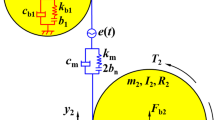
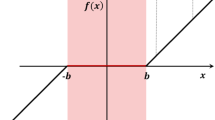
Abstract
By considering the lubricant in gear system, one degree-of-freedom model is set up which incorporates the pinion’s speed and the drag torque as the excitation sources. By introducing a permissible error (\(\varepsilon \)), a new computational algorithm using double-changed time steps is proposed in order to reduce the ill-conditioning arising from the numerical stiffness of the gear system and validated by comparison with Runge–Kutta–Fehlberg integration scheme. Then, the influences of the lubricant on the vibration of the gear system are analyzed. The results obtained in this paper indicate that the proposed numerical algorithm not only improves the accuracy of the solution, but also accelerates the calculation speed of the whole system. And according to the collision feature, the contributions of the lubricant on the system are totally different with different pinion’s speed and drag torque. Next, by introducing the proposed computational algorithm into the Floquet theory, the stability analyses of the gear system are investigated under the different excitation sources, which demonstrates that the excitation sources significantly affect the operating instability regions. In practice, particular instabilities can be minimized by the proper selection of pinion’s speed and drag torque, which can be adjusted according to the working requirements in advance.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\delta \) :
-
Dynamical transmission errors
- \(\dot{\delta }\) :
-
Relative speed
- \(\ddot{\delta }\) :
-
Relative acceleration
- C :
-
Nonlinear viscous damping
- K :
-
Nonlinear stiffness
- W :
-
Nonlinear torque
- c, k, w :
-
Intermediate variables for C, K, W
- L :
-
Total backlash
- t :
-
Time in second
- \(T_f\) :
-
Time of one excited period cycle
- \(\Delta t\) :
-
Time interval for any given time \(t_0\)
- \(\Delta t_{+k}\) :
-
Time interval from lubricant contact to solid contact
- \(\Delta t_{-k}\) :
-
Time interval from solid contact to lubricant contact
- \(\Delta t_{-,+}^{\max }\) :
-
Maximum time step for lubricant and solid contact
- \(\omega _\mathrm{p}\) :
-
Excitation frequency
- \(\zeta _{1,2}\) :
-
Critical viscous damping ratio of lubricant and solid
- \(k_{1,2}\) :
-
Stiffness of lubricant and solid
- \(I_\mathrm{p,g}\) :
-
Rotational inertia of the pinion and gear
- \(I_\mathrm{eq}\) :
-
Equivalent mass
- \(\theta _\mathrm{p,g}\) :
-
Rotational displacements of the pinion and gear
- \(\dot{\theta }_\mathrm{p,g}\) :
-
Rotational velocity of the pinion and gear
- \(\ddot{\theta }_\mathrm{p,g}\) :
-
Rotational acceleration of the pinion and gear
- \(R_\mathrm{p,g}\) :
-
Pitch radius of the pinion and gear
- \(\vartheta _\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Mean part of the pinion’s speed
- \(\vartheta _\mathrm{p}^i\) :
-
Amplitude of vibratory part of the ith harmonic for the pinion’s speed
- \(\varphi _i\) :
-
Initial phase of the ith harmonic for the pinion’s speed
- \(T_\mathrm{d}\) :
-
Drag torque
- \(\bar{T}_\mathrm{m}\) :
-
Mean part of the drag torque
- \(\bar{T}_\mathrm{p}^j\) :
-
Amplitude of vibratory part of the jth harmonic for the drag torque
- \(\phi _j\) :
-
Initial phase of the jth harmonic for the drag torque
- \(T_\mathrm{m}, T_\mathrm{p}^j\) :
-
Intermediate variables for \(\bar{T}_\mathrm{m}, \bar{T}_\mathrm{p}^j\)
- \(\varepsilon \) :
-
Small value defining transition area
- \(\varepsilon _{1,2}\) :
-
Perturbation number of the relative displacement and relative velocity
- \(\lambda _{1,2}\) :
-
Eigenvalues for the Jacobian matrix
- N :
-
Initial resolution of the numerical solution
- M :
-
Number of the period
- P :
-
Poincaré map
- \({[} \Pi {]}\) :
-
Jacobian matrix
- \(E{[} \,{]}\) :
-
Expectation operator
- \(\gamma \) :
-
Periods of the solution
- \(a_{\pm k} ,b_{\pm k} ,c_{\pm k}\) :
-
Intermediate variables for \(\Delta t_{\pm k}\)
References
Singh, R., Xie, H., Comparin, R.: Analysis of automotive neutral grear rattle. J. Sound Vib. 131(2), 177–196 (1989)
Theodossiades, S., Natsiavas, S.: Periodic and chaotic dynamics of motor-driven gear-pair systems with backlash. Chaos Solitons Fractals 12(13), 2427–2440 (2001)
Rocca, E., Russo, R.: Theoretical and experimental investigation into the influence of the periodic backlash fluctuations on the gear rattle. J. Sound Vib. 330(20), 4738–4752 (2011)
Tangasawi, O., Theodossiades, S., Rahnejat, H.: Lightly loaded lubricated impacts: idle gear rattle. J. Sound Vib. 308(3), 418–430 (2007)
Theodossiades, S., Tangasawi, O., Rahnejat, H.: Gear teeth impacts in hydrodynamic conjunctions promoting idle gear rattle. J. Sound Vib. 303(3), 632–658 (2007)
Brancati, R., Rocca, E., Russo, R.: An analysis of the automotive driveline dynamic behaviour focusing on the influence of the oil squeeze effect on the idle rattle phenomenon. J. Sound Vib. 303(3), 858–872 (2007)
Russo, R., Brancati, R., Rocca, E.: Experimental investigations about the influence of oil lubricant between teeth on the gear rattle phenomenon. J. Sound Vib. 321(3), 647–661 (2009)
Barbieri, M., Lubrecht, A.A., Pellicano, F.: Behavior of lubricant fluid film in gears under dynamic conditions. Tribol. Int. 62, 37–48 (2013)
Pedersen, R., Santos, I.F., Hede, I.A.: Advantages and drawbacks of applying periodic time-variant modal analysis to spur gear dynamics. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 24(5), 1495–1508 (2010)
Ma, R., Chen, Y., Cao, Q.: Research on dynamics and fault mechanism of spur gear pair with spalling defect. J. Sound Vib. 331(9), 2097–2109 (2012)
Jiang, H., Liu, F.: Dynamic features of three-dimensional helical gears under sliding friction with tooth breakage. Eng. Fail. Anal. 70, 305–322 (2016)
Fujimoto, T., Chikatani, Y., Kojima, J.: Reduction of idling rattle in manual transmission. SAE Technical Paper, No. 870395 (1987)
Shih, S., Yruma, J., Kittredge, P.: Drivetrain noise and vibration troubleshooting. SAE Technical Paper, No. 2001-01-2809 (2001)
Wang, M., Manoj, R., Zhao, W.: Gear rattle modelling and analysis for automotive manual transmissions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 215(2), 241–258 (2001)
Liu, F., Jiang, H., Zhang, H., Yu, X.: Dynamic behavior analysis of spur gears with constant & variable excitations considering sliding friction influence. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 30(12), 5363–5370 (2016)
Meisner, S., Campbell, B.: Development of gear rattle analytical simulation methodology. SAE Technical Paper, No. 951317 (1995)
Kartik, V., Houser, D.R.: An investigation of shaft dynamic effects on gear vibration and noise excitations. SAE Technical Paper, No. 2003-01-1491 (2003)
Kang, M.R., Kahraman, A.: Measurement of vibratory motions of gears supported by compliant shafts. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 29(5), 391–403 (2011)
Chang-Jian, C.W.: Strong nonlinearity analysis for gear-bearing system under nonlinear suspension-bifurcation and chaos. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(3), 1760–1774 (2010)
Wang, K.L., Cheng, H.S.: A numerical solution to the dynamic load, film thickness, and surface temperatures in spur gears, part I: analysis. J. Mech. Des. 103(1), 177–187 (1981)
Ene, N.M., Dimofte, F.: Effect of fluid film wave bearings on attenuation of gear mesh noise and vibration. Tribol. Int. 53, 108–114 (2012)
Huang, K.J., Wu, M.R., Tseng, J.T.: Dynamic analyses of gear pairs incorporating the effect of time-varying lubrication damping. J. Vib. Control 17(3), 355–363 (2011)
Ottewill, J.R., Neild, S.A., Wilson, R.E.: Intermittent gear rattle due to interactions between forcing and manufacturing errors. J. Sound Vib. 321(3), 913–935 (2009)
He, S., Rook, T., Singh, R.: Construction of semianalytical solutions to spur gear dynamics given periodic mesh stiffness and sliding friction functions. J. Mech. Des. 130(12), 122601 (2008)
Comparin, R., Singh, R.: Non-linear frequency response characteristics of an impact pair. J. Sound Vib. 134(2), 259–290 (1989)
Kahraman, A., Singh, R.: Non-linear dynamics of a spur gear pair. J. Sound Vib. 142(1), 49–75 (1990)
Azar, R., Crossley, F.: Digital simulation of impact phenomenon in spur gear systems. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 99(3), 792–798 (1977)
Bonori, G., Pellicano, F.: Non-smooth dynamics of spur gears with manufacturing errors. J. Sound Vib. 306(1), 271–83 (2007)
Ma, Q., Kahraman, A.: Period-one motions of a mechanical oscillator with periodically time-varying, piecewise-nonlinear stiffness. J. Sound Vib. 284(3), 893–914 (2005)
Yang, J., Peng, T., Lim, T.C.: An enhanced multi-term harmonic balance solution for nonlinear period-one dynamic motions in right-angle gear pairs. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 1053–1065 (2012)
Shen, Y., Yang, S., Liu, X.: Nonlinear dynamics of a spur gear pair with time-varying stiffness and backlash based on incremental harmonic balance method. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 48(11), 1256–1263 (2006)
Raghothama, A., Narayanan, S.: Bifurcation and chaos in geared rotor bearing system by incremental harmonic balance method. J. Sound Vib. 226(3), 469–492 (1999)
Al-Shyyab, A., Kahraman, A.: Non-linear dynamic analysis of a multi-mesh gear train using multi-term harmonic balance method: sub-harmonic motions. J. Sound Vib. 279(1), 417–451 (2005)
Al-Shyyab, A., Kahraman, A.: Non-linear dynamic analysis of a multi-mesh gear train using multi-term harmonic balance method: period-one motions. J. Sound Vib. 284(1), 151–172 (2005)
Moradi, H., Salarieh, H.: Analysis of nonlinear oscillations in spur gear pairs with approximated modelling of backlash nonlinearity. Mech. Mach. Theory 51, 14–31 (2012)
Lin, J., Parker, R.G.: Mesh stiffness variation instabilities in two-stage gear systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 124(1), 68–76 (2002)
Tordion, G., Gauvin, R.: Dynamic stability of a two-stage gear train under the influence of variable meshing stiffnesses. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 99(3), 785–791 (1977)
Amabili, M., Rivola, A.: Dynamic analysis of spur gear pairs: steady-state response and stability of the sdof model with time-varying meshing damping. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 11(3), 375–390 (1997)
Chen, C.S., Natsiavas, S., Nelson, H.D.: Stability analysis and complex dynamics of a gear-pair system supported by a squeeze film damper. J. Vib. Acoust. 119(1), 85–88 (1997)
Chang-Jian, C.W., Chang, S.M.: Bifurcation and chaos analysis of spur gear pair with and without nonlinear suspension. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 12(2), 979–989 (2011)
Farshidianfar, A., Saghafi, A.: Global bifurcation and chaos analysis in nonlinear vibration of spur gear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 75(4), 783–806 (2014)
Laschet, A.: Simulation of vibrations in power trains to minimise gear-rattling. In: Proceedings of EAEC Conference, pp. 139–146. Strasbourg (1989)
Szadkowski, A.: Mathematical model and computer simulation of idle gear rattle. SAE Technical Paper, No. 910641 (1991)
Johnson, O., Hirami, N.: Diagnosis and objective evaluation of gear rattle. SAE Technical Paper, No. 911082 (1991)
Rust, A., Brandl, F., Thien, G.: Investigations into gear rattle phenomena-key parameters and their influence on gearbox noise. Inst. Mech. Eng. C 404, 113–120 (1990)
Sakai, T., Doi, Y., Yamamoto, K.I., Ogasawara, T., Narita, M.: Theoretical and experimental analysis of rattling noise of automotive gearbox. SAE Technical Paper, No. 810773 (1981)
Seaman, R.L., Johnson, C.E., Hamilton, R.F.: Component inertial effects on transmission design. SAE Technical Paper, No. 841686 (1984)
Brancati, R., Rocca, E., Russo, R.: A gear rattle model accounting for oil squeeze between the meshing gear teeth. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 219(9), 1075–1083 (2005)
Guilbault, R., Lalonde, S., Thomas, M.: Nonlinear damping calculation in cylindrical gear dynamic modeling. J. Sound Vib. 331(9), 2110–2128 (2012)
Liu, F., Jiang, H., Zhang, L., Chen, L.: Analysis vibration characteristic for helical gear under hydrodynamic conditions. Adv. Mech. Eng. 9(1), 1–9 (2017)
Liu, F.: Dynamic analysis of drag torque for spur gear pairs considering the double-sided films. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. (2016). doi:10.1177/0954406216631370
Aiken, R.C.: Stiff Computation. Oxford University Press, New York (1985)
Padmanabhan, C., Barlow, R., Rook, T., Singh, R.: Computational issues associated with gear rattle analysis. J. Mech. Des. 117(1), 185–192 (1995)
Khabou, M., Bouchaala, N., Chaari, F., Fakhfakh, T., Haddar, M.: Study of a spur gear dynamic behavior in transient regime. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 25, 3089–3101 (2011)
Rahnejat, H.: Multi-Body Dynamics: Vehicles, Machines and Mechanisms. J. Appl. Mech. Bury St Edmunds (1998)
Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., Cao, Q.: Bifurcations and hysteresis of varying compliance vibrations in the primary parametric resonance for a ball bearing. J. Sound Vib. 350(18), 171–184 (2015)
Long, X., Liu, J., Meng, G.: Nonlinear dynamics of two harmonically excited elastic structures with impact interaction. J. Sound Vib. 333(5), 1430–1441 (2014)
Mailybaev, A.A., Spelsberg-Korspeter, G.: Combined effect of spatially fixed and rotating asymmetries on stability of a rotor. J. Sound Vib. 336(3), 227–239 (2015)
Howard, I., Jia, S., Wang, J.: The dynamic modelling of a spur gear in mesh including friction and a crack. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 15(5), 831–853 (2001)
Wu, S., Zuo, M.J., Parey, A.: Simulation of spur gear dynamics and estimation of fault growth. J. Sound Vib. 317(3), 608–624 (2008)
Liu, F., Theodossiades, S., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F., McFarland, D.M.: Analytical characterization of damping in gear teeth dynamics under hydrodynamic conditions. Mech. Mach. Theory 94, 141–147 (2015)
Bellomo, P., Cricenti, F., De Vito, N., Lang, C.H., Minervini, D.: Innovative vehicle powertrain systems engineering: beating the noisy offenders in vehicle transmissions. SAE Technical Paper, No. 2000-01-0033 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51305378), Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Automotive Engineering (QC201306), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded Project (2016M590643), Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Department (BY2015057-25) and the Research Laboratory of Mechanical Vibration (MVRLAB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Zhang, L. & Yu, X. Stability investigation of velocity-modulated gear system using a new computational algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 89, 1111–1128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3504-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3504-3