Abstract
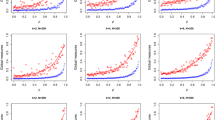
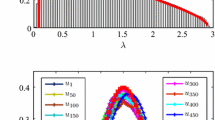
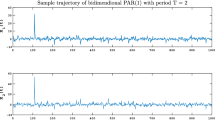
Zhao et al. (Nonlin. Dyn. 88, 477-487, 2017) presented the mutual information matrix (MIM) analysis for the study of nonlinear interactions in multivariate time series as an extension of Random Matrix Theory analysis. They considered the histogram estimation of mutual information based on Shannon entropy for discrete distributions. This paper is motivated by the latter, extending MIM analysis from a nonparametric and probabilistic discrete approach to a parametric and probabilistic continuous approach. Specifically, this paper presents the MIM based on Maximum Likelihood Estimators (MLEs) for flexible and tractable families of continuous multivariate distributions, called multivariate skew-elliptical families of distributions. This method focus on multivariate skew-Gaussian and skew-t distributions that allow modeling skewness and heavy-tails, respectively. Performance of the proposed methodology is illustrated by numerical results given by sinusoidal and vector autoregressive fractionally integrated moving-average models, and applied to a meteorological monitoring network data set. Results show that the consideration of skewness and heavy-tails in the transformed ozone time series produced some differences in the MIM estimations compared with those obtained by applying histogram estimations to transformed data. Given that mutual information index (MII) increases in line with the number of bins for the histogram estimator, the proposed methodology based on MLEs considered more robust estimators with respect to the histogram ones to determine the MII of multivariate time series.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, G.J., Xie, C., Chen, S., Yang, J.J., Yang, M.Y.: Random matrix theory analysis of cross-correlations in the US stock market: Evidence from Pearson’s correlation coefficient and detrended cross-correlation coefficient. Phys. A 392(17), 3715–3730 (2013)
Wang, B., Shen, Y.: A method on calculating high-dimensional mutual information and its application to registration of multiple ultrasound images. Ultrasonics 44(22), e79–e83 (2006)
Liu, C., Hu, S., Gu, J.J., Yang, J., Yu, M.: Brain image registration based on entropy of mutual information matrix. IEEE Can. Conf. Elec. Comput. Eng. 1163–1166, (2007)
Liu, F.: Quantum mutual information matrices. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15(1), 1750005 (2017)
Zhao, X., Shang, P., Wang, J.: Measuring information interactions on the ordinal pattern of stock time series. Phys. Rev. E 87(2), 022805 (2013)
Zhao, X., Shang, P., Huang, J.: Mutual-information matrix analysis for nonlinear interactions of multivariate time series. Nonlin. Dyn. 88(1), 477–487 (2017)
Lu, L., Ren, X., Cui, C., Luo, Y., Huang, M.: Tensor mutual information and its applications. Concurr. Comput. e5686, in press, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5686
Dionisio, A., Menezes, R., Mendes, D.A.: Mutual information: a measure of dependency for nonlinear time series. Phys. A 344(1–2), 326–329 (2004)
Kraskov, A., Stögbauer, H., Grassberger, P.: Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E 69(6), 066138 (2004)
Băbeanu, A.I.: A random matrix perspective of cultural structure: groups or redundancies? J. Phys. Complex. 2(2), 025008 (2021)
Branco, M., Dey, D.: A general class of multivariate skew-elliptical distribution. J. Multivar. Anal. 79(1), 93–113 (2001)
Azzalini, A., Dalla Valle, A.: The multivariate skew-normal distribution. Biometrika 83(4), 715–726 (1996)
Azzalini, A., Capitanio, A.: Distributions generated by perturbation of symmetry with emphasis on a multivariate skew t-distribution. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B 65(2), 367–389 (2003)
Maleki, M., Wraith, D., Mahmoudi, M.R., Contreras-Reyes, J.E.: Asymmetric heavy-tailed vector auto-regressive processes with application to financial data. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 90(2), 324–340 (2020)
Arellano-Valle, R.B., Contreras-Reyes, J.E., Genton, M.G.: Shannon entropy and mutual information for multivariate skew-elliptical distributions. Scand. J. Stat. 40(1), 42–62 (2013)
Abid, S.H., Quaez, U.J., Contreras-Reyes, J.E.: An information-theoretic approach for multivariate skew-\(t\) distributions and applications. Mathematics 9(2), 146 (2021)
Eltoft, T., Doulgeris, A., Anfinsen, S.N.: Analysis of textured PolSAR data by shannon entropy. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. (IGARSS) 1449–1452, 2012 (2012)
Madani, K., Kachurka, V., Sabourin, C., Amarger, V., Golovko, V., Rossi, L.: A human-like visual-attention-based artificial vision system for wildland firefighting assistance. Appl. Intell. 48(8), 2157–2179 (2018)
Contreras-Reyes, J.E.: Asymptotic form of the Kullback-Leibler divergence for multivariate asymmetric heavy-tailed distributions. Phys. A 395, 200–208 (2014)
Penev, S., Shevchenko, P.V., Wu, W.: The impact of model risk on dynamic portfolio selection under multi-period mean-standard-deviation criterion. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 273(2), 772–784 (2019)
Kobayashi, T.: Student-t policy in reinforcement learning to acquire global optimum of robot control. Appl. Intell. 49(12), 4335–4347 (2019)
Contreras-Reyes, J.E.: Chaotic systems with asymmetric and heavy-tailed noise: application to 3D attractors. Chaos Solit. Fract. 145, 110820 (2021)
Cover, T.M., Thomas, J.A.: Elements of Information Theory, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, NY, USA (2006)
Freedman, D., Diaconis, P.: On the histogram as a density estimator: \(L_2\) theory. Prob. Theor. Rel. Fields 57(4), 453–476 (1981)
Lai, D., Nardini, C.: A corrected normalized mutual information for performance evaluation of community detection. J. Stat. Mech. 2016(9), 093403 (2016)
Jones, K.R.W.: Entropy of random quantum states. J. Phys. A 23(23), L1247 (1990)
Contreras-Reyes, J.E.: Fisher information and uncertainty principle for skew-gaussian random variables. Fluct. Noise Lett. 20(5), 2150039 (2021)
R Core Team: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, (2019)
Piessens, R., deDoncker-Kapenga, E., Uberhuber, C., Kahaner, D.: Quadpack: a Subroutine Package for Automatic Integration. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany (1983)
Shang, B., Shang, P.: Complexity analysis of multiscale multivariate time series based on entropy plane via vector visibility graph. Nonlin. Dyn. 102(3), 1881–1895 (2020)
Mikhlin, Y.V., Rudnyeva, G.V.: Stability of similar nonlinear normal modes under random excitation. Nonlin. Dyn. 103, 3407–3415 (2021)
Chung, C.F.: Calculating and analyzing impulse responses for the vector ARFIMA model. Econ. Lett. 71(1), 17–25 (2001)
Silva, C., Quiroz, A.: Optimization of the atmospheric pollution monitoring network at Santiago de Chile. Atmos. Environ. 37(17), 2337–2345 (2003)
Seremi de Salud: Red MACAM: Indices de Calidad del Aire, Santiago de Chile, (2006). Available on http://www.seremisaludrm.cl/sitio/pag/aire/indexjs3aireindgasesdemo-prueba.asp
Zhao, X., Shang, P., Lin, A.: Distribution of eigenvalues of detrended cross-correlation matrix. Europhys. Lett. 107(4), 40008 (2014)
Contreras-Reyes, J.E., Idrovo-Aguirre, B.J.: Backcasting and forecasting time series using detrended cross-correlation analysis. Phys. A 560, 125109 (2020)
Lv, F., Yu, S., Wen, C., Principe, J.C.: Interpretable Fault Detection using Projections of Mutual Information Matrix. J. Franklin I., in press, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.02.016
Karasu, S., Altan, A., Saraç, Z., Hacıoğlu, R.: Estimation of fast varied wind speed based on NARX neural network by using curve fitting. Int. J. Ener. Appl. Tech. 4(3), 137–146 (2017)
Altan, A., Hacıoğlu, R.: Model predictive control of three-axis gimbal system mounted on UAV for real-time target tracking under external disturbances. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 138, 106548 (2020)
Acknowledgements
Research was fully supported by FONDECYT (Chile) grant No. 11190116. The author thanks the editor and two anonymous referees for their helpful comments and suggestions. All R codes used in this paper are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no known conflict of interest that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Contreras-Reyes, J.E. Mutual information matrix based on asymmetric Shannon entropy for nonlinear interactions of time series. Nonlinear Dyn 104, 3913–3924 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06498-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06498-w