedback form. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 51(2), 1354–1364 (2021)
Tsai, C.-C., Yu, C.-C., Wu, C.-W.: Adaptive distributed BLS-FONTSM formation control for uncertain networking heterogeneous omnidirectional mobile multirobots. J. Chin. Instit. Eng. 43(2), 171–185 (2019)
Yu, D., Long, J., Chen, C.L.P., Wang, Z.: Adaptive swarm control within saturated input based on nonlinear coupling degree. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 86, 1–12 (2021)
Chen, C.L.P., Liu, Z.: Broad learning system: an effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture. IEEE Trans. Neural Net. Learn. Syst. 29(1), 10–24 (2018)
Chen, C.L.P., Liu, Z., Feng, S.: Universal approximation capability of broad learning system and its structural variations. IEEE Trans. Neural Net. Learn. Syst. 30(4), 1191–1204 (2019)
Dong, W., Farrell, J.A., Polycarpou, M.M., Djapic, V., Sharma, M.: Command filtered adaptive backstepping. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 20(3), 566–580 (2012)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62006192, Grant 62025602 Grant 61751202, Grant 61751205, Grant 61572540, Grants U1803263 and Grants 11931015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Li, S., Yu, D. et al. BLS-based formation control for nonlinear multi-agent systems with actuator fault and input saturation. Nonlinear Dyn 109, 2657–2673 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07505-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07505-4