Abstract
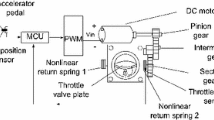
In order to enhance the rapidity and accuracy of throttle opening trajectory tracking for vehicle electronic throttle control (ETC) systems, a finite time servo control strategy is investigated by incorporating the particle swarm optimization (PSO) identification technique with the finite time stability theory. The PSO technique is adopted to identify the uncertain physical parameters of a real vehicle ETC system. In the PSO-based identification algorithm, the integrated square error between the actual and model throttle opening angles is regarded as the fitness function, and the mutation operation is added to prevent the particles from falling into local optimum. The designed servo controller is comprised of a feed-forward controller for trajectory tracking accuracy, a nonlinearity compensator for friction and return spring, and a feedback controller for finite time stability by utilizing additional power integrator and backstepping technique. The effectiveness of the proposed control strategy is verified by both the comparison results with the existing strategy in MATLAB/Simulink environment and the experiment results carried out on the electronic throttle hardware-in-loop test platform in several actual operating cases.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi, Z., Wang, Y., Ji, Z.: A multi-innovation recursive least squares algorithm with a forgetting factor for Hammerstein CAR systems with backlash. Circuits Syst. Signal Process 35(12), 4271–4289 (2016)
Shi, Z., Ji, Z.: Least squares based and two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithms for H-FIR-MA systems. Math. Probl. Eng. Vol. 2015, Article ID 516374, 8p, (2015) doi:10.1155/2015/516374
Loh, R.N.K., Thanom, W., Pyko, J.S., Lee, A.: Electronic throttle control system: modeling, identification and model-based control designs. Engineering 05(7), 587–600 (2013)
Yuan, X., Li, S., Wang, Y., Sun, W., Wu, L.: Parameter identification of electronic throttle using a hybrid optimization algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 63(4), 549–557 (2011)
Zhang, S., Yang, J., Zhu, G.: LPV modeling and mixed constrained \(H_2/H_\infty \) control of an electronic throttle. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. 20(5), 2120–2132 (2015)
Mercorelli, P.: Robust feedback linearization using an adaptive PD regulator for a sensorless control of a throttle valve. Mechatronics 19(8), 1334–1345 (2009)
Jiao, X., Zhang, J., Shen, T.: An adaptive servo control strategy for automotive electronic throttle and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(11), 6275–6284 (2014)
Yuan, X., Wang, Y.: Neural networks based self-learning PID control of electronic throttle. Nonlinear Dyn. 55(4), 385–393 (2009)
Wang, H., Yuan, X., Wang, Y., Yang, Y.: Harmony search algorithm-based fuzzy-PID controller for electronic throttle valve. Neural Comput. Appl. 22(2), 329–336 (2013)
Wang, S., Yan, B.: Fruit fly optimization algorithm based fractional order fuzzy-PID controller for electronic throttle. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(1), 611–619 (2013)
Wang, C.H., Huang, D.Y.: A new intelligent fuzzy controller for nonlinear hysteretic electronic throttle in modern intelligent automobiles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 60(6), 2332–2345 (2013)
Yuan, X., Yang, Y., Wang, H., Wang, Y.: Genetic algorithm-based adaptive fuzzy sliding mode controller for electronic throttle valve. Neural Comput. Appl. 23(S1), 209–217 (2013)
Li, Y., Yang, B., Zheng, T., Li, Y., Cui, M., Peeta, S.: Extended state observer based double loop integral sliding mode control of electronic throttle valve. IEEE Trans. Intell. Trans. Syst. 16(5), 2501–2510 (2015)
Wang, H., Liu, L., He, P., Yu, M., Do, M.T., Kong, H., Man, Z.: Robust adaptive position control of automotive electronic throttle valve using PID-type sliding mode technique. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(2), 1331–1344 (2016)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 38(3), 751–766 (2000)
Bhat, S.P., Bernstein, D.S.: Geometric homogeneity with applications to finite-time stability. Math. Control Signals Syst. 17(2), 101–127 (2005)
Huang, X., Lin, W., Yang, B.: Global finite-time stabilization of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Automatica 41(5), 881–888 (2005)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of 1995 IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Vol.4, pp.1942–1948. (1995)
Kameyama, K.: Particle swarm optimization : a survey. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 92(7), 1354–1361 (2009)
Kwok, N.M., Ha, Q.P., Nguyen, T.H.: A novel hysteretic model for magnetorheological fluid dampers and parameter identification using particle swarm optimization. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 132(2), 441–451 (2006)
Calvini, M., Carpita, M., Formentini, A., Marchesoni, M.: PSO-based self-commissioning of electrical motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(2), 768–776 (2015)
Ratnaweera, A., Halgamuge, S.K., Watson, H.C.: Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficients. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 8(3), 240–255 (2004)
MorKos, S., Kamal, A.H.: Adaptive mutation PSO for optimum design of PID controller in Robotic arm. Mediterr. J. Meas. Control 8(4), 477–484 (2012)
Deur, J., Pavkovic, D., Peric, N., Jansz, M., Hrovat, D.: An electronic throttle control strategy including compensation of friction and limp-home effects. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 40(3), 821–834 (2004)
Shieh, N.C.: Robust output tracking control of a linear brushless DC motor with time-varying disturbances. IEE Proc. Electric Power Appl. 149(1), 39–45 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61573304) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Grant No. F2017203210).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Jiao, X. Synthesis and validation of finite time servo control with PSO identification for automotive electronic throttle. Nonlinear Dyn 90, 1165–1177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3718-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3718-4