Abstract
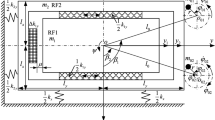
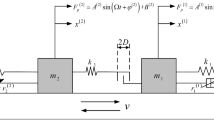
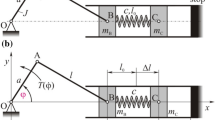
In this paper, the interactions of a translational vibratory feeder and the parts in the hop and the hop-sliding regimes are studied by means of an improved multi-term incremental harmonic balance method. It is an effective approach analyzing the interactions by introducing an analytical model of the motion of the feeding parts to the solution procedure. A generalized time-varying piece-wise linear dynamic model of the vibratory feeder is established to conduct a comprehensive investigation on the interactions, where the friction and the impact from the parts are included. The results indicate the dynamic response of the vibratory feeder affects the motion of the parts largely and the motion of the parts also affects the dynamic response in turn. The influences of the mass of the parts, the vibration angle, the installation angle, and the friction coefficient on the interactions of the vibratory feeder and the parts are discussed. The interactions are very important and not ignored.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashrafizadeh, H., Ziaei-Rad, S.: A numerical 2D simulation of part motion in vibratory bowl feeders by discrete element method. J. Sound Vib. 332(13), 3303–3314 (2013)
Mucchi, E., Di Gregorio, R., Dalpiaz, G.: Elastodynamic analysis of vibratory bowl feeders: Modeling and experimental validation. Mech. Mach. Theory. 60, 60–72 (2013)
Suresh, M., Narasimharaj, V., Arul Navalan, G.K., Chandra Bose, V.: Effect of orientations of an irregular part in vibratory part feeders. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 94(5), 2689–2702 (2018)
Sadasivam, U.: Development of vibratory part feeder for material handling in manufacturing automation: a survey. J. Automat. Mob. Robot. Intell. Syst. 9(4), 3–10 (2015)
Ramalingam, M., Samuel, G.L.: Investigation on the conveying velocity of a linear vibratory feeder while handling bulk-sized small parts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 44(3–4), 372–382 (2008)
Kobari, Y., Nammoto, T., Kinugawa, J., Kosuge, K.: Vision based compliant motion control for part assembly. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 293–298 (2013)
Han, I., Lee, Y.: Chaotic dynamics of repeated impacts in vibratory bowl feeders. J. Sound Vib. 249(3), 529–541 (2002)
Reinhart, G., Loy, M.: Design of a modular feeder for optimal operating performance. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 3(3), 191–195 (2010)
Lim, G.H.: Vibratory feeder motion study using Turbo C++ language. Adva. Eng. Softw. 18(1), 53–59 (1993)
Lim, G.H.: On the conveying velocity of a vibratory feeder. Comput. Struct. 62(1), 197–203 (1997)
Kong, X., Xing, J., Wen, B.: Analysis of motion of the part on the linear vibratory conveyor. J. Northeast. Univ. 36(6), 827–831 (2015)
Wen, B., Zhang, H., Liu, S., He, Q., Zhao, C.: Theory and techniques of vibrating machinery and their applications. Science Press, Beijing (2010)
Kong, X., Zhang, X., Li, Q., Wen, B.: Dynamical analysis of vibratory feeder and feeding parts considering interactions by an improved increment harmonic balance method. P I Mech. Eng. C.-J. Mech. 229(6), 1029–1040 (2015)
Vilán Vilán, J.A., Segade Robleda, A., García Nieto, P.J., Casqueiro Placer, C.: Approximation to the dynamics of transported parts in a vibratory bowl feeder. Mech. Mach. Theory 44(12), 2217–2235 (2009)
Han, I., Gilmore, B.J.: Multi-Body Impact motion with friction–analysis, simulation, and experimental validation. J. Mech. Design. 115(3), 412–422 (1993)
Lau, S.L., Zhang, W.S.: Nonlinear Vibrations of piecewise-linear systems by incremental harmonic balance method. J. Appl. Mech. 59(1), 153–160 (1992)
Duan, C., Singh, R.: Super-harmonics in a torsional system with dry friction path subject to harmonic excitation under a mean torque. J. Sound Vib. 285(4–5), 803–834 (2005)
Kim, T.C., Rook, T.E., Singh, R.: Super- and sub-harmonic response calculations for a torsional system with clearance nonlinearity using the harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 281(3–5), 965–993 (2005)
Duan, C., Singh, R.: Dynamic analysis of preload nonlinearity in a mechanical oscillator. J. Sound Vib. 301(3–5), 963–978 (2007)
Sen, O.T., Dreyer, J.T., Singh, R.: Envelope and order domain analyses of a nonlinear torsional system decelerating under multiple order frictional torque. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 35(1–2), 324–344 (2013)
Teng, J.G., Lou, Y.F.: Post-collapse bifurcation analysis of shells of revolution by the accumulated arc-length method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 40(13), 2369–2383 (1997)
De Souza Neto, E.A., Feng, Y.T.: On the determination of the path direction for arc-length methods in the presence of bifurcations and ‘snap-backs’. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 179(1–2), 81–89 (1999)
Leung, A.Y.T., Chui, S.K.: Non-linear vibration of coupled duffing oscillators by an improved incremental harmonic balance method. J. Sound. Vib. 181(4), 619–633 (1995)
Barrios, G.K.P., de Carvalho, R.M., Kwade, A., Tavares, L.M.: Contact parameter estimation for DEM simulation of iron ore pellet handling. Powder Technol. 248, 84–93 (2013)
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51705337, 51375080, 51675350) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017M611258)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, X., Chen, C. & Wen, B. Dynamic and stability analysis of the vibratory feeder and parts considering interactions in the hop and the hop-sliding regimes. Nonlinear Dyn 93, 2213–2232 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4320-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4320-0