Abstract
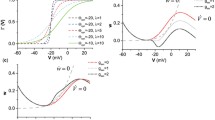
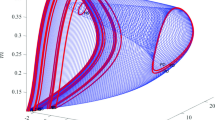
The neuronal excitability related to the transition between firing and resting states is a basic and important dynamic behavior which has different bifurcation characteristics and spiking frequency responses. In this work, we study the response dynamics and the excitability of a Morris–Lecar neuron for two temperature-sensitive ion channels, calcium and leak current, respectively. The codimension-1 bifurcations and the frequency–response curves for different temperatures show that the neuronal excitability is from Class II to I with increasing temperature in the case of the temperature-sensitive calcium current but is from Class I to II for the case of the leak current. The further extensive codimension-2 bifurcations uncover that the neurons undergo different routes of the neuronal dynamics under increasing external current for different temperatures even the same neuronal excitability. These results provide insight into understanding the effect of temperature on the neuronal dynamics and response behaviors with the diversity of temperature-sensitive ion channels.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, J., Jun, T.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1569–1578 (2017)
Alexander, G.D., Aurel, A.L., Jonathan, D.V.: Information theory in neuroscience. J. Comput. Neurosci. 30(1), 1–5 (2011)
Wang, L.F., Wang, H.T., Yu, L.C., Chen, Y.: Spike-threshold variability originated from separatrix-crossing in neuronal dynamics. Sci. Rep. 6, 31719 (2016)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 10(6), 1171–1266 (2000)
Rudiger, K., Fabrizio, G.: Burst firing in sensory systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5(1), 13–23 (2004)
Lu, Z.S., Chen, L.N., Duan, L.X.: Bifurcation analysis of mixed bursting in the pre-Botzinger complex. Appl. Math. Model. 67, 234–251 (2019)
Li, Y.Y., Gu, H.G., Ding, X.L.: Bifurcations of enhanced neuronal bursting activities induced by the negative current mediated by inhibitory autapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2091–2105 (2019)
Hodgkin, A.L.: The local electric changes associated with repetitive action in a non-medullated axon. J. Physiol. 107(2), 165–181 (1948)
Wang, H.T., Wang, L.F., Yu, L.C., et al.: Response of Morris–Lecar neuron to various stimuli. Phys. Rev. E 83, 021915 (2011)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Dynamical systems in neuroscience: the geometry of excitability and bursting. MIT Press, Cambridge (2007)
Meng, X.G., Huguet, G., Rinzel, J.: Type III excitability, slope sensitivity and coincidence detection. Discrete Contin. Dyn. A 32(8), 2729–2757 (2012)
Tsumoto, K., Kitajima, H., Yoshinaga, T., et al.: Bifurcations in Morris–Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69(4), 293–316 (2006)
Tsuji, S., Ueta, T., Kawakami, H., et al.: Bifurcations in two-dimensional hindmarsh-rose type model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 17(3), 985–998 (2007)
Liu, C.M., Liu, X.L., Liu, S.Q.: Bifurcation analysis of a Morris–Lecar neuron model. Biol. Cybern. 108(1), 75–84 (2014)
Calim, A., Hovel, P., Ozer, M., et al.: Chimera states in networks of type-I Morris–Lecar neurons. Phys. Rev. E 98(6), 062217 (2018)
Zhao, Z.G., Gu, H.G.: Transitions between classes of neuronal excitability and bifurcations induced by autapse. Sci. Rep. UK 7, 6760 (2017)
Xie, Y., Chen, L., Kang, Y.M., et al.: Controlling the onset of Hopf bifurcation in the Hodgkin–Huxley model. Phys. Rev. E 77(6), 061921 (2008)
Li, B., He, Q.: Bifurcation analysis of a two-dimensional discrete Hindmarsh–Rose type model. Adv. Differ. Equ. 124, 1–7 (2019)
Zhao, Z.G., Li, L., Gu, H.G.: Dynamical mechanism of hyperpolarization-activated non-specific cation current induced resonance and spike-timing precision in a neuronal model. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 12, 62 (2018)
Loos, H.V.D., Glaser, E.M.: Autapses in neocortex cerebri: synapses between a pyramidal cell’s axon and its own dendrites. Brain Res. 48, 355–360 (1972)
Song, X.L., Wang, H.T., Chen, Y.: Autapse-induced firing pattern transitions in the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 96, 2341–2350 (2019)
Hille, B.: Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland (2001)
OLeary, T., Marder, E.: Temperature-robust neural function from activity-dependent ion channel regulation. Curr. Biol. 26(21), 2935–2941 (2016)
Wang, L.F., Jia, F., Liu, X.Z., et al.: Temperature effects on information capacity and energy efficiency of Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Chin. Phys. Lett. 32(10), 108701 (2015)
Caplan, J.S., Williams, A.H., Marder, E.: Many parameter sets in a multicompartment model oscillator are robust to temperature perturbations. J. Neurosci. 34(14), 4963–4975 (2014)
Dhooge, A., Govaerts, W., Kuznetsov, Y.A.: MATCONT: a matlab package for numerical bifurcation analysis of ODEs. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 29(2), 141–164 (2003)
Ermentrout, B.: Simulating, Analyzing, and Animating Dynamical Systems: A Guide to XPPAUT for Researchers and Students. SIAM, Philadelphia (2002)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barancle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Prescott, S.A., De Koninck, Y., Sejnowski, T.J.: Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 4(10), e1000198 (2008)
Rinberg, A., Taylor, A.L., Marder, E.: The effects of temperature on the stability of a neuronal oscillator. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9(1), e1002857 (2013)
Tang, L.S., Goeritz, M.L., Caplan, J.S., et al.: Precise temperature compensation of phase in a rhythmic motor pattern. PLoS Biol. 8(1), e1000469 (2010)
Tang, L.S., Taylor, A.L., Rinberg, A., Marder, E.: Robustness of a rhythmic circuit ot short- and long-term temperature changes. J. Neurosci. 32, 10075–10085 (2012)
Caterina, M.J.: Transient receptor potential ion channels as participants in thermosensation and thermoregulation. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 292(1), R64–R76 (2007)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Wu, F.Q., Wang, C.N., Jin, W.Y., et al.: Dynamical responses in a new neuron model subjected to electromagnetic induction and phase noise. Phys. A 469, 81–88 (2017)
Jia, B., Gu, H.G., Xue, L.: A basic bifurcation structure from bursting to spiking of injured nerve fibers in a two-dimensional parameter space. Cogn. Neurodyn. 11(2), 189–200 (2017)
Gu, H.G.: Different bifurcation scenarios of neural firing patterns observed in the biological experiment on identical pacemakers. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(12), 1350195 (2013)
Gu, H.G., Jia, B., Chen, G.R.: Experimental evidence of a chaotic region in a neural pacemaker. Phys. Lett. A 377(9), 718–720 (2013)
Guo, D., Chen, M., Perc, M., et al.: Firing regulation of fast-spiking interneurons by autaptic inhibition. EPL (Europhys. Lett.) 114(3), 30001 (2016)
Pekala, D., Szkudlarek, H., Raastad, M.: Typical gray matter axons in mammalian brain fail to conduct action potentials faithfully at fever-like temperatures. Physiol. Rep. 4(19), e12981 (2016)
Song, X.L., Wang, H.T., Chen, Y., Lai, Y.C.: Emergence of an optimal temperature in action potential propagation through myelinated axons. Phys. Rev. E 100, 032416 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant No. 11872084 (ZQY), No. 11675008 (YC), and No. 21434001 (YC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no any conflict with the publication of this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, M., Song, X., Yang, Z. et al. Bifurcations and excitability in the temperature-sensitive Morris–Lecar neuron. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 2687–2698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05667-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05667-7