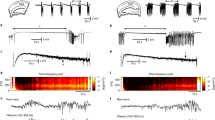
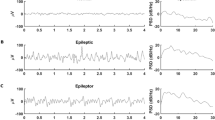
Abstract
Epilepsy is a group of chronic neurological disorders characterized with recurrent and hypersynchronous discharge. In the epileptic brain, epileptogenic zone (EZ) with abnormal firing patterns is considered as the culprit of hyperexcitable neuronal behaviors, increasingly manifested as alterations in dynamics. Meanwhile, the brain networks of epileptic patients show greater seizure susceptibility than those from healthy controls, referred as epileptogenic networks. There is a growing recognition of an intimate, but also complex, relationship between the self-organization of epileptogenic networks and abnormal dynamics of the EZ. In this review, we discussed the short- and long-term effects of recurrent epileptiform discharge on neural circuits, involving the regulation of connection weights and network topology. In addition, progressive abnormalities associated with secondary epileptogenesis imply that the excitability of regions connected with EZ may be enhanced, leading to frequent transitions from normal to epileptic states. From the perspective of network dynamics, EZ plays a dynamical pacemaker role in the evolution of epileptogenic networks as well as the activities generated by these networks. It may provide novel insights into the mechanism of epileptogenesis and inspire new therapeutic strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moraes, M.F.D., de Castro Medeiros, D., Mourao, F.A.G., Cancado, S.A.V., Cota, V.R.: Epilepsy as a dynamical system, a most needed paradigm shift in epileptology. Epilepsy Behav. 106838 (2019)
Connors, B.W., Gutnick, M.J., Prince, D.A.: Electrophysiological properties of neocortical neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 48, 1302 (1982)
Young, J.C., Nasser, H.M., Casillas-Espinosa, P.M., O’Brien, T.J., Jackson, G.D., Paolini, A.G.: Multiunit cluster firing patterns of piriform cortex and mediodorsal thalamus in absence epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 97, 229–243 (2019)
da Silva, F.H.L., Harding, G.F.A.: Transition to seizure in photosensitive epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 97, 278–282 (2011)
Milton, J.G.: Epilepsy as a dynamic disease: a tutorial of the past with an eye to the future. Epilepsy Behav. 18, 33–44 (2010)
Stefanescu, R.A., Shivakeshavan, R.G., Talathi, S.S.: Computational models of epilepsy. Seizure 21, 748–759 (2012)
Ryzí, M., Brázdil, M., Novák, Z., Hemza, J., Chrastina, J., Ošlejšková, H., Rektor, I., Kuba, R.: Long-term outcomes in patients after epilepsy surgery failure. Epilepsy Res. 110, 71–77 (2015)
Woldman, W., Cook, M.J., Terry, J.R.: Evolving dynamic networks: an underlying mechanism of drug resistance in epilepsy? Epilepsy Behav. 94, 264–268 (2019)
Panzica, F., Varotto, G., Rotondi, F., Spreafico, R., Franceschetti, S.: Identification of the epileptogenic zone from stereo-EEG signals: a connectivity-graph theory approach. Front. Neurol. 4, 175 (2013)
Bernasconi, N., Duchesne, S., Janke, A., Lerch, J., Collins, D.L., Bernasconi, A.: Whole-brain voxel-based statistical analysis of gray matter and white matter in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 23, 717–723 (2004)
Taylor, P.N., Han, C.E., Schoene-Bake, J.-C., Weber, B., Kaiser, M.: Structural connectivity changes in temporal lobe epilepsy: Spatial features contribute more than topological measures. NeuroImage Clin 8, 322–328 (2015)
Hutchings, F., Han, C.E., Keller, S.S., Weber, B., Taylor, P.N., Kaiser, M.: Predicting surgery targets in temporal lobe epilepsy through structural connectome based simulations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11, e1004642 (2015)
Sinha, N., Dauwels, J., Kaiser, M., Cash, S.S., Brandon Westover, M., Wang, Y., Taylor, P.N.: Predicting neurosurgical outcomes in focal epilepsy patients using computational modelling. Brain 140, 319–332 (2017)
Goodfellow, M., Rummel, C., Abela, E., Richardson, M.P., Schindler, K., Terry, J.R.: Estimation of brain network ictogenicity predicts outcome from epilepsy surgery. Sci. Rep. 6, 29215 (2016)
Benjamin, O., Fitzgerald, T.H., Ashwin, P., Tsaneva-Atanasova, K., Chowdhury, F., Richardson, M.P., Terry, J.R.: A phenomenological model of seizure initiation suggests network structure may explain seizure frequency in idiopathic generalised epilepsy. J. Math. Neurosci. 2, 1 (2012)
Terry, J.R., Benjamin, O., Richardson, M.P.: Seizure generation: the role of nodes and networks. Epilepsia 53, e166–e169 (2012)
Bayati, M., Valizadeh, A.: Effect of synaptic plasticity in the structure and dynamics of disordered networks of coupled neurons. Physical Review E. 86, 011925 (2012)
Torres, J.J., Kappen, H.J.: Emerging phenomena in neural networks with dynamic synapses and their computational implications. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 7, 30 (2013)
Schindewolf, C., Kim, D., Bel, A., Rotstein, H.G.: Complex patterns in networks of hyperexcitable neurons. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 633, 71–82 (2016)
Volo, M.D., Torcini, A.: Transition from asynchronous to oscillatory dynamics in balanced spiking networks with instantaneous synapses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 128301 (2018)
Majak, K., Pitkänen, A.: Do seizures cause irreversible cognitive damage? Evidence from animal studies. Epilepsy Behav. 5, 35–44 (2004)
Citraro, R., Iannone, M., Leo, A., De Caro, C., Nesci, V., Tallarico, M., Abdalla, K., Palma, E., Arturi, F., De Sarro, G., Constanti, A., Russo, E.: Evaluation of the effects of liraglutide on the development of epilepsy and behavioural alterations in two animal models of epileptogenesis. Brain Res. Bull. 153, 133–142 (2019)
Hempel, C.M., Hartman, K.H., Wang, X.-J., Turrigiano, G.G., Nelson, S.B.: Multiple forms of short-term plasticity at excitatory synapses in rat medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 3031–3041 (2000)
Bernasconi, N., Natsume, J., Bernasconi, A.: Progression in temporal lobe epilepsy: differential atrophy in mesial temporal structures. Neurology 65, 223–228 (2005)
Bragin, A., Wilson, C.L., Engel, J.: Chronic epileptogenesis requires development of a network of pathologically interconnected neuron clusters: a hypothesis. Epilepsia 41, S144–S152 (2000)
Bernasconi, N.: Mesial temporal damage in temporal lobe epilepsy: a volumetric MRI study of the hippocampus, amygdala and parahippocampal region. Brain 126, 462–469 (2003)
Yang, C., Liu, Z., Luan, G., Wang, Q.: The extension of epileptogenicity as the driving force of the epileptogenic network evolution and complex symptoms. Brain Res. 1748, 147073 (2020)
Kobylarek, D., Iwanowski, P., Lewandowska, Z., Limphaibool, N., Szafranek, S., Labrzycka, A., Kozubski, W.: Advances in the potential biomarkers of epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 10, 685 (2019)
Liguori, C., Costa, C., Franchini, F., Izzi, F., Spanetta, M., Cesarini, E.N., Di Santo, S., Manfredi, N., Farotti, L., Romoli, M., Lanari, A., Salvadori, N., Parnetti, L., Calabresi, P., Mercuri, N.B., Placidi, F.: Cognitive performances in patients affected by late-onset epilepsy with unknown etiology: a 12-month follow-up study. Epilepsy Behav. 101, 106592 (2019)
Süße, M., Hamann, L., Flöel, A., von Podewils, F.: Nonlesional late-onset epilepsy: semiology, EEG, cerebrospinal fluid, and seizure outcome characteristics. Epilepsy Behav. 91, 75–80 (2019)
Ochoa, J.G., Hentgarden, D., Paulzak, A., Ogden, M., Pryson, R., Lammle, M., Rusyniak, W.G.: Subtle pathological changes in neocortical temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 71, 17–22 (2017)
Jacobs, J., Staba, R., Asano, E., Otsubo, H., Wu, J.Y., Zijlmans, M., Mohamed, I., Kahane, P., Dubeau, F., Navarro, V., Gotman, J.: High-frequency oscillations (HFOs) in clinical epilepsy. Prog. Neurobiol. 98, 302–315 (2012)
Jirsch, J.D.: High-frequency oscillations during human focal seizures. Brain 129, 1593–1608 (2006)
Bragin, A., Engel, J., Wilson, C.L., Fried, I., Mathern, G.W.: Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in human epileptic brain and in kainic acid-treated rats with chronic seizures. Epilepsia 40, 127–137 (1999)
Leung, H., Zhu, C.X.L., Chan, D.T.M., Poon, W.S., Shi, L., Mok, V.C.T., Wong, L.K.S.: Ictal high-frequency oscillations and hyperexcitability in refractory epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126, 2049–2057 (2015)
Kobayashi, K., Agari, T., Oka, M., Yoshinaga, H., Date, I., Ohtsuka, Y., Gotman, J.: Detection of seizure-associated high-frequency oscillations above 500Hz. Epilepsy Res. 88, 139–144 (2010)
Hao, J., Cui, Y., Liu, B., Yu, L., Lin, Y., Xia, Y., Yao, D., Guo, D.: Roles of very fast ripple (500–1000Hz) in the hippocampal network during status epilepticus. Int. J. Neural Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065721500027
Frauscher, B., Bartolomei, F., Kobayashi, K., Cimbalnik, J., van 't Klooster, M.A., Rampp, S., Otsubo, H., Höller, Y., Wu, J.Y., Asano, E., Engel, J., Kahane, P., Jacobs, J., Gotman, J.: High-frequency oscillations: the state of clinical research. Epilepsia. 58, 1316–1329 (2017)
Koc, G., Gokcil, Z., Bek, S., Kasikci, T., Eroglu, E., Odabasi, Z.: Effects of continuous theta burst transcranial magnetic stimulation on cortical excitability in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 77, 26–29 (2017)
Koenig, T., Smailovic, U., Jelic, V.: Past, present and future EEG in the clinical workup of dementias. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 306, 111182 (2020)
Tatum, W.O., Rubboli, G., Kaplan, P.W., Mirsatari, S.M., Radhakrishnan, K., Gloss, D., Caboclo, L.O., Drislane, F.W., Koutroumanidis, M., Schomer, D.L., Kasteleijn-Nolst Trenite, D., Cook, M., Beniczky, S.: Clinical utility of EEG in diagnosing and monitoring epilepsy in adults. Clin. Neurophysiol. 129, 1056–1082 (2018)
Liu, X., Wu, S., Daif, A., Sun, T., Chauhan, V., Issa, N.P., Rose, S., Tao, J.X.: Clinical implications of scalp ictal EEG pattern in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 130, 1604–1610 (2019)
Fangsaad, T., Assawabumrungkul, S., Visudtibhan, A.: Clinical course and long-term outcome in children with alteration of consciousness underwent continuous EEG monitoring: a prospective observational study in Thailand. J. Clin. Neurosci. 47, 93–96 (2018)
van Mierlo, P., Carrette, E., Hallez, H., Vonck, K., Van Roost, D., Boon, P., Staelens, S.: Accurate epileptogenic focus localization through time-variant functional connectivity analysis of intracranial electroencephalographic signals. Neuroimage 56, 1122–1133 (2011)
Chionis, D., Dokhane, A., Ferroukhi, H., Pautz, A.: Application of causality analysis on nuclear reactor systems. Chaos 29, 043126 (2019)
Bartolomei, F., Chauvel, P., Wendling, F.: Epileptogenicity of brain structures in human temporal lobe epilepsy: a quantified study from intracerebral EEG. Brain 131, 1818–1830 (2008)
Lehnertz, K., Elger, C.E.: Spatio-temporal dynamics of the primary epileptogenic area in temporal lobe epilepsy characterized by neuronal complexity loss. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 95, 108–117 (1995)
Andrzejak, R.G., Widman, G., Lehnertz, K., Rieke, C., David, P., Elger, C.E.: The epileptic process as nonlinear deterministic dynamics in a stochastic environment: an evaluation on mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 44, 129–140 (2001)
Andrzejak, R.G., Schindler, K., Rummel, C.: Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys. Rev. E 86, 046206 (2012)
Yang, C., Luan, G., Liu, Z., Wang, Q.: Dynamical analysis of epileptic characteristics based on recurrence quantification of SEEG recordings. Physica A 523, 507–515 (2019)
Li, X., Ouyang, G., Yao, X., Guan, X.: Dynamical characteristics of pre-epileptic seizures in rats with recurrence quantification analysis. Phys. Lett. A 333, 164–171 (2004)
Suffczynski, P., da Silva, F.H.L., Parra, J., Velis, D.N., Bouwman, B.M., van Rijn, C.M., van Hese, P., Boon, P., Khosravani, H., Derchansky, M., Carlen, P., Kalitzin, S.: Dynamics of epileptic phenomena determined from statistics of Ictal transitions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 53, 524–532 (2006)
Panahi, S., Aram, Z., Jafari, S., Ma, J., Sprott, J.C.: Modeling of epilepsy based on chaotic artificial neural network. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 105, 150–156 (2017)
Panahi, S., Shirzadian, T., Jalili, M., Jafari, S.: A new chaotic network model for epilepsy. Appl. Math. Comput. 346, 395–407 (2019)
Yan, J., Wang, Y., Ouyang, G., Yu, T., Li, X.: Using max entropy ratio of recurrence plot to measure electrocorticogram changes in epilepsy patients. Physica A 443, 109–116 (2016)
Acharya, U.R., Sree, S.V., Chattopadhyay, S., Yu, W., Ang, P.C.A.: Application of recurrence quantification analysis for the automated identification of epileptic EEG signals. Int. J. Neural Syst. 21, 199–211 (2011)
Ngamga, E.J., Bialonski, S., Marwan, N., Kurths, J., Geier, C., Lehnertz, K.: Evaluation of selected recurrence measures in discriminating pre-ictal and inter-ictal periods from epileptic EEG data. Phys. Lett. A 380, 1419–1425 (2016)
Lehnertz, K., Elger, C.E.: Can epileptic seizures be predicted? evidence from nonlinear time series analysis of brain electrical activity. Physiol. Rev. Lett. 80, 5019–5022 (1998)
Stacey, W., Le Van Quyen, M., Mormann, F., Schulze-Bonhage, A.: What is the present-day EEG evidence for a preictal state? Epilepsy Res. 97, 243–251 (2011)
Suffczynski, P., Kalitzin, S.: Epileptic transitions: model predictions and experimental validation. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 22, 13 (2005)
Laxpati, N.G., Kasoff, W.S., Gross, R.E.: Deep brain stimulation for the treatment of epilepsy: circuits, targets, and trials. Neurotherapeutics 11, 508–526 (2014)
Kalitzin, S.N., Velis, D.N., da Silva, F.H.L.: Stimulation-based anticipation and control of state transitions in the epileptic brain. Epilepsy Behav. 17, 310–323 (2010)
Balamurugan, E., Aggarwal, M., Lamba, A., Dang, N., Tripathi, M.: Perceived trigger factors of seizures in persons with epilepsy. Seizure 22, 743–747 (2013)
Gilby, K.L., O’Brien, T.J.: Epilepsy, autism, and neurodevelopment: kindling a shared vulnerability? Epilepsy Behav. 26, 370–374 (2013)
da Silva, F.H.L., Blanes, W., Kalitzin, S.N., Parra, J., Suffczynski, P., Velis, D.N.: Epilepsies as dynamical diseases of brain systems: basic models of the transition between normal and epileptic activity. Epilepsia 44, 72–83 (2003)
Freeman, W.J., Kozma, R., Werbos, P.J.: Biocomplexity: adaptive behavior in complex stochastic dynamical systems. Biosystems 59, 109–123 (2001)
Tankus, A.: Exploring human epileptic activity at the single-neuron level. Epilepsy Behav. 58, 11–17 (2016)
Kalitzin, S., Velis, D., Suffczynski, P., Parra, J., da Silva, F.H.L.: Electrical brain-stimulation paradigm for estimating the seizure onset site and the time to ictal transition in temporal lobe epilepsy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 116, 718–728 (2005)
Barker, B.S., Nigam, A., Ottolini, M., Gaykema, R.P., Hargus, N.J., Patel, M.K.: Pro-excitatory alterations in sodium channel activity facilitate subiculum neuron hyperexcitability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 108, 183–194 (2017)
Truccolo, W., Donoghue, J.A., Hochberg, L.R., Eskandar, E.N., Madsen, J.R., Anderson, W.S., Brown, E.N., Halgren, E., Cash, S.S.: Single-neuron dynamics in human focal epilepsy. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 635–641 (2011)
Litt, B., Esteller, R., Echauz, J., D’Alessandro, M., Shor, R., Henry, T., Pennell, P., Epstein, C., Bakay, R., Dichter, M., Vachtsevanos, G.: Epileptic seizures may begin hours in advance of clinical onset: a report of five patients. Neuron 30, 51–64 (2001)
Avoli, M., de Curtis, M., Köhling, R.: Does interictal synchronization influence ictogenesis? Neuropharmacology 69, 37–44 (2013)
Righes Marafiga, J., Vendramin Pasquetti, M., Calcagnotto, M.E.: GABAergic interneurons in epilepsy: more than a simple change in inhibition. Epilepsy Behav. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.106935
Rich, S., Chameh, H.M., Rafiee, M., Ferguson, K., Skinner, F.K., Valiante, T.A.: Inhibitory network bistability explains increased interneuronal activity prior to seizure onset. Front. Neural Circuits 13, 81 (2020)
Proix, T., Jirsa, V.K., Bartolomei, F., Guye, M., Truccolo, W.: Predicting the spatiotemporal diversity of seizure propagation and termination in human focal epilepsy. Nat. Commun. 9, 1088 (2018)
Perucca, P., Dubeau, F., Gotman, J.: Intracranial electroencephalographic seizure-onset patterns: effect of underlying pathology. Brain 137, 183–196 (2014)
Wang, Y., Goodfellow, M., Taylor, P.N., Baier, G.: Phase space approach for modeling of epileptic dynamics. Phys. Rev. E. 85, 061918 (2012)
Jirsa, V.K., Stacey, W.C., Quilichini, P.P., Ivanov, A.I., Bernard, C.: On the nature of seizure dynamics. Brain 137, 2210–2230 (2014)
Guo, D., Xia, C., Wu, S., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Xia, Y., Yao, D.: Stochastic fluctuations of permittivity coupling regulate seizure dynamics in partial epilepsy. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 60, 995–1002 (2017)
Proix, T., Bartolomei, F., Chauvel, P., Bernard, C., Jirsa, V.K.: Permittivity coupling across brain regions determines seizure recruitment in partial epilepsy. J. Neurosci. 34, 15009–15021 (2014)
Zhang, L., Wang, Q., Baier, G.: Dynamical features of a focal epileptogenic network model for stimulation-based control. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 28, 1856–1865 (2020)
Zhang, L., Wang, Q., Baier, G.: Spontaneous transitions to focal-onset epileptic seizures: a dynamical study. Chaos 30, 103114 (2020)
Badawy, R.A.B., Harvey, A.S., Macdonell, R.A.L.: Cortical hyperexcitability and epileptogenesis: understanding the mechanisms of epilepsy–Part 1. J. Clin. Neurosci. 16, 355–365 (2009)
Whelan, C.D., Altmann, A., Botía, J.A., et al.: Structural brain abnormalities in the common epilepsies assessed in a worldwide ENIGMA study. Brain 141, 391–408 (2018)
Focke, N.K., Yogarajah, M., Bonelli, S.B., Bartlett, P.A., Symms, M.R., Duncan, J.S.: Voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. Neuroimage 40, 728–737 (2008)
van Mierlo, P., Carrette, E., Hallez, H., Raedt, R., Meurs, A., Vandenberghe, S., Van Roost, D., Boon, P., Staelens, S., Vonck, K.: Ictal-onset localization through connectivity analysis of intracranial EEG signals in patients with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 54, 1409–1418 (2013)
Wilke, C., van Drongelen, W., Kohrman, M., He, B.: Identification of epileptogenic foci from causal analysis of ECoG interictal spike activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 120, 1449–1456 (2009)
Zhang, L., Liang, Y., Li, F., Sun, H., Peng, W., Du, P., Si, Y., Song, L., Yu, L., Xu, P.: Time-varying networks of inter-ictal discharging reveal epileptogenic zone. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 77 (2017)
Ben-Ari, Y., Tremblay, E., Ottersen, O.P., Naquet, R.: Evidence suggesting secondary epileptogenic lesions after kainic acid: pretreatment with diazepam reduces distant but not local brain damage. Brain Res. 165, 362–365 (1979)
Alamir, M., Welsh, J.S., Goodwin, G.C.: Synaptic plasticity based model for epileptic seizures. Automatica 47, 1183–1192 (2011)
Wiemann, M., Altrup, U., Speckmann, E.-J.: Epileptic neurons induce augmenting synaptic depolarizations in non-epileptic neurons (buccal ganglia, Helix pomatia). Neurosci. Lett. 237, 101–104 (1997)
Lehnertz, K., Ansmann, G., Bialonski, S., Dickten, H., Geier, C., Porz, S.: Evolving networks in the human epileptic brain. Physica D 267, 7–15 (2014)
Kurths, J.: Bistable firing pattern in a neural network model. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 13, 8 (2019)
Gilson, M.: STDP in recurrent neuronal networks. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 4, 23 (2010)
Luccioli, S., Angulo-Garcia, D., Cossart, R., Malvache, A., Módol, L., Sousa, V.H., Bonifazi, P., Torcini, A.: Modeling driver cells in developing neuronal networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 14, e1006551 (2018)
Bayati, M., Valizadeh, A., Abbassian, A., Cheng, S.: Self-organization of synchronous activity propagation in neuronal networks driven by local excitation. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 9, 69 (2015)
Raiesdana, S., Firoozabadi, S.M.P., Gholpayegani, S.M.H.: An evolutionary network model of epileptic phenomena. Neurocomputing 74, 617–628 (2011)
Zucker, R.S., Regehr, W.G.: Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 355–405 (2002)
Fuhrmann, G., Segev, I., Markram, H., Tsodyks, M.: Coding of temporal information by activity-dependent synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 87, 140–148 (2002)
Thomson, A.M.: Activity-dependent properties of synaptic transmission at two classes of connections made by rat neocortical pyramidal axons in vitro. J. Physiol. 502, 131–147 (1997)
Gonzalez-Burgos, G.: Synaptic efficacy during repetitive activation of excitatory inputs in primate dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 14, 530–542 (2004)
Molaee-Ardekani, B., Benquet, P., Bartolomei, F., Wendling, F.: Computational modeling of high-frequency oscillations at the onset of neocortical partial seizures: from ‘altered structure’ to ‘dysfunction.’ Neuroimage 52, 1109–1122 (2010)
Gutkin, B.S., Laing, C.R., Colby, C.L., Chow, C.C., Ermentrout, G.B.: Turning on and off with excitation: the role of spike-timing asynchrony and synchrony in sustained neural activity. J. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 121–134 (2001)
Yang, C., Liu, Z., Wang, Q., Luan, G., Zhai, F.: Epileptic seizures in a heterogeneous excitatory network with short-term plasticity. Cogn Neurodyn. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09582-w
González, O.C., Krishnan, G.P., Timofeev, I., Bazhenov, M.: Ionic and synaptic mechanisms of seizure generation and epileptogenesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 130, 104485 (2019)
Jiang, H., Cai, Z., Worrell, G.A., He, B.: Multiple oscillatory push–pull antagonisms constrain seizure propagation. Ann. Neurol. 86, 683–694 (2019)
Wasling, P., Hanse, E., Gustafsson, B.: Long-term depression in the developing hippocampus: low induction threshold and synapse nonspecificity. J. Neurosci. 22, 1823–1830 (2002)
Lippman-Bell, J.J., Zhou, C., Sun, H., Feske, J.S., Jensen, F.E.: Early-life seizures alter synaptic calcium-permeable AMPA receptor function and plasticity. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 76, 11–20 (2016)
Lynch, G., Kramár, E.A., Babayan, A.H., Rumbaugh, G., Gall, C.M.: Differences between synaptic plasticity thresholds result in new timing rules for maximizing long-term potentiation. Neuropharmacology 64, 27–36 (2013)
David, O., Woźniak, A., Minotti, L., Kahane, P.: Preictal short-term plasticity induced by intracerebral 1 Hz stimulation. Neuroimage 39, 1633–1646 (2008)
Bertram, E.: The relevance of kindling for human epilepsy. Epilepsia 48, 65–74 (2007)
Wang, Y., Chen, Z.: An update for epilepsy research and antiepileptic drug development: toward precise circuit therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 201, 77–93 (2019)
Ma, J., Yang, Z., Yang, L., Tang, J.: A physical view of computational neurodynamics. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A. 20, 639–659 (2019)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569–1578 (2017)
Roth, B.L.: DREADDs for neuroscientists. Neuron 89, 683–694 (2016)
Adamantidis, A.R., Zhang, F., Aravanism, A.M., Deisseroth, K., Lecea, L.D.: Neural substrates of awakening probed with optogenetic control of hypocretin neurons. Nature 450, 420–424 (2007)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics of collective behaviors of network of neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58, 2038–2045 (2015)
Yang, L.-X., Jin, C.-L., Zhu-Ge, Z.-B., Wang, S., Wei, E.-Q., Bruce, I.C., Chen, Z.: Unilateral low-frequency stimulation of central piriform cortex delays seizure development induced by amygdaloid kindling in rats. Neuroscience 138, 1089–1096 (2006)
Sun, H., Zhang, S., Zhong, K., Xu, Z., Zhu, W., Fang, Q., Wu, D., Hu, W., Xiao, B., Chen, Z.: Mode-dependent effect of low-frequency stimulation targeting the hippocampal CA3 subfield on amygdala-kindled seizures in rats. Epilepsy Res. 90, 83–90 (2010)
Neal, E.G., Maciver, S., Schoenberg, M.R., Vale, F.L.: Surgical disconnection of epilepsy network correlates with improved outcomes. Seizure 76, 56–63 (2020)
Briellmann, R.S., Jackson, G.D., Pell, G.S., Mitchell, L.A., Abbott, D.F.: Structural abnormalities remote from the seizure focus: a study using T2 relaxometry at 3 T. Neurology 63, 2303–2308 (2004)
Bernasconi, N., Bernasconi, A., Caramanos, Z., Andermann, F., Dubeau, F., Arnold, D.L.: Morphometric MRI analysis of the parahippocampal region in temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 911, 495–500 (2006)
Scott, R.C.: Abnormalities in hippocampi remote from the seizure focus: a T2 relaxometry study. Brain 126, 1968–1974 (2003)
Klviinen, R., Salmenper, T.: Do recurrent seizures cause neuronal damage? A series of studies with MRI volumetry in adults with partial epilepsy. Prog. Brain Res. 135, 279–295 (2002)
Meldrum, B.S.: Concept of activity-induced cell death in epilepsy: historical and contemporary perspectives. Prog. Brain Res. 135, 3–11 (2002)
Wu, J., Gao, M., Shen, J., Qiu, S., Kerrigan, J.F.: Mechanisms of intrinsic epileptogenesis in human gelastic seizures with hypothalamic hamartoma. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 21, 104–111 (2015)
Castro, L.H., Ferreira, L.K., Teles, L.R., Jorge, C.L., Arantes, P.R., Ono, C.R., Adda, C.C., Valerio, R.F.: Epilepsy syndromes associated with hypothalamic hamartomas. Seizure 16, 50–58 (2007)
Scholly, J., Staack, A.M., Kahane, P., Scavarda, D., Régis, J., Hirsch, E., Bartolomei, F.: Hypothalamic hamartoma: epileptogenesis beyond the lesion? Epilepsia 58, 32–40 (2017)
Scholly, J., Valenti, M.-P., Staack, A.M., Strobl, K., Bast, T., Kehrli, P., Steinhoff, B.J., Hirsch, E.: Hypothalamic hamartoma: is the epileptogenic zone always hypothalamic? Arguments for independent (third stage) secondary epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 54, 123–128 (2013)
Goddard, G.V.: Development of epileptic seizures through brain stimulation at lowintensity. Nature 214, 1020–1021 (1967)
Goodfellow, M., Taylor, P.N., Wang, Y., Garry, D.J., Baier, G.: Modelling the role of tissue heterogeneity in epileptic rhythms: tissue heterogeneity in epileptic rhythms. Eur. J. Neurosci. 36, 2178–2187 (2012)
Wang, Y., Trevelyan, A.J., Valentin, A., Alarcon, G., Taylor, P.N., Kaiser, M.: Mechanisms underlying different onset patterns of focal seizures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 13, e1005475 (2017)
Wang, Y., Goodfellow, M., Taylor, P.N., Baier, G.: Dynamic mechanisms of neocortical focal seizure onset. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10, e1003787 (2014)
Kalitzin, S., Koppert, M., Petkov, G., Velis, D., da Silva, F.H.L.: Computational model prospective on the observation of proictal states in epileptic neuronal systems. Epilepsy Behav. 22, S102–S109 (2011)
Kalitzin, S., Koppert, M., Petkov, G., da Silva, F.H.L.: Multiple oscillatory states in models of collective neuronal dynamics. Int. J. Neural Syst. 24, 1450020 (2014)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 116, 473–496 (1952)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equation. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B. 221, 87–102 (1984)
Burkitt, A.N.: A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I Homogeneous synaptic input. Biol. Cybern. 95, 1–19 (2006)
Jansen, B.H., Zouridakis, G., Brandt, M.E.: A neurophysiologically-based mathematical model of flash visual evoked potentials. Biol. Cybern. 68, 275–283 (1993)
Wendling, F., Bartolomei, F., Bellanger, J.J., Chauvel, P.: Epileptic fast activity can be explained by a model of impaired GABAergic dendritic inhibition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 15, 1499–1508 (2002)
Wang, Z., Tian, C., Dhamala, M., Liu, Z.: A small change in neuronal network topology can induce explosive synchronization transition and activity propagation in the entire network. Sci. Rep. 7, 561 (2017)
Gerster, M., Berner, R., Sawicki, J., Zakharova, A., Škoch, A., Hlinka, J., Lehnertz, K., Schöll, E.: FitzHugh–Nagumo oscillators on complex networks mimic epileptic-seizure-related synchronization phenomena. Chaos 30, 123130 (2020)
Liu, Z., Luan, G., Yang, C., Guan, Y., Liu, C., Wang, J., Wang, M., Wang, Q.: Distinguishing dependent-stage secondary epileptogenesis in a complex case of giant hypothalamic hamartoma with assistance of a computational method. Front. Neurol. 11, 478 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grants 11932003, 81790650, 81790654).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CY contributed to conceptualization, investigation, writing–original draft. ZL contributed to resources, writing—review, and editing. QW contribted to writing—review and editing. QW contributed to project administration and funding acquisition. ZL contributed to investigation, writing—review and editing. GL supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no any interest conflict with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Liu, Z., Wang, Q. et al. Epilepsy as a dynamical disorder orchestrated by epileptogenic zone: a review. Nonlinear Dyn 104, 1901–1916 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06420-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06420-4