Abstract
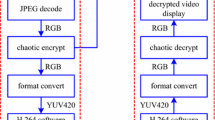
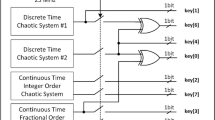
In this paper, a novel video chaotic secure communication scheme and its ARM-embedded hardware implementation are investigated, based on the H.264 selective encryption and multi-core multi-process. A six-dimensional discrete-time hyperchaotic system equipped with a nonlinear nominal matrix is firstly constructed, and the corresponding chaotic encryption algorithm is then designed. During H.264 encoding, the difference components of motion vectors in both the horizontal and vertical directions, as well as the DC transform coefficients, are selectively encrypted by using such a chaotic encryption algorithm, respectively, so as to enhance the safety performance. To improve the processing speed and transmission frame rate of the whole hardware system, an ARM-based hardware platform with multi-core multi-process is further adopted to realize the H.264 selective video chaotic secure communication, where the sender collects and encrypts the original video with four-core four-process mode, and the receiver decrypts the encrypted video with three-core three-process mode, in which one core binds one process. Finally, the security performance of the designed system is tested using the TESTU01 statistical test suites and some other statistical security analysis. Both theoretical analysis and experimental results validate the feasibility and reliability of the proposed scheme.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dufaux, F., Ebrahimi, T.: Scrambling for privacy protection in video surveillance systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 18(8), 1168–1174 (2008)
Arachchi, H.K., Perramon, X., Dogan, S., Kondoz, A.M.: Adaptation-aware encryption of scalable H.264/AVC video for content security. Signal Process. Image Commun. 24(6), 468–483 (2009)
Hellwagner, H., Kuschnig, R., Stütz, T., Uhl, A.: Efficient in-network adaptation of encrypted H.264/SVC content. Signal Process. Image Commun. 24(9), 740–758 (2009)
Liu, F., Koenig, H.: A survey of video encryption algorithms. Comput. Secur. 29(1), 3–15 (2010)
Wang, Y., O’Neill, M., Kurugollu, F., O’Sullivan, E.: Privacy region protection for H.264/AVC with enhanced scrambling effect and a low bitrate overhead. Signal Process. Image Commun. 35, 71–84 (2015)
Unterweger, A., Uhl, A.: Slice groups for post-compression region of interest encryption in H.264/AVC and its scalable extension. Signal Process. Image Commun. 16(2), 111–133 (2014)
Peng, F., Zhu, X., Long, M.: An ROI privacy protection scheme for H.264 video based on FMO and chaos. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 8(10), 1688–1699 (2013)
Tong, L., Dai, F., Zhang, Y., Li, J.: Prediction restricted H.264/AVC video scrambling for privacy protection. Electron. Lett. 46(1), 47–49 (2010)
Lian, S., Liu, Z., Ren, Z., Wang, H.: Commutative encryption and watermarking in video compression. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 17(6), 774–778 (2007)
Lin, Z., Yu, S., Lü, J., Cai, S., Chen, G.: Design and ARM-embedded implementation of a chaotic map-based real-time secure video communication system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 25(7), 1203–1216 (2015)
Lian, S., Liu, Z., Ren, Z., Wang, H.: Secure advanced video coding based on selective encryption algorithms. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 52(2), 621–629 (2006)
Yeung, S.K.A., Zhu, S., Zeng, B.: Perceptual video encryption using multiple 8\(\times \)8 transforms in H.264 and MPEG-4. In: International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (2011)
Shahid, Z., Puech, W.: Visual protection of HEVC video by selective encryption of CABAC binstrings. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 16(1), 24–36 (2014)
Su, P.C., Hsu, C.W., Wu, C.Y.: A practical design of content protection for H.264/AVC compressed videos by selective encryption and fingerprinting. Multimed. Tools Appl. 52(2–3), 529–549 (2010)
Zhu, B.B., Yuan, C., Wang, Y., Li, S.: Scalable protection for MPEG-4 fine granularity scalability. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 7(2), 222–223 (2005)
Zeng, B., Yeung, S.K.A., Zhu, S., Gabbouj, M.: Perceptual encryption of H.264 videos: embedding sign-flips into the integer-based transforms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 9(2), 309–320 (2014)
Shahid, Z., Chaumont, M., Puech, W.: Fast protection of H.264/AVC by selective encryption of CAVLC and CABAC for I and P frames. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 21(5), 565–576 (2011)
Asghar, M.N., Ghanbari, M.: An efficient security system for CABAC bin-strings of H.264/SVC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 23(3), 425–437 (2013)
Lui, O.Y., Wong, K.W.: Chaos-based selective encryption for H.264/AVC. J. Syst. Softw. 86(12), 3183–3192 (2013)
Jiang, J., Liu, Y., Su, Z., Zhang, G., Xing, S.: An improved selective encryption for H.264 video based on intra prediction mode scrambling. J. Multimed. 5(5), 464–472 (2010)
Chou, H.G., Chuang, C.F., Wang, W.J., Lin, J.C.: A fuzzy-model-based chaotic synchronization and its implementation on a secure communication system. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 8(12), 2177–2185 (2013)
Chung, Y., Lee, S., Jeon, T., Park, D.: Fast video encryption using the H.264 error propagation property for smart mobile devices. Sensors 15, 7953–7968 (2015)
Zou, Y., Huang, T., Gao, W., Huo, L.: H.264 video encryption scheme adaptive to DRM. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 5(4), 1289–1297 (2006)
Chen, P., Yu, S., Zhang, X., He, J., Lin, Z., Li, C., Lü, J.: ARM-embedded implementation of a video chaotic secure communication via WAN remote transmission with desirable security and frame rate. Nonlinear Dyn. 86(2), 725–740 (2016)
Alvarez, G., Li, S.: Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 16(8), 2129–2151 (2006)
Kocarev, L.: Chaos-based cryptography: a brief overview. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 1(3), 6–21 (2002)
Kocarev, L., Lian, S.: Chaos-Based Cryptography Theory, Algorithms and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Banerjee, S., Kurths, J.: Chaos and cryptography: a new dimension in secure communications. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 223(8), 1441–1445 (2014)
Annovazzi-Lodi, V., Benedetti, M., Merlo, S., Norgia, M., Provinzano, B.: Optical chaos masking of video signals. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 17(9), 1995–1997 (2005)
Sadoudi, S., Tanougast, C., Azzaz, M.S., Dandache, A.: Design and FPGA implementation of a wireless hyperchaotic communication system for secure real-time image transmission. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 43, 1–18 (2013)
Enayatifar, R., Abdullah, A.H., Isnin, I.F.: Chaos-based image encryption using a hybrid genetic algorithm and a DNA sequence. Opt. Lasers Eng. 56, 83–93 (2014)
Massoudi, A., Lefebvre, F., Vleeschouwer, C.D., Macq, B., Quisquater, J.J.: Overview on selective encryption of image and video, challenges and perspectives. EURASIP J. Inf. Secur. 2008, 1–18 (2008)
Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Pano-Azucena, A.D., Rangel-Magdaleno, J.J., Carbajal-Gomez, V.H., Rodriguez-Gomez, G.: Generating a 50-scroll chaotic attractor at 66 MHz by using FPGAs. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(4), 2143–2157 (2016)
Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Rangel-Magdaleno, J.J., Pano-Azucena, A.D., Obeso-Rodelo, P.J., Nunez-Perez, J.C.: FPGA realization of multi-scroll chaotic oscillators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 27(1–3), 66–80 (2015)
Carbajal-Gomez, V.H., Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Fernandez, F.V.: Optimizing the positive Lyapunov exponent in multi-scroll chaotic oscillators with differential evolution algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 219(15), 8163–8168 (2013)
de la Fraga, L.G., Tlelo-Cuautle, E.: Optimizing the maximum Lyapunov exponent and phase space portraits in multi-scroll chaotic oscillators. Nonlinear Dyn. 76(2), 1503–1515 (2014)
Trejo-Guerra, R., Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Cruz-Hernandez, C., Sanchez-lopez, C.: Chaotic communication system using Chua’s oscillators realized with CCII+s. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 19(12), 4217–4226 (2009)
Tlelo-Cuautle, E., Carbajal-Gomez, V.H., Obeso-Rodelo, P.J., Rangel-Magdaleno, J.J., Nuñez-Perez, J.C.: FPGA realization of a chaotic communication system applied to image processing. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(4), 1879–1892 (2015)
Pano-Azucena, A.D., de Jesus Rangel-Magdaleno, J., Tlelo-Cuautle, E., de Jesus Quintas-Valles, A.: Arduino-based chaotic secure communication system using multi-directional multi-scroll chaotic oscillators. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 2203–2217 (2017)
Li, C.: Cracking a hierarchical chaotic image encryption algorithm based on permutation. Signal Process. 118, 203–210 (2016)
Li, C., Liu, Y., Zhang, L.Y., Chen, M.Z.Q.: Breaking a chaotic image encryption algorithm based on modulo addition and XOR operation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(4), 1350075 (2013)
Xie, E.Y., Li, C., Yu, S., Lü, J.: On the cryptanalysis of Fridrich’s chaotic image encryption scheme. Signal Process. 132, 150–154 (2017)
Chang, J.F., Yang, Y.S., Liao, T.L., Yan, J.J.: Parameter identification of chaotic systems using evolutionary programming approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 35(4), 2074–2079 (2008)
Sun, J., Zhao, J., Wu, X., Fang, W., Cai, Y., Xu, W.: Parameter estimation for chaotic systems with a drift particle swarm optimization method. Phys. Lett. A 374(28), 2816–2822 (2010)
Ho, W.H., Chou, J.H., Guo, C.Y.: Parameter identification of chaotic systems using improved differential evolution algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 61(1–2), 29–41 (2010)
Chen, Z., Yuan, X., Yuan, Y., Iu, H.H.C., Fernando, T.: Parameter identification of chaotic and hyper-chaotic systems using synchronization-based parameter observer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 63(9), 1464–1475 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFB0800401), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61532020, 61671161, 61172023), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (No. 201510010136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Yu, S., Chen, P. et al. Design and ARM-embedded implementation of a chaotic secure communication scheme based on H.264 selective encryption. Nonlinear Dyn 89, 1949–1965 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3563-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3563-5