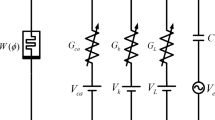
Abstract
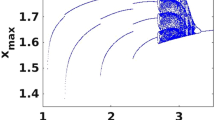
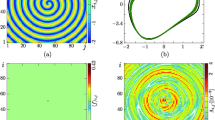
An extended Morris–Lecar neuron model incorporating electromagnetic flux coupling and external excitation is proposed. The complete dynamical behavior of the new model is investigated as autonomous and non-autonomous forms. Multistability and coexisting attractors are shown for the new neuron model. It is shown that when external excitation is introduced, the complete dynamical behavior of the system changes compared to the non-excited version. To study the wave propagation pattern, we construct a network of the extended neuron model and study the generation of spiral waves under various conditions of coupling strength, stimuli parameters and system parameters. We have also studied the wave propagation pattern considering the time-based chaotic-periodic neurons in the network.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
FitzHugh, R.: Mathematical models of threshold phenomena in the nerve membrane. Bull. Math. Biophys. 17, 257–278 (1955)
FitzHugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1, 445–466 (1961)
Fitz, H.R.: Chapter 1: Mathematical models of excitation and propagation in nerve. In: Schwan, H.P. (ed.) Biological Engineering, pp. 1–85. McGraw-Hill Book Co., Nork York (1969)
Nagumo, J., Arimoto, S., Yoshizawa, S.: An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc IRE. 50, 2061–2070 (1962)
Hodgkin, A., Huxley, A.: Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J. Physiol. 116(4), 449–472 (1952)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Chen, P.-L.: Some aspects of the Morris–Lecar model and the myelinated axon models with Morris–Lecar dynamics. Math. Comput. Modell. 17(8), 85–97 (1993)
Tsumoto, K., Kitajima, H., Yoshinaga, T., Aihara, K., Kawakami, H.: Bifurcations in Morris–Lecar neuron model. Neurocomputing 69, 293–316 (2006)
Wang, H.X., Lu, Q.S., Wang, Q.Y.: Generation of firing rhythm patterns and synchronization in the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 6, 7–12 (2005)
Wang, H.X., Lu, Q.S., Wang, Q.Y.: Bursting and synchronization transition in the coupled modified M–L neurons. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 1668–1675 (2008)
Xinlin, S., Hengtong, W., Yong, C.: Autapse-induced firing patterns transitions in the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04925-7
Farjami, S., Kirk, V., Osinga, H.M.: Interactions between a locally separating stable manifold and a bursting periodic orbit. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 227, 603–614 (2018)
Vetriveeran, R., Maheshwar, P.D.S., Zubaer, I.M., Hyongsuk, K., Leon, C.: Third-order memristive Morris–Lecar model of barnacle muscle fiber. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27(4), 1730015 (2017)
Congmin, L., Xuanliang, L., Shenquan, L.: Bifurcation analysis of a Morris–Lecar neuron model. Biol. Cybern. 108, 75–84 (2014)
Prescott, S.A., De Koninck, Y., Sejnowski, T.J.: Biophysical basis for three distinct dynamical mechanisms of action potential initiation. PLOS Comput. Biol. 4, 1–18 (2008)
Bocheng, B., Qinfeng, Y., Lei, Z., Han, B., Quan, X., Yajuan, Y., Mo, C.: Chaotic bursting dynamics and coexisting multistable firing patterns in 3D autonomous Morris–Lecar model and microcontroller-based validations. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29(10), 1950134–1950152 (2019)
Alexandre, W., Miguel, A.F.S., Jose, M.C., Kazuyuki, A.: Building electronic bursters with the Morris–Lecar neuron model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 16(12), 3617–3630 (2006)
Jiang, W., Meili, L., Huiyan, L.: Synchronization of coupled equations of Morris–Lecar model. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 1169–1179 (2008)
Kuramoto, Y., Battogtokh, D.: Coexistence of coherence and incoherence in nonlocally coupled phase oscillators. Nonlinear Phenom. Complex Syst. 5(4), 380–385 (2002)
Shima, S., Kuramoto, Y.: Rotating spiral waves with phase-randomized core in nonlocally coupled oscillators. Phys. Rev. E 69, 036213 (2004)
Kuramoto, Y., Shima, S.: Rotating spirals without phase singularity in reaction-diffusion systems. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 150, 115 (2003)
Kuramoto, Y., Shima, S., Battogtokh, D., Shiogai, Y.: Mean-field theory revives in self-oscillatory fields with non-local coupling. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 161, 127 (2006)
Erik, A.M., Carlo, R.L., Steven, H.S.: Solvable model of spiral wave chimeras. Phys. Rev. Lett. 3, 150 (2010)
Samie, F.H., Mandapati, R., Gray, R.A., Watanabe, Y., Zuur, C.: A mechanism of transition from ventricular fibrillation to tachycardia. Circ. Res. 86, 684–691 (2000)
Samie, F.H., Jalife, J.: Mechanisms underlying ventricular tachycardia and its transition to ventricular fibrillation in the structurally normal heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 50, 242–250 (2001)
Yuan, G.Y., Wang, G.R., Chen, S.G.: Control of spiral waves and spatiotemporal chaos by periodic perturbation near the boundary. Europhys. Lett. 72, 908 (2005)
Fenton, F.H., Cherry, E.M., Hastings, H.M., Evans, S.J.: Multiple mechanisms of spiral wave breakup. Chaos 12, 852–892 (2002)
Aranson, I., Kessler, D., Mitkov, I.: Drift of spiral wave in excitable media. Physica D 85, 142–155 (1995)
Zykov, V.S.: Kinematics of rigidly rotating spiral waves. Physica D 238, 931–940 (2009)
Heather, A., Brooks, P.C.B.: Quasicycles in the stochastic hybrid Morris–Lecar neural model. Phys. Rev. E 92, 012704 (2015)
Hou, Z.H., Xin, H.W.: Noise-sustained spiral waves: effect of spatial and temporal memory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 280601 (2002)
Gu, H.G., Jia, B., Li, Y.Y., Chen, G.R.: White noise-induced spiral waves and multiple spatial coherence resonances in a neuronal network with type I excitability. Physica A 67, 169 (2013)
Ali, C., Philipp, H., Mahmut, O., Muhammet, U.: Chimera states in networks of type-I Morris–Lecar neurons. Phys. Rev. E 98, 062217 (2018)
Xinyi, W., Jun, M.: The formation mechanism of defects, spiral wave in the network of neurons. Plos One 8, 1 (2013)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 10, 1171–1266 (2000)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomput 205(3), 75–81 (2016)
Karthikeyan, R., Fahimeh, N., Anitha, K., Ahmed, A., Tasawar, H., Viet-Thanh, P.: Dynamics of a neuron exposed to integer order and fractional order discontinuous external magnetic flux. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 20, 584–590 (2019)
Fatemeh, P., Karthikeyan, R., Fawaz, E.A., Tasawar, H., Pham, V.-T., Iqtadar, H.: Birth and Death of spiral waves in a network of Hindmarsh-Rose neurons with exponential magnetic flux and excitable media. Appl. Math. Comput. 354, 377–384 (2019)
Karthikeyan, R., Fatemeh, P., Hamed, A., Boshra, H., Sajad, J., Vesna, B.: Spiral waves in externally excited neuronal network: solvable model with a monotonically differentiable magnetic flux. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 29(4), 043109 (2019)
Rajagopal, K., Khalaf, A.J.M., Parastesh, F., et al.: Dynamical behavior and network analysis of an extended Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn 98, 477–487 (2019)
Jun, M., Ya, W., Chunni, W., Ying, X., Guodong, R.: Mode selection in electrical activities of myocardial cell exposed to electromagnetic radiation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 99, 219–225 (2017)
Wolf, A., Swift, J.B., Swinney, H.L., Vastano, J.A.: Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Physica D Nonlinear Phenom. 16, 285–317 (1985)
Wu, F., Ma, J., Zhang, G.: Energy estimation and coupling synchronization between biophysical neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63, 625–636 (2020)
Ma, J., Yang, Z., Yang, L., Tang, J.: A physical view of computational neurodynamics. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 20(9), 639–659 (2019)
Funding
There is no funding received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajagopal, K., Moroz, I., Karthikeyan, A. et al. Wave propagation in a network of extended Morris–Lecar neurons with electromagnetic induction and its local kinetics. Nonlinear Dyn 100, 3625–3644 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05643-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05643-1