Abstract
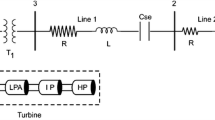
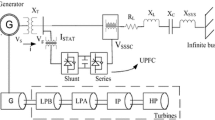
Series compensation of the transmission line increases the power flow capability of the system. Hybrid series compensation is a combination of active and passive series compensation provided by static synchronous series compensator with energy storage (SSSC-ES) and capacitor, respectively. This paper investigates the presence of bifurcations of subsynchronous resonance (SSR) in such a system. The results show that, as the series compensation level is varied, the system without SSSC-ES experiences periodic and quasiperiodic oscillations eventually leading to the catastrophic bifurcation. With the inclusion of SSSC-ES into the system, the number of periodic bifurcations of SSR reduces. This paper proposes a novel composite subsynchronous modal voltage injection (CSMVI) technique using SSSC-ES which controls catastrophic bifurcations of SSR. The CSMVI employs modal speed deviations that are derived from multi-mass section speed deviations and is used to modulate the reactive voltage injection of SSSC-ES. The study system for the analysis of SSR is IEEE First Benchmark model. Validation of the results obtained from bifurcation theory is carried out by performing the transient simulation using MATLAB/SIMULINK.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayfeh, A.H., Harb, A.M., Chin, C.M.: Bifurcation in a power system model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 6, 497–512 (1996)
Chiang, H.D.: Application of bifurcation analysis to power systems. In: Chen G., Hill D.J., Yu X. (eds) Bifurcation Control. Lecture Notes in Control and Information Science, vol. 293. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Padiyar, K.R., Prabhu, N.: Analysis of Subsynchronous Resonance with Three Level Twelve Pulse VSC Based SSSC. IEEE TENCON, Bangalore (2003)
Thirumalaivasan, R., Janaki, M., Prabhu, N.: Damping of SSR using subsynchronous current suppressor with SSSC. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 28(1), 6474 (2013)
Thirumalaivasan, R., Janaki, M., Xu, Y.: Kalman filter based detection and mitigation of subsynchronous resonance with SSSC. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 32(2), 1400–1409 (2017)
Bongiorno, M., Svensson, J., ngquist, L.: On control of static synchronous series compensator for SSR mitigation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 23(2), 735–743 (2008)
Rai, D., Faried, S.O., Ramakrishna, G., Aty Edris, A.: An SSSC-based hybrid series compensation scheme capable of damping of subsynchronous resonance. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 27(2), 531–540 (2012)
Arsoy, A., Liu, Y., Chen, S., Yang, Z., Crow, M.L., Ribeiro, P.F.: Dynamic performance of a static synchronous compensator with energy storage. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Power Engineering Society Winter Meeting, pp. 605–610 (2001)
Anderson, P.M., Agrawal, B.L., Van Ness, J.E.: Subsynchronous Resonance in Power Systems. IEEE Press, New York (1989)
Padiyar, K.R.: Analysis of Subsynchronous Resonance in Power Systems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston (1999)
Nayfeh, A.H., Harb, A.M., Chin, C.M., Hamdan, A.M.A., Mili, L.: Application of bifurcation theory to subsynchronous resonance in power systems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 8, 157–172 (1998)
Iravani, M.R., Semlyen, A.: Hopf bifurcations in torsional dynamics. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 7, 2836 (1992)
Zhu, W., Mohler, R.R., Spee, R., Mittelstadt, W.A., Maratukulam, D.: Hopf bifurcations in a SMIB power system with SSR. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 11, 15791584 (1996)
Harb, A.M., Widyan, M.S.: Controlling chaos and bifurcation of subsynchronous resonance in power system. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 7(2), 1536 (2002)
Widyan, M.S.: Controlling chaos and bifurcations of SMIB power system experiencing SSR phenomenon using SSSC. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 49, 66–75 (2013)
http://sourceforge.net/projects/matcont/files/matcont/matcont5p3/
Dhooge, A., Govaerts, W., Kuznestov, Y.A., Meijer, H.G., Sautois, B.: New features of the software MATCONT for the bifurcation analysis of dynamical systems. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 14(2), 147–175 (2008)
Mala, R.C., Prabhu, N., Gururaja Rao, H.V.: Impact of SSSC-ES on bifurcations of SSR. Energy Procedia 117C, 559–566 (2017)
Ali, H.: Nayfeh and Balakumar Balachandran: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
Static Exciter: \(K_E= 200\), \(T_E= 0.025\), \(Efd\max = 6\), \(Efd\min = -6\);
PSS with torsional filter: \(Kpss= 3, Tw= 2\), \(T1=T3= 0.1\), \(T2=T4= 0.025\), \(\omega _n= 22\), \(\zeta = 0.7\); \(Vs\max = 0.1\), \(Vs\min = -0.1\);
SSSC-ES: 175MVA, \(\rho _{\mathrm{se}}= 1/6\), \(Vdc= 0.7\);
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mala, R.C., Prabhu, N. & Rao, H.V.G. Control of catastrophic bifurcations of SSR in a hybrid series compensated system. Nonlinear Dyn 95, 971–981 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4608-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4608-0