Abstract
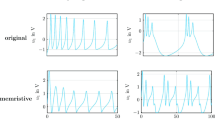
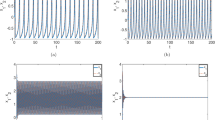
Different architectures and techniques have developed in the neuromorphic field to mimic and investigate the activity of biological neural networks. This paper presents a set of piece-wise linear approximations of a two-dimensional Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model for digital circuit implementation to achieve higher speeds and lower hardware costs in large-scale implementation of the biological neural networks. The performance of the model was evaluated with a time domain signal error. Synthesis and hardware implementation on a field-programmable gate array, as a proof of concept, indicates that the proposed model reproduces several neuronal behaviors similar to the original model with higher performance and considerably lower implementation costs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bluebrain|EPFL (2016). http://bluebrain.epfl.ch
Benjamin, B.V., Gao, P., McQuinn, E., Choudhary, S., Chandrasekaran, A.R., Bussat, J.M., Alvarez-Icaza, R., Arthur, J.V., Merolla, P.A., Boahen, K.: A mixed-analog-digital multichip system for large-scale neural simulations. Proc. IEEE 102(5), 699–716 (2014)
Brette, R.: Adaptive exponential integrate-and-fire model as an effective description of neuronal activity. J. Neurophysiol. 94(5), 3637–3642 (2005)
Brink, S., Nease, S., Hasler, P., Ramakrishnan, S., Wunderlich, R., Basu, A., Degnan, B.: A learning-enabled neuron array IC based upon transistor channel models of biological phenomena. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 7(1), 71–81 (2013)
Cognitive Computation Project (2016). http://ibm.com
Cameron, S.H.: Piece-wise linear approximations. Technical Report CSTN-106, Computer Science Division , IIT Research Institute, Chicago, IL (1996)
Cassidy, A.S., Georgiou, J., Andreou, A.G.: Design of silicon brains in the nano-cmos era: spiking neurons, learning synapses and neural architecture optimization. Neural Netw. 45, 4–26 (2013)
Chen, S.S., Chrng, C.Y., Lin, Y.R.: Application of a two-dimensional hindmarsh-rose type model for bifurcation analysis. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(03), 1350,055 (2013)
Dahasert, N., Öztürk, İ., Kiliç, R.: Experimental realizations of the hr neuron model with programmable hardware and synchronization applications. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(4), 2343–2358 (2012)
FitzHugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1, 445–466 (1961)
Gallego, G., Berjon, D., Garcia, N.: Optimal polygonal \(l_{1}\) linearization and fast interpolation of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Papers 61(11), 3225–3234 (2014)
Ghosh-Dastidar, S., Adeli, H.: Spiking Neural Networks: Third Generation Neural Networks. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Gomar, S., Ahmadi, A.: Digital multiplierless implementation of biological adaptive-exponential neuron model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Papers 61(4), 1206–1219 (2014)
Grassia, F., Levi, T., Kohno, T., Saghi, S.: Silicon neuron: digital hardware implementation of the quartic model. Artif Life Robot. 19(3), 215–219 (2014)
Hayati, M., Nouri, M., Abbott, D., Haghiri, S.: Digital multiplierless realization of two-coupled biological hindmarsh; rose neuron model. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 63(5), 463–467 (2016)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. Bull. Math. Biol. 52(1–2), 25–71 (1990)
Indiveri, G., Linares-Barranco, B., Hamilton, T.J., van Schaik, A., Etienne-Cummings, R., Delbruck, T., Liu, S.C., Dudek, P., Hafliger, P., Renaud, S., Schemmel, J., Cauwenberghs, G., Arthur, J., Hynna, K., Folowosele, F., Saighi, S., Serrano-Gotarredona, T., Wijekoon, J., Wang, Y., Boahen, K.: Neuromorphic silicon neuron circuits. Front. Neurosci. 5, 73 (2011)
Izhikevich, E.: Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(6), 1569–1572 (2003)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Which model to use for cortical spiking neurons? IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 15(5), 1063–1070 (2004)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Dynamical Systems in Neuroscience. MIT Press, Cambridge (2007)
Kazemi, A., Ahmad, A., Ahmad, S.: A digital synthesis of hindmarsh-rose neuron: a thalamic neuron model of the brain. In: 2014 22nd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), pp. 238–241 (2014)
Kosslyn, S.M., Andersen, R.A.: Frontiers in Cognitive Neuroscience. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Lee, Y.J., Lee, J., Kim, Y.B., Ayers, J., Volkovskii, A., Selverston, A., Abarbanel, H., Rabinovich, M.: Low power real time electronic neuron vlsi design using subthreshold technique. In: Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2004. ISCAS ’04, vol. 4, pp. 744–747 (2004)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., Ma, J., Song, X.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–1490 (2016)
Matsubara, T., Torikai, H., Hishiki, T.: A generalized rotate-and-fire digital spiking neuron model and its on-FPGA learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits and Syst. II Express Br. 58(10), 677–681 (2011)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Morrison, A., Diesmann, M., Gerstner, W.: Phenomenological models of synaptic plasticity based on spike timing. Biol. Cybern. 98(6), 459–478 (2008)
Nemo (2016). http://nemosim.sourceforge.net/
Nest Simulator|The Neural Simulation Tool (2016). http://www.nest-simulator.org/
Neil, D., Liu, S.C.: Minitaur, an event-driven fpga-based spiking network accelerator. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 22(12), 2621–2628 (2014)
Oliveri, A., Reimers, M., Storace, M.: Automatic domain partitioning of piecewise-affine simplicial functions implementing model predictive controllers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 62(9), 886–890 (2015)
Poggi, T., Sciutto, A., Storace, M.: Piecewise linear implementation of nonlinear dynamical systems: from theory to practice. Electron. Lett. 45(19), 966–967 (2009)
Ponulak, F., Kasinski, A.: Introduction to spiking neural networks: information processing, learning and applications. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 71(4), 409–433 (2011)
Postnov, D., Ryazanova, L., Sosnovtseva, O.: Functional modeling of neural-glial interaction. Biosystems 89(1–3), 84–91 (2007)
Radhika, E., Kumar, S., Kumari, A.: Low power analog VLSI implementation of cortical neuron with threshold modulation. In: 2015 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), pp. 561–566 (2015)
Rose, R.M., Hindmarsh, J.L.: The assembly of ionic currents in a thalamic neuron I. The three-dimensional model. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 237(1288), 267–288 (1989)
Sharifipoor, O., Ahmadi, A.: An analog implementation of biologically plausible neurons using CCII building blocks. Neural Netw. 36, 129–135 (2012)
Soleimani, H., Ahmadi, A., Bavandpour, M.: Biologically inspired spiking neurons: piecewise linear models and digital implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits and Syst. I Regul. Papers 59(12), 2991–3004 (2012)
Song, X., Wang, C., Ma, J., Tang, J.: Transition of electric activity of neurons induced by chemical and electric autapses. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 58(6), 1007–1014 (2015)
Starzyk, J.A.: Basawaraj: memristor crossbar architecture for synchronous neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Papers 61(8), 2390–2401 (2014)
Storace, M., Linaro, D., de Lange, E.: The Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model: bifurcation analysis and piecewise-linear approximations. Chaos 18(3), 033128 (2008)
The Brain Spiking Neural Network Simulator (2016). http://briansimulator.org/
The Human Brain Project (2016). https://www.humanbrainproject.eu
Tewari, S.G., Majumdar, K.K.: A mathematical model of the tripartite synapse: astrocyte-induced synaptic plasticity. J. Biol. Phys. 38(3), 465–496 (2012)
Torikai, H.: Learning of digital spiking neuron and its application potentials. In: Applications of Nonlinear Dynamics: Model and Design of Complex Systems, pp. 273–285. Springer, Heidelberg (2009)
Tsuji, S., Ueta, T., Kawakami, H., Fujii, H., Aihara, K.: Bifurcations in two-dimensional Hindmarsh–Rose type mode. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 17(03), 985–998 (2007)
Wilson, H.R.: Simplified dynamics of human and mammalian neocortical neurons. J. Theor. Biol. 200(4), 375–388 (1999)
Yamashita, Y., Torikai, H.: A novel PWC spiking neuron model: neuron-like bifurcation scenarios and responses. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Papers 59(11), 2678–2691 (2012)
Yildiz, N., Cesur, E., Kayaer, K., Tavsanoglu, V., Alpay, M.: Architecture of a fully pipelined real-time cellular neural network emulator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 62(1), 130–138 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heidarpur, M., Ahmadi, A. & Kandalaft, N. A digital implementation of 2D Hindmarsh–Rose neuron. Nonlinear Dyn 89, 2259–2272 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3584-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3584-0