Abstract
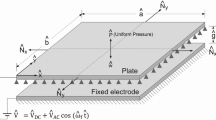
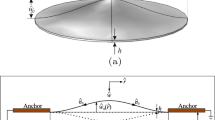
In this paper, the effects of initial deflection on the static and dynamic behaviors of circular capacitive transducers are experimentally investigated. The obtained results are in good agreement with numerical simulations. It is shown that the initial deflection has a major impact on the static response of the resonator by shifting the pull-in voltage, and on its dynamic response by increasing the resonance frequency and modifying the bifurcation topology from softening to hardening behavior. Moreover, the dynamic behavior of the microplate may display nonlinear periodic and quasiperiodic responses due to geometric and electrostatic nonlinearities.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
Raw data were generated using the experimental equipments of FEMTO-ST institute. Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the first author Aymen Jallouli on request.
References
Alcheikh, N., Hajjaj, A., Younis, M.I.: Highly sensitive and wide-range resonant pressure sensor based on the veering phenomenon. Sens. Actuators, A 300, 111652 (2019)
Alkharabsheh, S.A., Younis, M.I.: Statics and dynamics of mems arches under axial forces. J. Vib. Acoust. 135(2), 021007 (2013)
Alneamy, A.M., Khater, M.E., Abdel-Aziz, A.K., Heppler, G.R., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Electrostatic arch micro-tweezers. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 118, 103298 (2020)
Bataineh, A.M., Younis, M.I.: Dynamics of a clamped-clamped microbeam resonator considering fabrication imperfections. Microsyst. Technol. 21(11), 2425–2434 (2015)
Bellaredj, M., Bourbon, G., Walter, V., Le Moal, P., Berthillier, M.: Anodic bonding using soi wafer for fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24(2), 025009 (2014)
Braun, T., Barwich, V., Ghatkesar, M.K., Bredekamp, A.H., Gerber, C., Hegner, M., Lang, H.P.: Micromechanical mass sensors for biomolecular detection in a physiological environment. Phys. Rev. E 72(3), 031907 (2005)
Brent, R.P.: Algorithms for Minimization without Derivatives. Courier Corporation, USA (2013)
Celep, Z.: Free flexural vibration of initially imperfect thin plates with large elastic amplitudes. ZAMM-J. Appl. Math. Mech./Z. für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik 56(9), 423–428 (1976)
Celep, Z.: Shear and rotatory inertia effects on the large amplitude vibration of the initially imperfect plates. J. Appl. Mech. 47(3), 662–666 (1980)
Chu, W.H., Mehregany, M.: A study of residual stress distribution through the thickness of p/sup+/silicon films (thermal oxidation effects). IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 40(7), 1245–1250 (1993)
Comini, E., Faglia, G., Sberveglieri, G.: Solid State Gas Sensing, vol. 20. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2008)
Duffy, S., Bozler, C., Rabe, S., Knecht, J., Travis, L., Wyatt, P., Keast, C., Gouker, M.: Mems microswitches for reconfigurable microwave circuitry. IEEE Microwave Wirel. Compon. Lett. 11(3), 106–108 (2001)
Ganji, B.A., Majlis, B.Y.: Slotted capacitive microphone with sputtered aluminum diaphragm and photoresist sacrificial layer. Microsyst. Technol. 16(10), 1803–1809 (2010)
Hafiz, M.A.A., Kosuru, L., Younis, M.I.: Microelectromechanical reprogrammable logic device. Nature Commun. 7, 11137 (2016)
Hirsch, P., Roberts, S.: The brittle-ductile transition in silicon. Philos. Mag. A 64(1), 55–80 (1991)
Jallouli, A., Kacem, N., Bourbon, G., Le Moal, P., Walter, V., Lardies, J.: Pull-in instability tuning in imperfect nonlinear circular microplates under electrostatic actuation. Phys. Lett. A 380(46), 3886–3890 (2016)
Jallouli, A., Kacem, N., Lardies, J.: Investigations of the effects of geometric imperfections on the nonlinear static and dynamic behavior of capacitive micomachined ultrasonic transducers. Micromachines 9(11), 575 (2018)
Jallouli, A., Kacem, N., Najar, F., Bourbon, G., Lardies, J.: Modeling and experimental characterization of squeeze film effects in nonlinear capacitive circular microplates. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 127, 68–88 (2019)
Jia, X.L., Yang, J., Kitipornchai, S.: Pull-in instability of geometrically nonlinear micro-switches under electrostatic and casimir forces. Acta Mech. 218(1–2), 161–174 (2011)
Juillard, J., Bonnoit, A., Avignon, E., Hentz, S., Kacem, N., Colinet, E.: From MEMS to NEMS: Closed-loop actuation of resonant beams beyond the critical Duffing amplitude. In: SENSORS, 2008 IEEE, Lecce, Italy, pp. 510–513 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSENS.2008.4716489
Kacem, N., Baguet, S., Hentz, S., Dufour, R.: Nonlinear phenomena in nanomechanical resonators: mechanical behaviors and physical limitations. Mech. Indus. 11(6), 521–529 (2010)
Kacem, N., Hentz, S., Baguet, S., Dufour, R.: Forced large amplitude periodic vibrations of non-linear mathieu resonators for microgyroscope applications. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 46(10), 1347–1355 (2011)
Krylov, S., Ilic, B.R., Schreiber, D., Seretensky, S., Craighead, H.: The pull-in behavior of electrostatically actuated bistable microstructures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18(5), 055026 (2008)
Mallik, S., Chowdhury, D., Chttopadhyay, M.: Development and performance analysis of a low-cost mems microphone-based hearing aid with three different audio amplifiers. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 15(1), 17–25 (2019)
Medina, L., Gilat, R., Krylov, S.: Bistable behavior of electrostatically actuated initially curved micro plate. Sens. Actuators, A 248, 193–198 (2016)
Medina, L., Gilat, R., Krylov, S.: Modeling strategies of electrostatically actuated initially curved bistable micro plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 118–119, 1–13 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.04.027
Medina, L., Gilat, R., Krylov, S.: Bistability criterion for electrostatically actuated initially curved micro plates. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 130, 75–92 (2018)
Naeli, K., Brand, O.: Dimensional considerations in achieving large quality factors for resonant silicon cantilevers in air. J. Appl. Phys. 105(1), 014908 (2009)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical, Computational and Experimental Methods. John Wiley & Sons, New York (2008)
Ouakad, H.M.: An electrostatically actuated mems arch band-pass filter. Shock Vib. 20(4), 809–819 (2013)
Ouakad, H.M.: Simple and accurate analytical solution to the post-buckling response of an electrostatically actuated mems curled cantilever. Microsyst. Technol. 22(9), 2251–2258 (2016)
Ouakad, H.M., Younis, M.I.: The dynamic behavior of mems arch resonators actuated electrically. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 45(7), 704–713 (2010)
Rabenimanana, T., Walter, V., Kacem, N., Le Moal, P., Bourbon, G., Lardiès, J.: Functionalization of electrostatic nonlinearities to overcome mode aliasing limitations in the sensitivity of mass microsensors based on energy localization. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117(3), 033502 (2020)
Rabenimanana, T., Walter, V., Kacem, N., Le Moal, P., Bourbon, G., Lardiès, J.: Mass sensor using mode localization in two weakly coupled mems cantilevers with different lengths: Design and experimental model validation. Sens. Actuators, A 295, 643–652 (2019)
Rhoads, J.F., Shaw, S.W., Turner, K.L.: Nonlinear dynamics and its applications in micro-and nanoresonators. J. Dyn. Sys. Meas. Control. 132(3), 034001 (2010)
Ruzziconi, L., Younis, M.I., Lenci, S.: An efficient reduced-order model to investigate the behavior of an imperfect microbeam under axial load and electric excitation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dynam. 8(1), 011014 (2013)
Saghir, S., Bellaredj, M., Ramini, A., Younis, M.I.: Initially curved microplates under electrostatic actuation: theory and experiment. J. Micromech. Microeng. 26(9), 095004 (2016)
Saghir, S., Ilyas, S., Jaber, N., Younis, M.I.: An experimental and theoretical investigation of the mechanical behavior of multilayer initially curved microplates under electrostatic actuation. J. Vib. Acoust. 139(4), 040901 (2017)
Saghir, S., Younis, M.I.: An investigation of the mechanical behavior of initially curved microplates under electrostatic actuation. Acta Mech. 229(7), 2909–2922 (2018)
Sakhaee-Pour, A., Ahmadian, M., Vafai, A.: Applications of single-layered graphene sheets as mass sensors and atomistic dust detectors. Solid State Commun. 145(4), 168–172 (2008)
Sazonova, V.A.: A tunable carbon nanotube resonator. Ph.D. thesis, Cornell University (2006)
Shmulevich, S., Lerman, M., Elata, D.: On the quality of quality-factor in gap-closing electrostatic resonators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 23(11), 115010 (2013)
Thomas, O., Touzé, C., Chaigne, A.: Asymmetric non-linear forced vibrations of free-edge circular plates. part ii: experiments. J. Sound Vib. 265(5), 1075–1101 (2003)
Touzé, C., Thomas, O., Chaigne, A.: Asymmetric non-linear forced vibrations of free-edge circular plates. part 1: Theory. J. Sound Vib. 258(4), 649–676 (2002)
Walter, V., Bourbon, G., Le Moal, P., Kacem, N., Lardiès, J.: Electrostatic actuation to counterbalance the manufacturing defects in a mems mass detection sensor using mode localization. Procedia Engineering 168, 1488 – 1491 (2016). Proceedings of the 30th anniversary Eurosensors Conference – Eurosensors 2016, 4-7. Sepember 2016, Budapest, Hungary
Wang, Z., Ren, J.: Nonlinear coupled vibration of electrically actuated arch with flexible supports. Micromachines 10(11), 729 (2019)
Wang, Z., Ren, J.: Three-to-one internal resonance in mems arch resonators. Sensors 19(8), 1888 (2019)
Williams, M.D., Griffin, B.A., Reagan, T.N., Underbrink, J.R., Sheplak, M.: An aln mems piezoelectric microphone for aeroacoustic applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 21(2), 270–283 (2012)
Younis, M.I.: MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics, 20th edn. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2011)
Younis, M.I.: Analytical expressions for the electrostatically actuated curled beam problem. Microsyst. Technol. 21(8), 1709–1717 (2015)
Younis, M.I., Ouakad, H.M., Alsaleem, F.M., Miles, R., Cui, W.: Nonlinear dynamics of mems arches under harmonic electrostatic actuation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 19(3), 647–656 (2010)
Zhang, Y.: Large deflection of clamped circular plate and accuracy of its approximate analytical solutions. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 59(2), 624602 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region and the EUR EIPHI program (ANR 17-EURE-0002).
Funding
This project was funded by the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
The code has been implemented using the commercial software Matlab.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jallouli, A., Kacem, N., Bourbon, G. et al. Experimental characterization of nonlinear static and dynamic behaviors of circular capacitive microplates with initial deflection. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 2329–2343 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06242-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06242-4