Abstract
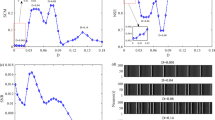
We study the effects of different coupling strengths and network topologies on signal detection in small-world neuronal networks. Research has previously revealed that the ability of detecting subthreshold signals could be significantly enhanced by appropriately fine-tuning the noise intensity. Here we show that the coupling strength and the structure of the underlying network can also lead toward enhanced signal detection. In particular, we show that there are two levels of the coupling strength at which the subthreshold signal can be detected at an appropriate noise intensity and network structure. We also show that the network structure has little impact on signal detection if the coupling is weak. On the other hand, for intermediate coupling strengths, we show that the shorter the average path length, the better the signal detection. Finally, if the coupling is strong, we show that there exists an intermediate average path length at which signal detection becomes optimal.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Notation: A small-world network topology is applied in this paper. In order to satisfy the statistic characteristics of small-world network topology, the network size should be not too small. Usually, the network size should be larger than 100. Thus, we choose N be 200 in this paper. And for different network size N, we need to modulate value of k to keep the obtained results be preserved.
References
Collins, J.J., Chow, C.C., Imhoff, T.T.: Stochastic resonance without tuning. Nature 376, 236–238 (1995)
Benzi, R., Parisi, G., Sutera, A., Vulpiani, A.: Stochastic resonance in climatic change. Tellus 34, 10–16 (1982)
Benzi, R., Sutera, A., Vulpiani, A.: The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 14, L453 (1999)
Wiesenfeld, K., Moss, F.: Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature 373, 33–36 (1995)
Gammaitoni, L.: Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 45–105 (1998)
Yilmaz, E., Uzuntarla, M., Ozer, M., Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance in hybrid scale-free neuronal networks. Physica A 392, 5735–5741 (2013)
Pikovsky, A.S., Kurths, J.: Coherence resonance in a noise-driven excitable system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 775–778 (1997)
Giacomelli, G., Giudici, M., Balle, S., Tredicce, J.R.: Experimental evidence of coherence resonance in an optical system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 3298 (2000)
Lee, S.G., Neiman, A., Kim, S.: Coherence resonance in a Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Phys. Rev. E 57, 3292–3297 (1998)
Vilar, J.M.G., Rubí, J.M.: Stochastic multiresonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 2882–2885 (1997)
Hessler, N.A., Shirke, A.M., Malinow, R.: The probability of transmitter release at a mammalian central synapse. Nature 366, 569 (1993)
Mcdonnell, M.D., Ward, L.M.: The benefits of noise in neural systems: bridging theory and experiment. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 415–426 (2011)
Faisal, A.A., Selen, L.P.J., Wolpert, D.M.: Noise in the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 292–303 (2008)
Faure, P., Korn, H.: A nonrandom dynamic component in the synaptic noise of a central neuron. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 6506 (1997)
Jacobson, G.A., Diba, K., Yaronjakoubovitch, A., Oz, Y., Koch, C., Segev, I., Yarom, Y.: Subthreshold voltage noise of rat neocortical pyramidal neurones. J. Physiol. 564, 145–160 (2005)
Wang, Q.Y., Zhang, H.Z., Perc, M., Chen, G.R.: Multiple firing coherence resonances in excitatory and inhibitory coupled neurons. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 17, 3979–3988 (2012)
Chen, Y.L., Yu, L.C., Chen, Y.: Reliability of weak signals detection in neurons with noise. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 59, 1–7 (2016)
Wang, C.N., Ma, J.: A review and guidance for pattern selection in spatiotemporal system. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32, 1830003 (2018)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569–1578 (2017)
Li, H.Y., Sun, X.J., Xiao, J.H.: Stochastic multiresonance in coupled excitable FHN neurons. Chaos 28, 043113 (2018)
Sun, X., Liu, Z.: Combined effects of time delay and noise on the ability of neuronal network to detect the subthreshold signal. Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 1707–1717 (2018)
Azevedo, F.A., Carvalho, L.R., Grinberg, L.T., Farfel, J.M., Ferretti, R.E., Leite, R.E., Jacob, F.W., Lent, R., Herculano-Houzel, S.: Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 513, 532–541 (2009)
Haydon, P.G.: GLIA: listening and talking to the synapse. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 185–193 (2001)
Liang, X., Tang, M., Dhamala, M., Liu, Z.: Phase synchronization of inhibitory bursting neurons induced by distributed time delays in chemical coupling. Phys. Rev. E 80, 066202 (2009)
Inchiosa, M.E., Bulsara, A.R.: Coupling enhances stochastic resonance in nonlinear dynamic elements driven by a sinusoid plus noise. Phys. Lett. A 200, 283–288 (1995)
Wu, D., Zhu, S., Luo, X., Wu, L.: Effects of adaptive coupling on stochastic resonance of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. E 84, 021102 (2011)
Zhang, R., Hu, M., Xu, Z.: Synchronization in complex networks with adaptive coupling. Phys. Lett. A 368, 276–280 (2007)
Ren, Q., Zhao, J.: Adaptive coupling and enhanced synchronization in coupled phase oscillators. Phys. Rev. E 76, 016207 (2007)
Sun, X.J., Zheng, Y.H.: Effects of time-periodic intercoupling strength on the spiking regularity of a clustered neuronal network. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 24, 186 (2014)
Sun, X.J., Han, F., Wiercigroch, M., Shi, X.: Effects of time-periodic intercoupling strength on burst synchronization of a clustered neuronal network. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 70, 119–125 (2015)
Markram, H., Lübke, J., Frotscher, M., Sakmann, B.: Regulation of synaptic efficacy by coincidence of postsynaptic APs and EPSPs. Science 275, 213–215 (1997)
Izhikevich, E., Desai, N.: Relating STDP to BCM. Neural Comput. 15, 1511–1523 (2003)
Saudargiene, A., Porr, B., Wörgötter, F.: How the shape of pre- and postsynaptic signals can influence STDP: a biophysical model. Neural Comput. 16, 595–625 (2004)
Xie, H., Gong, Y., Wang, Q.: Effect of spike-timing-dependent plasticity on coherence resonance and synchronization transitions by time delay in adaptive neuronal networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 89, 1–7 (2016)
Yu, H.T., Guo, X.M., Wang, J., Liu, C., Deng, B., Wei, X.L.: Adaptive stochastic resonance in self-organized small-world neuronal networks with time delay. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 29, 346–358 (2015)
Liao, X., Vasilakos, A.V., He, Y.: Small-world human brain networks: perspectives and challenges. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 77, 286–300 (2017)
Watts, D.J., Strogatz, S.H.: Collective dynamics of small-world networks. Nature 393, 440–442 (1998)
Faghiri, A., Stephen, J.M., Wang, Y.P., Wilson, T.W., Calhoun, V.D.: Changing brain connectivity dynamics: from early childhood to adulthood. Hum. Brain Mapp. 39, 1108–1117 (2018)
Cao, M., Wang, J.H., Dai, Z.J., Cao, X.Y., Jiang, L.L., Fan, F.M., Song, X.W., Xia, M.R., Shu, N., Dong, Q.: Topological organization of the human brain functional connectome across the lifespan. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 7, 76 (2014)
Cao, M., Shu, N., Cao, Q., Wang, Y., He, Y.: Imaging functional and structural brain connectomics in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 50, 1111–1123 (2014)
Cao, Q., Shu, N., An, L., Wang, P., Sun, L., Xia, M.R., Wang, J.H., Gong, G.L., Zang, Y.F., Wang, Y.F.: Probabilistic diffusion tractography and graph theory analysis reveal abnormal white matter structural connectivity networks in drug-naive boys with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Neurosci. 33, 10676–10687 (2013)
Ozer, M., Perc, M., Uzuntarla, M.: Stochastic resonance on Newman–Watts networks of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with local periodic driving. Phys. Lett. A 373, 964–968 (2009)
Yu, H.T., Wang, J., Du, J.W., Deng, B., Wei, X.L., Liu, C.: Effects of time delay on the stochastic resonance in small-world neuronal networks. Chaos 23, 013128 (2013)
Yu, H.T., Wang, J., Liu, C., Deng, B., Wei, X.L.: Stochastic resonance on a modular neuronal network of small-world subnetworks with a subthreshold pacemaker. Chaos 21, 047502 (2011)
Sun, X.J., Li, G.F.: Synchronization transitions induced by partial time delay in a excitatory-inhibitory coupled neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1–12 (2017)
Yan, H., Sun, X.J.: Impact of partial time delay on temporal dynamics of Watts–Strogatz small-world neuronal networks. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 1750112 (2017)
Yu, W.T., Tang, J., Ma, J., Yang, X.: Heterogeneous delay-induced asynchrony and resonance in a small-world neuronal network system. EPL-Europhys. Lett. 114, 50006 (2016)
Zhu, J., Chen, Z., Liu, X.: Effects of distance-dependent delay on small-world neuronal networks. Phys. Rev. E 93, 042417 (2016)
Yu, H., Wang, J., Du, J., Deng, B., Wei, X., Liu, C.: Effects of time delay and random rewiring on the stochastic resonance in excitable small-world neuronal networks. Phys. Rev. E 87, 052917 (2013)
Wang, Q.Y., Perc, M., Duan, Z.S., Chen, G.R.: Impact of delays and rewiring on the dynamics of small-world neuronal networks with two types of coupling. Physica A 389, 3299–3306 (2010)
Wang, Q.Y., Duan, Z.S., Perc, M., Chen, G.R.: Synchronization transitions on small-world neuronal networks: effects of information transmission delay and rewiring probability. EPL-Europhys. Lett. 83(5), 50008 (2008)
Perc, M.: Stochastic resonance on excitable small-world networks via a pacemaker. Phys. Rev. E 76, 066203 (2007)
Wang, Q.Y., Perc, M., Duan, Z.S., Chen, G.R.: Delay-induced multiple stochastic resonances on scale-free neuronal networks. Chaos 19, 023112 (2009)
Wang, Q.Y., Chen, G.R., Perc, M.: Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS ONE 6, e15851 (2011)
Jia, Y.B., Gu, H.G.: Transition from double coherence resonances to single coherence resonance in a neuronal network with phase noise. Chaos 25(12), L453 (2015)
Sun, X.J., Perc, M., Lu, Q.S., Kurths, J.: Effects of correlated Gaussian noise on the mean firing rate and correlations of an electrically coupled neuronal network. Chaos 20(3), 1104 (2010)
FitzHugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1, 445–466 (1961)
Nagumo, J., Arimoto, S., Yoshizawa, S.: An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. IRE 50, 2061–2070 (1962)
Fox, R.F., Gatland, I.R., Roy, R., Vemuri, G.: Fast, accurate algorithm for numerical simulation of exponentially correlated colored noise. Phys. Rev. A 38, 5938 (1988)
Acknowledgements
Xiaojuan Sun thanks for the supports by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11472061, 11772069) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University (No. 2018XKJC02). Matjaž Perc acknowledges support from the Slovenian Research Agency (Grant Nos. P5-0027 and J1-7009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Liu, Z. & Perc, M. Effects of coupling strength and network topology on signal detection in small-world neuronal networks. Nonlinear Dyn 96, 2145–2155 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04914-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04914-w