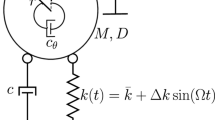Abstract
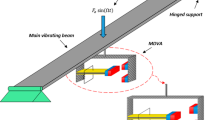
We present an investigation of the dynamic behavior of an electrostatically actuated resonant structure, resonator, under the simultaneous excitation of primary and subharmonic resonances. A comprehensive analytical solution is obtained via the method of Multiple Time Scales (MTS), which is applicable for generic electrostatic loading cases. Results using different MTS scaling methods in the equations of motion and loading conditions are compared. These results are further verified against results obtained using direct time integration of the equation of motion. It is observed that for a generic parallel-plate electrostatic loading case, the direct forcing component at the excitation frequency, and the direct and parametric excitation components at double the excitation frequency must be considered for accurate prediction of the structure’s response. Further, the case of simultaneous excitations of primary and subharmonic resonance, where both excitations are of comparable strength, is examined under various electrostatic loading conditions. We show mixed behaviors of the resonator transiting from a subharmonic-dominated response, characterized by the sudden jumps in amplitude and smaller monostable regime, to primary-dominated response exhibiting gradual amplitude increase and larger monostable regimes. This transition behavior can be potentially used for applications, such as electrometers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W., Turner, K.L.: Application of parametric resonance amplification in a single-crystal silicon micro-oscillator based mass sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 122, 23–30 (2005)
Bouchaala, A., Jaber, N., Shekhah, O., Chernikova, V., Eddaoudi, M., Younis, M.I.: A smart microelectromechanical sensor and switch triggered by gas. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 013502 (2016)
Mahboob, I., Flurin, E., Nishiguchi, K., Fujiwara, A., Yamaguchi, H.: Interconnect-free parallel logic circuits in a single mechanical resonator. Nat. Commun. 2, 198 (2011)
Hafiz, M.A.A., Kosuru, L., Younis, M.I.: Microelectromechanical reprogrammable logic device. Nat. Commun. 7, 11137 (2016)
Guerra, D.N., Bulsara, A.R., Ditto, W.L., Sinha, S., Murali, K., Mohanty, P.: A noise-assisted reprogrammable nanomechanical logic gate. Nano Lett. 10, 1168–1171 (2010)
Ilyas, S., Arevalo, A., Bayes, E., Foulds, I.G., Younis, M.I.: Torsion based universal MEMS logic device. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 236, 150–158 (2015)
Sinha, N., Jones, T.S., Guo, Z., Piazza, G.: Body-biased complementary logic implemented using AlN piezoelectric MEMS switches. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 21, 484–496 (2012)
Wong, A.C., Nguyen, C.C.: Micromechanical mixer-filters (“mixlers”). J. Microelectromech. Syst. 13, 100–112 (2004)
Ilyas, S., Chappanda, K.N., Younis, M.I.: Exploiting nonlinearities of micro-machined resonators for filtering applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 110, 253508 (2017)
Suh, J., LaHaye, M.D., Echternach, P.M., Schwab, K.C., Roukes, M.L.: Parametric amplification and back-action noise squeezing by a qubit-coupled nanoresonator. Nano Lett. 10, 3990–3994 (2010)
Eichler, A., Chaste, J., Moser, J., Bachtold, A.: Parametric amplification and self-oscillation in a nanotube mechanical resonator. Nano Lett. 11, 2699–2703 (2011)
Rugar, D., Grütter, P.: Mechanical parametric amplification and thermomechanical noise squeezing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 699 (1991)
Rhoads, J.F., Shaw, S.W., Turner, K.L., Baskaran, R.: Tunable microelectromechanical filters that exploit parametric resonance. J. Vib. Acoust. 127, 423–430 (2005)
Ilyas, S., Ramini, A., Arevalo, A., Younis, M.I.: An experimental and theoretical investigation of a micromirror under mixed-frequency excitation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 24, 1124–1131 (2005)
Ilyas, S., Jaber, N., Younis, M.I.: MEMS logic using mixed-frequency excitation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 26, 1140–1146 (2017)
Kim, C.H., Lee, C.W., Perkins, N.C.: Nonlinear vibration of sheet metal plates under interacting parametric and external excitation during manufacturing. In: ASME 2003 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, pp. 2481–2489 (2003)
Krylov, S., Gerson, Y., Nachmias, T., Keren, U.: Excitation of large-amplitude parametric resonance by the mechanical stiffness modulation of a microstructure. J. Micromech. Microeng. 20, 015041 (2009)
Shahgholi, M., Khadem, S.E.: Primary and parametric resonances of asymmetrical rotating shafts with stretching nonlinearity. Mech. Mach. Theory 51, 131–144 (2012)
Dolev, A., Bucher, I.: Optimizing the dynamical behavior of a dual-frequency parametric amplifier with quadratic and cubic nonlinearities. Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 1955–1974 (2018)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Introduction to Perturbation Techniques. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.H.: Secondary resonances of electrically actuated resonant microsensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 491 (2003)
Nayfeh, A.H.: The response of single degree of freedom systems with quadratic and cubic non-linearities to a subharmonic excitation. J. Sound Vib. 89, 457–470 (1983)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I.: Dynamics of MEMS resonators under superharmonic and subharmonic excitations. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1840 (2005)
Jin, Z., Wang, Y.: Electrostatic resonator with second superharmonic resonance. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 64, 273–279 (1998)
Nayfeh, A.H.: The response of non-linear single-degree-of-freedom systems to multifrequency excitations. J. Sound Vib. 102, 403–414 (1985)
Younis, M.I., Alsaleem, F.: Exploration of new concepts for mass detection in electrostatically-actuated structures based on nonlinear phenomena. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 4, 021010 (2009)
Ouakad, H.M., Younis, M.I.: Nonlinear dynamics of electrically actuated carbon nanotube resonators. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 5, 011009 (2010)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Quenching of primary resonance by a superharmonic resonance. J. Sound Vib. 92, 363–377 (1984)
Gallacher, B.J., Burdess, J.S., Harish, K.M.: A control scheme for a MEMS electrostatic resonant gyroscope excited using combined parametric excitation and harmonic forcing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 320 (2006)
Zhang, W.M., Meng, G.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of electrostatically actuated resonant MEMS sensors under parametric excitation. IEEE Sens. J. 7, 370–380 (2007)
DeMartini, B.E., Rhoads, J.F., Turner, K.L., Shaw, S.W., Moehlis, J.: Linear and nonlinear tuning of parametrically excited MEMS oscillators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16, 310–318 (2007)
Zhang, W., Baskaran, R., Turner, K.L.: Changing the behavior of parametric resonance in MEMS oscillators by tuning the effective cubic stiffness. In: The Sixteenth Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, pp. 173–176 (2003)
Rhoads, J.F., Shaw, S.W., Turner, K.L., Moehlis, J., DeMartini, B.E., Zhang, W.: Generalized parametric resonance in electrostatically actuated microelectromechanical oscillators. J. Sound Vib. 296, 797–829 (2006)
Younis, M.I.: MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Xu, T., Younis, M.I.: Nonlinear dynamics of carbon nanotubes under large electrostatic force. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11, 021009 (2016)
Jalil, J., Zhu, Y., Ekanayake, C., Ruan, Y.: Sensing of single electrons using micro and nano technologies: a review. Nanotechnology 28, 142002 (2017)
Zhao, J., Ding, H., Xie, J.: Electrostatic charge sensor based on a micromachined resonator with dual micro-levers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 233505 (2015)
Chen, D., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Xie, J.: An electrostatic charge sensor based on micro resonator with sensing scheme of effective stiffness perturbation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 27, 065002 (2017)
Zhang, H., Huang, J., Yuan, W., Chang, H.: A high-sensitivity micromechanical electrometer based on mode localization of two degree-of-freedom weakly coupled resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 25, 937–946 (2016)
Ilyas, S., Alfosail, F.K., Bellaredj, M.L., Younis, M.I.: On the response of MEMS resonators under generic electrostatic loadings: experiments and applications. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(3), 2263–2274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4690-3
Acknowledgements
This publication is based upon work supported by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) research funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ilyas, S., Alfosail, F.K. & Younis, M.I. On the response of MEMS resonators under generic electrostatic loadings: theoretical analysis. Nonlinear Dyn 97, 967–977 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05024-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05024-3