Abstract
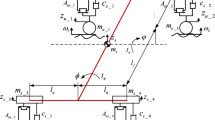
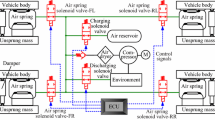
This paper addresses the tasks of height and posture motion control for an electronically controlled active air suspension (AAS) system. A mathematical model of a vehicle body with AAS system is established to describe the dynamic characteristics and then formulated into a multi-input multi-output nonlinear system by considering parametric uncertainties and unmodelled dynamics. Based on this mathematical model, a synchronization control strategy is proposed to adjust the heights of adjacent AASs simultaneously, driving the pitch and roll angles closely to an arbitrarily neighborhood of zero, achieving global uniform ultimate boundedness. The proposed controller is robust to parametric uncertainties and external disturbances. A projection operator is utilized to limit the estimated parameters to their corresponding prescribed bounds in finite time. A co-simulation is conducted by combining a virtual vehicle plant with ASS system in AMEsim with the proposed synchronization controller in MATLAB/Simulink. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed synchronization controller is effective and robust.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aly, A.A., Salem, F.A.: Vehicle suspension systems control: a review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2(2), 46–54 (2013)
Zhao, J., Wong, P.K., Ma, X.B., Xie, Z.C.: Chassis integrated control for active suspension, active front steering and direct yaw moment systems using hierarchical strategy. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 55(1), 72–103 (2017)
Zhao, J., Wong, P.K., Xie, Z.C., Wei, C.Y., He, F.: Integrated variable speed-fuzzy PWM control for ride height adjustment of active air suspension systems. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference, pp. 1–3, Chicago, America (2015)
Zhao, J., Wong, P.K., Xie, Z.C., Ma, X.B., Hua, X.: Design and control of an automotive variable hydraulic damper using cuckoo search optimized PID method. Int. J. Autom. Technol. 20(1), 51–63 (2019)
Ma, X.B., Wong, P.K., Zhao, J., Xie, Z.C.: Cornering stability control for vehicles with active front steering system using TS fuzzy based sliding mode control strategy. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 347–364 (2019)
Braun, J.: Race Track Development of a Hydraulic Ride Height Control System. SAE Technical Paper (1996)
Kim, H., Lee, H., Kim, H.: Asynchronous and synchronous load levelling compensation algorithm in air spring suspension. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Control, Automatic Systems, Seoul, South Korea (2007)
Kim, H., Lee, H.: Height and levelling control of automotive air suspension system using sliding mode approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 60(5), 2027–2041 (2011)
Sun, X.Q., Cai, Y.F., Chen, L., Liu, Y.L., Wang, S.H.: Vehicle height and posture control of the electronic air suspension system using the hybrid system approach. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 54(3), 328–352 (2016)
Zhao, J., Wong, P.K., Xie, Z.C., Wei, C.Y., Zhao, R.C.: Design and evaluation of a rode comfort of based suspension system using an optimal stiffness-determination method. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 40(5), 773–785 (2016)
Sun, X.Q., Cai, Y.F., Wang, S.H., Liu, Y.L., Chen, L.: Design of a hybrid model predictive controller for the vehicle height adjustment system of an electronic air suspension. Proc. IMechE. D J. Automob. Eng. 230(11), 1504–1520 (2016)
Ma, X.B., Wong, P.K., Zhao, J., Zhong, J.H., Huang, Y., Xu, X.: Design and testing of a nonlinear model predictive controller for ride height control of automotive semi-active air suspension systems. IEEE Access 6, 63777–63793 (2018)
Chang, F., Lu, Z.H.: Dynamic model of an air spring and integration into a vehicle dynamics model. Proc. IMechE. D J. Automob. Eng. 222(10), 1813–1825 (2008)
Lee, S.J.: Development and analysis of an air spring model. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 11(4), 471–479 (2010)
Löcken, F., Welsch, M.: The dynamic characteristic and hysteresis effect of an air spring. Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 20(1), 127–145 (2015)
Qin, Y.C., Wang, Z.F., Xiang, C.L., Hashemi, E., Khajepour, A., Huang, Y.J.: Speed independent road classification strategy based on vehicle response: theory and experimental validation. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 117, 653–666 (2019)
Qin, Y.C., Wang, Z.F., Xiang, C.L., Dong, M.M., Hu, C., Wang, R.R.: A novel global sensitivity analysis on the observation accuracy of the coupled vehicle model. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 57(10), 1445–1466 (2019)
Nieto, A.J., Morales, A.L., Gonzalez, A., Chicharro, J.M., Pintado, P.: An analytical model of pneumatic suspensions based on an experimental characterization. J. Sound Vib. 313(1), 290–307 (2008)
Carneiro, J.F., de Almeida, F.G.: Reduced-order thermodynamic models for servo-pneumatic actuator chambers. Proc. IMechE. I J. Syst. Control Eng. 220(4), 301–314 (2006)
Wong, P.K., Xie, Z.C., Zhao, J., Xu, T., He, F.: Analysis of automotive rolling lobe air spring under alternative factors with finite element model. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 28(12), 5069–5081 (2014)
Zhao, R.C., Xie, W., Wong, P.K., Cabecinhas, D., Silvestre, C.: Robust ride height control for active air suspension systems with multiple unmodeled dynamics and parametric uncertainties. IEEE Access 7, 59185–59199 (2019)
Lee, H.K., Choi, G.S., Choi, G.H.: A study on tracking position control of pneumatic actuators. Mechatronics 12(64), 813–831 (2002)
Taghizadeh, M., Najafi, F., Ghaffari, A.: Multimodel PD-control of a pneumatic actuator under variable loads. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 48(5–8), 655–662 (2010)
Boubakir, A., Plestan, F., Labiod, S., Boudjema, F.: Design and experimentation of an observer-based linear adaptive control applied to an electropneumatic actuator. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(11), 1288–1298 (2016)
Boubakir, A., Plestan, F., Labiod, S., Boudjema, F.: Design and experimental study of a dynamical adaptive backstepping-sliding mode control scheme for position tracking and regulating of a low-cost pneumatic cylinder. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 26(4), 853–875 (2016)
Zhao, F., Ge, S.S., Tu, F.W., Qin, Y.C., Dong, M.M.: Adaptive neural network control for active suspension system with actuator saturation. IET Control Theory Appl. 10(14), 1696–1705 (2016)
Tsai, Y.C., Huang, A.C.: Multiple-surface sliding controller design for pneumatic servo systems. Mechatronics 18(9), 506–512 (2008)
Girin, A., Plestan, F., Brun, X., Glumineau, A.: High-order sliding-mode controllers of an electropneumatic actuator: application to an aeronautic benchmark. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(3), 633–645 (2009)
Sun, X.Q., Cai, Y.F., Yuan, C.C., Wang, S.H., Chen, L.: Fuzzy sliding mode control for the vehicle height and levelling adjustment system of an electronic air suspension. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 31(25), UNSP25 (2018)
Smaoui, M., Brun, X., Thomasset, D.: A study on tracking position control of an electropneumatic system using backstepping design. Control Eng. Pract. 14(8), 923–933 (2006)
Rao, Z., Bone, G.M.: Nonlinear modeling and control of servo pneumatic actuators. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 16(3), 562–569 (2008)
Taheri, B., Case, D., Richer, E.: Force and stiffness backstepping-sliding mode controller for pneumatic cylinders. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 19(6), 1799–1809 (2014)
Meng, D.Y., Tao, G.L., Li, A.M., Li, W.: Precision synchronization motion trajectory tracking control of multiple pneumatic cylinders. Asian J. Control 18(5), 1749–1764 (2016)
Koren, Y.: Cross-coupled biaxial computer control for manufacturing systems. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Contr. 102(4), 265–272 (1980)
Sun, D.: Position synchronization of multiple motion axes with adaptive coupling control. Automatica 39(6), 997–1005 (2003)
Pan, H.H., Sun, W.C., Gao, H.J., Jing, X.J.: Disturbance observer-based adaptive tracking control with actuator saturation and its application. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 13(2), 868–875 (2016)
Sun, W.C., Liu, Y.B., Gao, H.J.: Constrained sampled-data arc for a class of cascaded nonlinear systems with applications to motor-servo systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 15(2), 766–775 (2019)
Yao, B., Tomizuka, M.: Adaptive robust control of MIMO nonlinear systems in semi-strict feedback forms. Automatica 38(9), 1305–1321 (2001)
Cai, Z., de Queiroz, M.S., Dawson, D.M.: A sufficiently smooth projection operator. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 51(1), 135–139 (2006)
Polycarpou, M.M.: Stable adaptive neural control scheme for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 41(3), 447–451 (1996)
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the University of Macau Research Grant (Grant Numbers MYRG-2016-00212-FST, MYRG-2017-00135-FST and MYRG-2018-00198-FST), and by the Portuguese Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) through ISR (Grant Number LARSyS UID/EEA/50009/2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, R., Xie, W., Wong, P.K. et al. Adaptive vehicle posture and height synchronization control of active air suspension systems with multiple uncertainties. Nonlinear Dyn 99, 2109–2127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05412-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05412-9