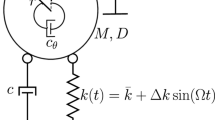Abstract
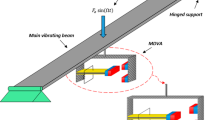
Devices with displacement dependent stiffness have been explored for vibration isolation. In this paper, an adjustable template stiffness device (ATSD) is presented. The ATSD is made up of pre-compressed springs attached to rollers, rolling along curved templates that allow adjustment of stiffness as a predetermined function of displacement. The ATSD configuration is presented in detail, and an analytical model is developed and validated using test results. The ATSD is tested under harmonic motion to determine its force–displacement behavior; then, it is connected to a single degree of freedom system, with an additional linear elastic stiffness spring, and tested on a shaking table to determine its vibration characteristics. The combination of the ATSD and the additional linear spring results in a composite nonlinear elastic spring with an initial softening behavior followed by hardening behavior or vice versa, i.e., depending on the chosen curved template. Frequency response curves obtained from test results are presented to demonstrate the capability of the ATSD. The new ATSD can be used for vibration isolation studies in future studies.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabuzhev, P., Rivin, E.I.: Vibration Protection and Measuring Systems with Quasi-Zero Stiffness. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1989)
Ibrahim, R.: Recent advances in nonlinear passive vibration isolators. J. Sound Vib. 314(3), 371–452 (2008)
Wang, Y., Li, S., Neild, S.A., Jiang, J.Z.: Comparison of the dynamic performance of nonlinear one and two degree-of-freedom vibration isolators with quasi-zero stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(1), 635–654 (2017)
Zou, K., Nagarajaiah, S.: The solution structure of the Düffing oscillators transient response and general solution. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1–2), 621–639 (2015)
Benacchio, S., Malher, A., Boisson, J., Touzé, C.: Design of a magnetic vibration absorber with tunable stiffnesses. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(2), 893–911 (2016)
Acar, M., Yilmaz, C.: Design of an adaptive–passive dynamic vibration absorber composed of a string–mass system equipped with negative stiffness tension adjusting mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 332(2), 231–245 (2013)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M., Waters, T., Shin, K.: On the design of a high-static–low-dynamic stiffness isolator using linear mechanical springs and magnets. J. Sound Vib. 315(3), 712–720 (2008)
Carrella, A., Brennan, M., Kovacic, I., Waters, T.: On the force transmissibility of a vibration isolator with quasi-zero-stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 322(4), 707–717 (2009)
Dong, L., Lakes, R.S.: Advanced damper with negative structural stiffness elements. Smart Mater. Struct. 21(7), 075026 (2012)
Franchek, M., Ryan, M., Bernhard, R.: Adaptive passive vibration control. J. Sound Vib. 189(5), 565–585 (1996)
Kovacic, I., Brennan, M.J., Waters, T.P.: A study of a nonlinear vibration isolator with a quasi-zero stiffness characteristic. J. Sound Vib. 315(3), 700–711 (2008)
Lee, C.-M., Goverdovskiy, V., Temnikov, A.: Design of springs with negative stiffness to improve vehicle driver vibration isolation. J. Sound Vib. 302(4), 865–874 (2007)
Le, T.D., Ahn, K.K.: A vibration isolation system in low frequency excitation region using negative stiffness structure for vehicle seat. J. Sound Vib. 330(26), 6311–6335 (2011)
Lu, L.-Y., Chu, S.-Y., Yeh, S.-W., Chung, L.-L.: Seismic test of least-input-energy control with ground velocity feedback for variable-stiffness isolation systems. J. Sound Vib. 331(4), 767–784 (2012)
Pasala, D., Sarlis, A., Nagarajaiah, S., Reinhorn, A., Constantinou, M., Taylor, D.: Adaptive negative stiffness: new structural modification approach for seismic protection. J. Sound Vib. 139(7), 1112–1123 (2012)
Platus, D.L.: Negative-stiffness-mechanism vibration isolation systems. In: SPIE’s International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation, pp. 98–105. International Society for Optics and Photonics (1999)
Sarlis, A., Pasala, D., Constantinou, M., Reinhorn, A., Nagarajaiah, S., Taylor, D.: Negative stiffness device for seismic protection of structures. J. Struct. Eng. 139(7), 1124–1133 (2012)
Shi, X., Zhu, S.: Magnetic negative stiffness dampers. Smart Mater. Struct. 24(7), 072002 (2015)
Spencer Jr., B., Nagarajaiah, S.: State of the art of structural control. J. Struct. Eng. 129(7), 845–856 (2003)
Virgin, L., Davis, R.: Vibration isolation using buckled struts. J. Sound Vib. 260(5), 965–973 (2003)
Walsh, P., Lamancusa, J.: A variable stiffness vibration absorber for minimization of transient vibrations. J. Sound Vib. 158(2), 195–211 (1992)
Weber, F., Boston, C.: Clipped viscous damping with negative stiffness for semi-active cable damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 20(4), 045007 (2011)
Yilmaz, C., Kikuchi, N.: Analysis and design of passive band-stop filter-type vibration isolators for low-frequency applications. J. Sound Vib. 291(3), 1004–1028 (2006)
Zhou, N., Liu, K.: A tunable high-static–low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator. J. Sound Vib. 329(9), 1254–1273 (2010)
Sun, C., Nagarajaiah, S., Dick, A.: Experimental investigation of vibration attenuation using nonlinear tuned mass damper and pendulum tuned mass damper in parallel. Nonlinear Dyn. 78(4), 2699–2715 (2014)
Zou, K., Nagarajaiah, S.: Study of a piecewise linear dynamic system with negative and positive stiffness. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 22(1), 1084–1101 (2015)
Attary, N., Symans, M., Nagarajaiah, S., Reinhorn, A., Constantinou, M., Sarlis, A., Pasala, D., Taylor, D.: Performance evaluation of negative stiffness devices for seismic response control of bridge structures via experimental shake table tests. J. Earthq. Eng. 19(2), 249–276 (2015)
Attary, N., Symans, M., Nagarajaiah, S., Reinhorn, A.M., Constantinou, M.C., Sarlis, A.A., Pasala, D.T., Taylor, D.P.: Experimental shake table testing of an adaptive passive negative stiffness device within a highway bridge model. Earthq. Spectra 31(4), 2163–2194 (2015)
Nagarajaiah, S.: Adaptive passive, semiactive, smart tuned mass dampers: identification and control using empirical mode decomposition, Hilbert transform, and short-term Fourier transform. Struct. Control Health Monit. 16(7–8), 800–841 (2009)
Sun, T., Lai, Z., Nagarajaiah, S., Li, H.-N.: Negative stiffness device for seismic protection of smart base isolated benchmark building. Struct. Control Health Monit. 24(11), e1968 (2017)
Li, H.-N., Sun, T., Lai, Z., Nagarajaiah, S.: Effectiveness of negative stiffness system in the benchmark structural-control problem for seismically excited highway bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 23(3), 04018001 (2018)
Feldman, M.: Non-linear system vibration analysis using Hilbert transform—I. Free vibration analysis method ‘freevib’. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 8(2), 119–127 (1994)
Feldman, M.: Hilbert transform in vibration analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 25(3), 735–802 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, Z., Sun, T. & Nagarajaiah, S. Adjustable template stiffness device and SDOF nonlinear frequency response. Nonlinear Dyn 96, 1559–1573 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04871-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04871-4