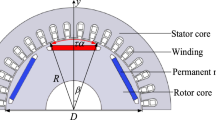
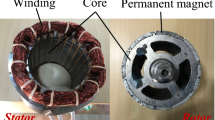
Abstract
Conventional finite element analysis (FEA) performed in electromagnetic-vibration coupling calculation of motor suffers from several significant drawbacks, such as large memory space, high computational cost and heavy reliance on mesh quality for accurate solution. With the traditional meshless method, special attention needs to be paid to correctly impose the boundary condition like FEA. Besides, the matrix is easily prone to be ill-conditioned due to introducing large amount of higher-order basis functions. We propose a novel multi-physical coupling method combining FEA and optimized meshless method. The proposed methodology is further evaluated on the vibration analysis of a 12-slot 10-pole permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM). Firstly, 2D stator electromagnetic force is simulated and derived based on the local Jacobian derivative method through FEA. The electromagnetic force spectrum is calculated using FFT analysis and further imported into commercial meshless structural simulation software SimSolid for stator harmonic response analysis. Correct force boundary condition and data mapping between meshless and FEA simulation interface are key to the accuracy of the proposed combined multi-physical modeling methodology. This is achieved by introducing new high-dimensional ramp function in the transition region between FEA and meshless domains, which are defined with the shape functions composed of the FEA and meshless method. This function satisfies the continuity and consistency of the displacement function and ensures the convergence of coupled FEA-meshless method. Subsequently, construction of basis function is key to the establishment of convention meshless discrete equation for the elastic problem of rotating machinery. This is designed by using moving least square theory in cylindrical coordinate system. A harmonic response with meshless method is analyzed by using the mode superposition method to obtain detailed mode shape data, acceleration and displacement distribution of stator. Finally, the tangential continuity and robustness are not well considered in the traditional simulation with FEA coupled meshless method. To mitigate this problem, we propose an optimized meshless method based on modified local basis functions to recalculate the harmonic response motion. Then, the coupling electromagnetic-vibration simulation results of traditional coupled FEA-meshless method, optimized coupled FEA-meshless method and complete FEA coupled method are compared. It is worth noting that the optimized method significantly improves accuracy, robustness and computational speed at the same time. In short, the proposed electromagnetic-structure coupling calculation method provides a novel alternative for the multi-physical coupling calculation of rotating machinery combining FEA and meshless simulation methods.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Y., Zhu, Z.Q., Feng, J.H., et al.: Investigation of unbalanced magnetic force in fractional-slot permanent magnet machines having an odd number of stator slots. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 34(4), 1954–1963 (2020)
Lin, F., Zuo, S.Q., Deng, W.Z., et al.: Reduction of vibration and acoustic noise in permanent magnet synchronous motor by optimizing magnetic forces. J. Sound Vib. 429, 193–205 (2018)
You, Y.M.: Multi-objective optimization of a permanent magnet synchronous motor based on an automated design and analysis procedure. Micro Syst. Technol.-Micro- Process. Syst. 34(11), 3477–3488 (2020)
Hong, J.F., Wang, S.M., Sun, Y.G., et al.: Piecewise stagger poles with continuous skew edge for vibration reduction in surface-mounted. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(9), 8498–8506 (2021)
Mao, Y.N., Zhao, W.X., Zhu, S.D., et al.: Vibration investigation of spoke-type PM machine with asymmetric rotor considering modulation effect of stator teeth. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(10), 9092–9103 (2021)
Hu, S.L., Zuo, S.G., Liu, M.T., et al.: Modeling and analysis of radial electromagnetic force and vibroacoustic behavior in switched reluctance motors. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 142, 106778 (2020)
Wu, L.J., Zhu, Z.Q., Station, D.A., et al.: Comparison of analytical models of cogging torque in surface-mounted PM machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(6), 2414–2425 (2012)
Zarko, D., Ban, D., Lipo, T.A., et al.: Analytical solution for electromagnetic torque in surface permanent-magnet motors using conformal mapping. IEEE Trans. Magn. 45(7), 2943–2954 (2009)
Zhang, W.J., Xu, Y.L., Zhou, G.X.: Research on a novel transverse flux permanent magnet motor with hybrid stator core and disk-type rotor for industrial robot applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(11), 11223–11233 (2021)
Sun, S.L., Leng, F.G., Su, X.K., et al.: Performance of a novel dual-magnet tri-stable piezoelectric energy harvester subjected to random excitation. Energy Convers. Manag. 239, 114246 (2021)
Zhou, Y., Xue, Z.Q.: Analytical method for calculating the magnetic field of spoke-type permanent magnet machines accounting for eccentric magnetic pole. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(3), 2096–2107 (2021)
Deng, W.Z., Zuo, S.G.: Analytical modeling of the electromagnetic vibration and noise for an external rotor axial flux in-wheel motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(3), 1991–2000 (2018)
Fang, H.Y., Li, D.W., Qu, R.H., et al.: Modulation effect of slotted structure on vibration response in electrical machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(4), 2998–3007 (2019)
Zhang, Z.H., An, Y.J., Li, M., et al.: Influence of asymmetrical stator axes on the performance and multi-physical field of canned permanent magnet machine for vacuum dry pump with vector converter supply. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 35(4), 2129–2140 (2020)
Cao, Y., Yao, L.Q., Yin, L.: New treatment of essential boundary conditions in EFG method by coupling with RPIM. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 26(3), 302–316 (2013)
Pal, R.S.C., Mohanty, A.R.: A simplified dynamical model of mixed eccentricity fault in a three-phase induction motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(5), 4341–4350 (2021)
Guo, Y.F., Hai, Y.Q.: Adaptive surface mesh remeshing based on a sphere packing method and a node insertion/deletion method. Appl. Math. Model. 98, 1–13 (2021)
Liang, W., Luk, P.C., Fei, W.: Analytical investigation of sideband electromagnetic vibration in integral-slot PMSM drive with SVPWM technique. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 32(6), 4785–4795 (2017)
Zhang, Y.Q., Ge, W.J., Zhang, Y.H., et al.: Topology optimization of hyperelastic structure based on a directly coupled finite element and element-free Galerkin method. Adv. Eng. Softw. 123, 25–37 (2018)
Kumar, S., Singh, I.V., Mishra, B.K., et al.: A coupled finite element and element-free Galerkin approach for the simulation of stable crack growth in ductile materials. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 70, 49–58 (2014)
Bourantas, G., Zwick, B.F., Joldes, G.R., et al.: Simple and robust element-free Galerkin method with almost interpolating shape functions for finite deformation elasticity. Appl. Math. Model. 96, 284–303 (2021)
Chen, L., Li, X.: Boundary element-free methods for exterior acoustic problems with arbitrary and high wave numbers. Appl. Math. Model. 72(4), 85–103 (2019)
Boroomand, B., Parand, S.: Towards a general interpolation scheme. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 381, 113830 (2021)
Zhang, H., Sladek, J., Sladek, V., et al.: Fracture analysis of functionally graded material by hybrid meshless displacement discontinuity method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 371, 107591 (2021)
Wu, C.J., Wang, D.D.: An accuracy analysis of Galerkin meshfree methods accounting for numerical integration. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 375, 113631 (2021)
Fornberg, B., Flyer, N.: Solving PDEs with radial basis functions. Acta Numer. 24, 215–258 (2015)
Crespo, A.J.C., Dominguez, J.M., Rogers, B.D., et al.: DualSPHysics: open-source parallel CFD solver based on smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Comput. Phys. Commun. 187, 204–216 (2015)
Habibirad, A., Roohi, R., Hesameddini, E., et al.: A reliable algorithm to determine the pollution transport within underground reservoirs: implementation of an efficient collocation meshless method based on the moving Kriging interpolation. Eng. Comput. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01430-7. (early access)
Wang, L.H., Qian, Z.B.: A meshfree stabilized collocation method (SCM) based on reproducing kernel approximation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 371, 113303 (2020)
Wu, S.W., Xiang, Y.: A weak-form meshfree coupled with infinite element method for predicting acoustic radiation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 107, 63–78 (2019)
Li, S.Q., Ling, L.: Collocation methods for Cauchy problems of elliptic operators via conditional stabilities. Commun. Comput. Phys. 26(3), 785–805 (2019)
Abbaszadeh, M., Dehghan, M.: Numerical investigation of reproducing kernel particle Galerkin method for solving fractional modified distributed-order anomalous sub-diffusion equation with error estimation. Appl. Math. Comput. 392, 125718 (2021)
Liu, Z., Wei, G.W., Wang, Z.M.: The radial basis reproducing kernel particle method for geometrically nonlinear problem of functionally graded materials. Appl. Math. Model. 85, 244–272 (2020)
Chen, L., Cheng, Y.M.: The complex variable reproducing kernel particle method for bending problems of thin plates on elastic foundations. Comput. Mech. 26(3), 67–80 (2018)
Lu, Y.Y., Belytschko, T., Gu, L.: A new implementation of the element Free Galerkin method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 113(3–4), 397–411 (1994)
Lopes, I.A., Ferreira, B.P., Pries, F.M.: On the efficient enforcement of uniform traction and mortar periodic boundary conditions in computational homogenisation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 384, 113930 (2021)
Moghaddam, M.R., Baradaran, G.H.: Three-dimensional free vibrations analysis of functionally graded rectangular plates by the meshless local Petrov–Galerkin (MLPG) method. Appl. Math. Comput. 304, 153–163 (2017)
Liu, Z., Gao, H.F., Wei, G.F., et al.: The meshfree analysis of elasticity problem utilizing radial basis reproducing kernel particle method. Results Phys. 17, 103037 (2020)
Lluch, E., Camara, O., Doste, R., et al.: Calibration of a fully coupled electromechanical meshless computational model of the heart with experimental data. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 364, 112869 (2020)
Tong, L., Yang, P.Y., Liu, M.B.: A novel coupling approach of smoothed finite element method with SPH for thermal fluid structure interaction problems. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 174, 105558 (2020)
Zhang, X., Liu, Y.: Meshless Methods. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2004)
Belytschko, T., Organ, D., Krongauz, Y.: A coupled finite element-element-free Galerkin method. Comput. Mech. 17(3), 186–195 (1995)
Dolbow, J., Belytschko, T.: Volumetric locking in the element free Galerkin method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 46(6), 925–942 (1999)
Li, X.L., Li, S.L.: Analyzing the nonlinear p-Laplacian problem with the improved element-free Galerkin method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 100, 48–58 (2019)
Yuan, S., Du, J.N.: Upper bound limit analysis using the weak form quadrature element method. Appl. Math. Model. 56, 551–563 (2018)
Hegen, D.: Element-free Galerkin methods in combination with finite element approaches. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 135, 143–166 (1996)
Liu, G.R., Gu, Y.T.: An Introduction to Meshless Methods and Their Programming. Springer, Dordrecht (2005)
Yang, J.J., Wen, P.H.: Meshless Methods: Theories and Approaches. Science Press, Beijing (2018)
Wu, Q., Liu, F.B., Cheng, Y.M.: The interpolating element-free Galerkin method for three-dimensional elastoplasticity problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 115, 156–167 (2020)
Joldes, G., Boutantas, G., Zwick, B., et al.: Suite of meshless algorithms for accurate computation of soft tissue deformation for surgical simulation. Med. Image Anal. 56, 152–171 (2019)
Milewski, S., Putanowicz, R.: Higher order meshless schemes applied to the finite element method in elliptic problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 77(3), 779–802 (2019)
Saravanan, T.J.: Convergence study on ultrasonic guided wave propagation modes in an axisymmetric cylindrical waveguide. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1842949. (early access)
Nemer, R., Larcher, A., Coupez, T., et al.: Stabilized finite element method for incompressible solid dynamics using an updated Lagrangian formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 384, 113923 (2021)
Rossi, R., Zorrilla, R., Codina, R.: A stabilised displacement-volumetric strain formulation for nearly incompressible and anisotropic materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 377, 113701 (2021)
Li, Q.M., Zhong, W., Liu, Y.Q., et al.: A new locking-free hexahedral element with adaptive subdivision for explicit coining simulation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 128, 105–115 (2017)
Nguyen, D.D., Nguyen, M.N., Nguyen, N.D., et al.: Enhanced nodal gradient finite elements with new numerical integration schemes for 2D and 3D geometrically nonlinear analysis. Appl. Math. Model. 93(1), 326–359 (2021)
Birda, A., Reuss, J., Hackl, C.M.: Synchronous optimal pulse width modulation for synchronous machines with highly operating point dependent magnetic anisotropy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 68(5), 3760–3769 (2021)
Xu, X.P., Han, Q.K.: A general electromagnetic model and vibration control for shape deviations in PMSM supported by three-pole active magnetic bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 158, 107710 (2021)
Lv, Y.J., Cheng, S.W., Ji, Z.K., et al.: Permeance distribution function: a powerful tool to analyze electromagnetic forces induced by PWM current harmonics in multiphase surface permanent-magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 35(7), 7379–7391 (2021)
Li, W.L., Wu, Z.G., Tang, H.Y., et al.: Research on multi-physical fields of high-power PMSM/G used for FESS during the process of controllable charging and uncontrollable discharging. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 35(1), 454–461 (2020)
Pappalardo, C.M., Zhang, Z.G., Shabana, A.A.: Use of independent volume parameters in the development of new large displacement ANCF triangular plate/shell elements. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(4), 2171–2202 (2018)
Li, S.Z., Han, Y., Liu, C.Z.: Coupled multiphysics field analysis of high-current irregular-shaped busbar. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 9(9), 1805–1814 (2019)
Shi, Z., Sun, X.D., Lei, G., et al.: Analysis and optimization of radial force of permanent-magnet synchronous hub motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 68, 1–4 (2020)
Fang, Y., Zhang, T.: Vibroacoustic characterization of a permanent magnet synchronous motor power train for electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 33(1), 272–280 (2018)
Chai, F., Li, Y., Pei, Y.L., et al.: Analysis of radial vibration caused by magnetic force and torque pulsation in interior permanent magnet synchronous motor considering Ai-Gap deformations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(9), 6703–6714 (2019)
Liu, J., Ye, W.B., Zang, Q.S., et al.: Deformation laminated and sandwich cylindrical shell with covered or embedded piezoelectric layers under compression and electrical loading. Compos. Struct. 240, 112041 (2020)
Yu, S.Y., Peng, M.J., Cheng, H., et al.: The improved element-free Galerkin method for three-dimensional elastoplasticity problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 104, 215–224 (2019)
Huang, Z.T., Lei, D., Han, Z., et al.: Boundary moving least squares method for 3D elasticity problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 121, 255–266 (2021)
Fahrendorf, F., Morganti, S., Reali, A., et al.: Mixed stress-displacement isogeometric collocation for nearly incompressible elasticity and elastoplasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 369, 113112 (2020)
Jung, Y.H., Park, M.R., Lim, M.S.: Asymmetric rotor design of IPMSM for vibration reduction under certain load condition. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 35(2), 928–937 (2020)
Lan, H., Zou, J.B., Xu, Y.X.: Effect of local tangential force on vibration performance in fractional-slot concentrated winding permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 34(2), 1082–1093 (2019)
Qin, X., Shen, Y.J., Chen, W., et al.: Bending and free vibration analyses of circular stiffened plates using the FSDT mesh-free method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 202, 106498 (2021)
Li, X.L.: Three-dimensional complex variable element-free Galerkin method. Appl. Math. Model. 63, 148–171 (2018)
Riker, C., Holze, S.M.: The mixed-cell-complex partition-of-unity method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1235–1248 (2009). (SI)
Wang, X.Y., Qi, H.B., Sun, Z.Y., et al.: A multiscale discrete-continuum mosaic method for nonlinear mechanical behaviors of periodic micro/nano-scale structures. Appl. Math. Model. 93, 376–394 (2021)
Bourantas, G.C., Mountris, K.A., Loukopoulos, V.C., et al.: Strong-form approach to elasticity: hybrid finite difference-meshless collocation method (FDMCM). Appl. Math. Model. 57, 316–338 (2018)
Aswathy, M., Arun, C.O.: An improved response function based stochastic meshless method for problems in elasto-statics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 372, 113419 (2020)
Jameel, A., Harmain, G.A.: Fatigue crack growth analysis of cracked specimens by the coupled finite element-element free Galerkin method. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 26(16), 1343–1356 (2019)
Pathak, H., Singh, A., Singh, I.V., et al.: Three-dimensional stochastic quasi-static fatigue crack growth simulations using coupled FE-EFG approach. Comput. Struct. 160, 1–19 (2015)
Shojaei, A., Galvanetto, U., Rabczuk, T., et al.: A generalized finite difference method based on the peridynamic differential operator for the solution of problems in bounded and unbounded domains. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 343, 100–126 (2019)
Yang, J.L., Zheng, J.L.: Approximate stability of moving least squares method. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. 35(4), 638–648 (2012)
Wang, S.M., Hong, J.F., Sun, Y.J., et al.: Filling force valley with interpoles for pole-frequency vibration reduction in surface-mounted PM synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 67(8), 6709–6720 (2020)
Liu, X.B., Du, P.A., Qiao, X.Y., et al.: Study on effect of master DOF on errors of substructure static condensation modal analysis. China Mech. Eng. 22(3), 274–304 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The work has been partially funded by “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities” (3216002101A2), the National “Double First-class” Construction Special Funds Project (4316002181) and Altair 2020 Young Talent Support Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xu, W. Vibration analysis of permanent magnet synchronous motor using coupled finite element analysis and optimized meshless method. Nonlinear Dyn 108, 167–189 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07238-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07238-4