Abstract
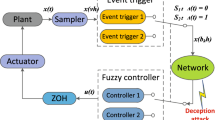
In this paper, a class of interval type-2 Takagi–Sugeno (IT2 T–S) fuzzy interconnected system subjected to deception attacks is investigated by developing a state-dependent asynchronous intermittent control scheme. Whether control actions should be imposed or not is decided by an asynchronous activated mechanism in each subsystem, which contains two exponential attenuation surfaces and three state-dependent subregions. Besides, a switching controller is designed, which includes three sub-controllers with respect to above three subregions. Specially, this new type controller not only can avoid potential chattering behaviors resulted from the switchings among sub-controllers, but also can describe the attack signals as an intermittent nonlinear term to decrease the potential success rate of cyber intrusions. Moreover, under the concept of exponentially input-to-state stable (EISS), the concerned system is verified to be EISS by transforming the attack signals into a residual term. Finally, the validity of the proposed control strategy is verified by two illustrative examples.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reppa, V., Polycarpou, M.M., Panayiotou, C.G.: Distributed sensor fault diagnosis for a network of interconnected cyber physical systems. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2(1), 11–23 (2015)
Massoud Amin, S., Wollenberg, B.F.: Toward a smart grid: power delivery for the 21st century. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 3(5), 34–41 (2005)
Su, A., Eichi, H., Zeng, W., Chow, M.Y.: A survey on the electrification of transportation in a smart grid environment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 8(1), 1–10 (2012)
Kumar, V., Rus, D., Sukhatme, G.S.: “Networked robots,” in Springer Handbook Robotics, pp. 943–958. Springer, New York (2008)
Antonelli, G.: Interconnected dynamic systems: an overview on distributed control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 33(1), 76–88 (2013)
Du, Z., Yan, Z., Zhao, Z.: Interval type-2 fuzzy tracking control for nonlinear systems via sampled-data controller. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 356, 92–112 (2019)
Rong, N., Wang, Z.: Fixed-time stabilization for IT2 T–S fuzzy interconnected systems via event-triggered mechanism: an exponential gain method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(2), 246–258 (2020)
Du, Z., Kao, Y., Park, Ju H.: New results for sampled-data control of interval type-2 fuzzy nonlinear systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 357(1), 121–141 (2020)
An, L., Yang, G.H.: Decentralized adaptive fuzzy secure control for nonlinear uncertain interconnected systems against intermittent dos attacks. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(3), 827–838 (2019)
Alireza, A., Arman, S., Parisa, F., et al.: Resilient control design for load frequency control system under false data injection attacks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (to be published). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2019.2944091
Jin, X., Haddad, W.M., Yucelen, T.: An adaptive control architecture for mitigating sensor and actuator attacks in cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 62(11), 6058–6064 (2017)
Mahmoud, M.S., Hamdan, M.M., Baroudi, U.A.: Modeling and control of cyber-physical systems subject to cyber attacks: a survey of recent advances and challenges. Neurocomputing 338, 101–115 (2019)
Anguluri, R., Katewa, V., Pasqualetti, F.: Attack detection in stochastic interconnected systems: centralized vs decentralized detectors. In: IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), IEEE, 2018, pp. 4541–4546 (2018)
Barboni, A., Rezaee, H., Boem, F., Parisini, T.: Distributed detection of covert attacks for interconnected systems. In: 18th European Control Conference (ECC), IEEE, pp. 2240–2245 (2019)
Ding, S., Xie, X., Liu, Y.: Event-triggered static/dynamic feedback control for discrete-time linear systems. Information Sciences 524, 33–45 (2020)
Gawthrop, P.J., Wang, L.: Event-driven intermittent control. Int. J. Control 82(12), 2235–2248 (2009)
Gawthrop, P., Loram, I., Lakie, M., Gollee, H.: Intermittent control: a computational theory of human control. Biol. Cybern. 104(1–2), 31–51 (2011)
Chen, S., Song, G., Zheng, B.C., Li, T.: Finite-time synchronization of coupled reactionCdiffusion neural systems via intermittent control. Automatica 109, 108564 (2019)
Xiao, Q., Lewis, F.L., Zeng, Z.: Containment control for multiagent systems under two intermittent control schemes. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 64(3), 1236–1243 (2019)
Zhang, Z.M., He, Y., Wu, M., Wang, Q.G.: Exponential synchronization of neural networks with time-varying delays via dynamic intermittent output feedback control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(3), 612–622 (2019)
Li, X., Fang, J.A., Li, H.: Exponential stabilisation of stochastic memristive neural networks under intermittent adaptive control. IET Control Theory Appl. 11(15), 2432–2439 (2017)
Chen, H., Shi, P., Lim, C.C.: Cluster synchronization for neutral stochastic delay networks via intermittent adaptive control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 30(11), 3246–3259 (2019)
Liu, X., Chen, T.: Synchronization of complex networks via aperiodically intermittent pinning control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 60(12), 3316–3321 (2015)
Fan, Y., Huang, X., et al.: Aperiodically intermittent control for quasi-synchronization of delayed memristive neural networks: an interval matrix and matrix measure combined method. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 49(11), 2254–2265 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Chen, S., Su, H.: Scaled consensus of second-order nonlinear multiagent systems with time-varying delays via aperiodically intermittent control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (to be published). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2883793
Guan, Z.H., Yue, D., et al.: Cluster synchronization of coupled genetic regulatory networks with delays via aperiodically adaptive intermittent control. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 16(7), 585–599 (2017)
Wang, Q., He, Y., Tan, G., Wu, M.: State-dependent intermittent control of non-linear systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 11(12), 1884–1893 (2017)
Ding, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, H.: Quasi-synchronization of delayed memristive neural networks via region-partitioning-dependent intermittent control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(12), 4066–4077 (2019)
Lam, H.K., Seneviratne, L.D.: Stability analysis of interval type-2 fuzzy-model-based control systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 38(3), 617–628 (2008)
Zeng, Y., Lam, Hak-Keung, Wu, L.: Hankel-norm-based model reduction for stochastic discrete-time nonlinear systems in interval type-2 T–S fuzzy framework. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (to be published). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2900844
Li, X.J., Yan, J.J., Yang, G.H.: Adaptive fault estimation for TS fuzzy interconnected systems based on persistent excitation condition via reference signals. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(8), 2822–2834 (2019)
Sontag, E.D.: Comments on integral variants of ISS. Syst. Control Lett. 34, 93–100 (1998)
Sontag, E.D.: Smooth stabilization implies coprime factorization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 34(4), 435–443 (1989)
Mazo, Jr, M., Anta, A., Tabuada, P.: An ISS self-triggered implementation of linear controllers. Automatica 46(8), 1310–1314 (2010)
Zhang, Z., Niu, Y., Song, J.: Input-to-state stabilization of interval type-2 fuzzy systems subject to cyber attacks: an observer-based adaptive sliding mode approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (to be published). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2902105
Wu, Z., Shi, P., Su, H., Chu, J.: Local synchronization of chaotic neural networks with sampled-data and saturating actuators. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44(12), 2635–2645 (2014)
Ding, S., Wang, Z., Zhang, H.: Event-triggered stabilization of neural networks with time-varying switching gains and input saturation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(10), 5045–5056 (2018)
Ohtake, H., Tanaka, K., Wang, H.O.: Fuzzy modeling via sector nonlinearity concept. Integr. Comput.-Aid. Eng. 10(4), 333–341 (2003)
Tanaka, K., Wang, H.O.: Fuzzy Control Systems Design and Analysis: A Linear Matrix Inequality Approach. Wiley, New York (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973070, 61433004 and Grant 61627809, LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program under Grant XLYC1802010, and in part by SAPI Fundamental Research Funds under Grant 2018ZCX22.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rong, N., Wang, Z. State-dependent asynchronous intermittent control for IT2 T–S fuzzy interconnected systems under deception attacks. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 3433–3448 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05669-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05669-5