Abstract
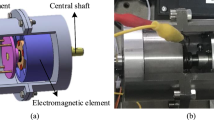
In this paper, a torsion–translational quasi-zero-stiffness (TT QZS) isolator with convex ball–roller mechanisms was proposed to attenuate the torsion and translational vibrations along shaft systems simultaneously. The mathematical model of the isolator was established, based on which the static characteristics of the isolator were analyzed and the quasi-zero-stiffness condition that the design parameters should satisfy was derived as well. Subsequently, the isolator was integrated into a shaft system to study its dynamical performances under excitations of two independent external forces. Unique phenomenon of so-called vibration frequency–interference was observed and elaborated theoretically with harmonic balance method. In addition, the amplitude–frequency characteristics of the two degrees-of-freedom (DOFs) system subjected to two independent harmonic excitations were analyzed by employing numerical simulations. Accordingly, the small-oscillation regions of the system were determined through the jump-down frequencies. Meanwhile, the force transmissibility in the small-amplitude-oscillation region was discussed by taking advantage of semi-analytical solutions and compared with that of the corresponding linear system. The results indicated that the TT QZS isolator has extra low-frequency vibration isolation performance in both torsion and translational DOFs.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(k_{\theta }\) :
-
Torsion stiffness of rubber (N m/rad)
- \(k_v\) :
-
Stiffness of axial spring (N/m)
- N :
-
Number of convex ball–roller mechanisms
- \(k_{\mathrm{h}}\) :
-
Stiffness of horizontal spring (N/m)
- \(F_{0}, F\) :
-
Axial payloads (N) and axial force (N)
- \(M_0, M\) :
-
Torsional payloads (N m) and torsional force (N m)
- z :
-
Axial coordinate of the isolator (m)
- \(\theta \) :
-
Torsional coordinate of the isolator (rad)
- \(\delta \) :
-
Pre-compressed deflection of horizontal spring (m)
- \(r_1,r_2 ,r_3\) :
-
Radius of shaft, convex balls and rollers (m)
- x :
-
Distance between centers of shaft and rollers (m)
- \(C(\bar{z}, \theta )\) :
-
Geometrical contact function
- \(K_z (\bar{z}, \theta )\) :
-
Axial stiffness of the isolator (N/m)
- \(K_{\theta } (\bar{z}, \theta )\) :
-
Torsional stiffness of the isolator (N m/rad)
- \(\varepsilon _{\bar{\mathrm{F}}}, \varepsilon _{\bar{\mathrm{M}}}\) :
-
Relative error of axial and torsional forces
- \(A_z, A_{\theta }\) :
-
Amplitudes of axial and torsional excitation forces (m)
- p, q :
-
Frequencies of axial and torsional excitation forces (rad/s)
- \(\varphi _z, \varphi _{\theta }\) :
-
Initial phases of axial and torsional excitation forces (rad)
- \(\zeta _z, \zeta _{\theta }\) :
-
Damping ratios of axial and torsional excitation forces
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Coefficients of Taylor series of axial FD function
- \(\lambda \) :
-
Coefficients of Taylor series of torsional FD function
- \(T_z, T_{\theta }\) :
-
Transmissibility of axial and torsional directions
- \(\varOmega _z, \varOmega _{\theta }\) :
-
Ratios between excitation forces and natural frequencies
References
Ibrahim, R.A.: Recent advances in nonlinear passive vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 314(3–5), 371–452 (2008)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P.: Static analysis of a passive vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 301(3–5), 678–689 (2007)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Kovacic, I., Waters, T.P.: On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 322(4–5), 707–717 (2009)
Kovacic, I., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P.: A study of a nonlinear vibration isolator with a quasi-zero stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 315(3), 700–711 (2008)
Margielewicz, J., Gąska, D., Litak, G.: Evolution of the geometric structure of strange attractors of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator. Chaos Solitons Fractals 118, 47–57 (2019)
Wang, Y., Li, S., Cheng, C.: Investigation on a quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator under random excitation. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 621, 621–632 (2016)
Lu, Z., Chen, L.-Q., Brennan, M.J., Yang, T., Ding, H., Liu, Z.: Stochastic resonance in a nonlinear mechanical vibration isolation system. J. Sound Vib. 370, 221–229 (2016)
Lu, Z., Brennan, M., Ding, H., Chen, L.: High-static-low-dynamic-stiffness vibration isolation enhanced by damping nonlinearity. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62(7), 1103–1110 (2019)
Lu, Z., Brennan, M.J., Chen, L.-Q.: On the transmissibilities of nonlinear vibration isolation system. J. Sound Vib. 375, 28–37 (2016)
Xu, D., Zhang, Y., Zhou, J., Lou, J.: On the analytical and experimental assessment of the performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness isolator. J. Vib. Control 20(15), 2314–2325 (2013)
Le, T.D., Ahn, K.K.: A vibration isolation system in low frequency excitation region using negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 330(26), 6311–6335 (2011)
Lan, C.-C., Yang, S.-A., Wu, Y.-S.: Design and experiment of a compact quasi-zero-stiffness isolator capable of a wide range of loads. J. Sound Vib. 333(20), 4843–4858 (2014)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P., Shin, K.: On the design of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness isolator using linear mechanical springs and magnets. J. Sound Vib. 315(3), 712–720 (2008)
Robertson, W.S., Kidner, M.R.F., Cazzolato, B.S., Zander, A.C.: Theoretical design parameters for a quasi-zero stiffness magnetic spring for vibration isolation. J. Sound Vib. 326(1–2), 88–103 (2009)
Xu, D., Yu, Q., Zhou, J., Bishop, S.R.: Theoretical and experimental analyses of a nonlinear magnetic vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 332(14), 3377–3389 (2013)
Wu, W., Chen, X., Shan, Y.: Analysis and experiment of a vibration isolator using a novel magnetic spring with negative stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 333(13), 2958–2970 (2014)
Liu, X., Huang, X., Hua, H.: On the characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator using Euler buckled beam as negative stiffness corrector. J. Sound Vib. 332(14), 3359–3376 (2013)
Meng, L., Sun, J., Wu, W.: Theoretical design and characteristics analysis of a quasi-zero stiffness isolator using a disk spring as negative stiffness element. Shock Vib. 2015, 1–19 (2015)
Lu, Z., Yang, T., Brennan, M.J., Liu, Z., Chen, L.-Q.: Experimental investigation of a two-stage nonlinear vibration isolation system with high-static-low-dynamic stiffness. J. Appl. Mech. 84(2), 021001 (2017)
Cheng, C., Li, S., Wang, Y., Jiang, X.: Force and displacement transmissibility of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with geometric nonlinear damping. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 2267–2279 (2017)
Araki, Y., Kimura, K., Asai, T., Masui, T., Omori, T., Kainuma, R.: Integrated mechanical and material design of quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator with superelastic Cu–Al–Mn shape memory alloy bars. J. Sound Vib. 358, 74–83 (2015)
Zhou, J., Wang, X., Xu, D., Bishop, S.: Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of a quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator with cam–roller–spring mechanisms. J. Sound Vib. 346, 53–69 (2015)
Zhou, J., Xu, D., Bishop, S.: A torsion quasi-zero stiffness vibration isolator. J. Sound Vib. 338, 121–133 (2015)
Wang, K., Zhou, J., Xu, D.: Sensitivity analysis of parametric errors on the performance of a torsion quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 134, 336–346 (2017)
Zheng, Y., Zhang, X., Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Xie, S.: Analytical study of a quasi-zero stiffness coupling using a torsion magnetic spring with negative stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 135–151 (2018)
Sun, X., Jing, X.: Multi-direction vibration isolation with quasi-zero stiffness by employing geometrical nonlinearity. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 62–63, 149–163 (2015)
Zhou, J., Xiao, Q., Xu, D., Ouyang, H., Li, Y.: A novel quasi-zero-stiffness strut and its applications in six-degree-of-freedom vibration isolation platform. J. Sound Vib. 394, 59–74 (2017)
Ding, H., Ji, J., Chen, L.-Q.: Nonlinear vibration isolation for fluid-conveying pipes using quasi-zero stiffness characteristics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 121, 675–688 (2019)
Wang, K., Zhou, J., Cai, C., Xu, D., Ouyang, H.: Mathematical modeling and analysis of a meta-plate for very low-frequency band gap. Appl. Math. Model. 73, 581–597 (2019)
Wang, K., Zhou, J., Xu, D., Ouyang, H.: Tunable low-frequency torsional-wave band gaps in a meta-shaft. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 52(5), 055104 (2019)
Zhou, J., Wang, K., Xu, D., Ouyang, H.: Multi-low-frequency flexural wave attenuation in Euler–Bernoulli beams using local resonators containing negative-stiffness mechanisms. Phys. Lett. A 381(37), 3141–3148 (2017)
Li, Y., Xu, D.: Vibration attenuation of high dimensional quasi-zero stiffness floating raft system. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 126, 186–195 (2017)
Sun, X., Xu, J., Jing, X., Cheng, L.: Beneficial performance of a quasi-zero-stiffness vibration isolator with time-delayed active control. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 82, 32–40 (2014)
Xu, J., Sun, X.: A multi-directional vibration isolator based on quasi-zero-stiffness structure and time-delayed active control. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 126–135 (2015)
Nayfeh, A., Mook, D.: Nonlinear oscillations. Wilery, Hoboken (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527617586
Acknowledgements
This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11472100, 11632011) and the High-tech Ship Research Projects Sponsored by MIIT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Xia, S., Xu, D. et al. A torsion–translational vibration isolator with quasi-zero stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn 99, 1467–1488 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05369-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05369-9