Abstract
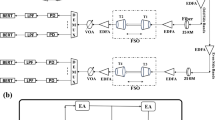
A physically enhanced secure wavelength division multiplexing chaos communication scheme in virtue of the chaos synchronization of two multimode semiconductor lasers (MSLs) is introduced. In this scheme, two communicating MSLs are subjected to identical optical injections from a chaotic external-cavity MSL, and each mode of the communicating MSLs is used as a chaotic carrier. The messages are divided into a set of blocks, and these blocks are transmitted by different modes in different time slots, according to a pre-negotiated pattern. The numerical results indicate that high-quality chaos synchronization with a wide operation region and relatively strong frequency detuning tolerance can be achieved between the communicating MSL modes, which can afford multiple simultaneous bidirectional message transmissions. Moreover, because of the carrier-consumption competition in the MSL cavity, the peak average power ratios of the chaotic carriers are much larger and more widely distributed with respect to selected single-mode injection or feedback cases, which can obviously enhance the link security against the attack of linear filtering. Also, the carrier-consumption competition induces a cross talk between the transmission messages, which can greatly improve the link security when eavesdroppers adopt the synchronization utilization method to attack the public link. Furthermore, with the non-fixed wavelength transmission technology, the system security can also be further improved greatly. The proposed scheme provides a new way to implement high-speed multichannel chaos communication with high physically enhanced security.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soriano, M.C., Garcia-Ojalvo, J., Mirasso, C.R., Fischer, I.: Complex photonics: dynamics and applications of delay-coupled semiconductor lasers. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 421–470 (2013). doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.85.421
Argyris, A., Syvrids, D., Larger, L., Annovazzi-Lodi, V., Colet, P., Fischer, I., Garcia-Ojalvo, J., Mirasso, C.R., Pesquera, L., Shore, K.A.: Chaos-based communications at high bit rates using commercial fibre-optic links. Nature 437, 343–346 (2005). http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v438/n7066/abs/nature04275.html
Li, N.Q., Pan, W., Yan, L.S., Luo, B., Zou, X.H.: Enhanced chaos synchronization and communication in cascade-coupled semiconductor ring lasers. Commun. Nonliner Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 1874–1883 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2013.09.036
Deng, T., Xia, G.Q., Wu, Z.M.: Broadband chaos synchronization and communication based on mutually coupled VCSELs subject to a bandwidth-enhanced chaotic signal injection. Nonlinear Dyn. 76, 399–407 (2014). doi:10.1007/s11071-013-1134-y
Klein, E., Gross, N., Rosenbluh, M., Kinzel, W., Khaykovich, L., Kanter, I.: Stable isochronal synchronization of mutually coupled chaotic lasers. Phys. Rev. E 73, 066214 (2006). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.73.066214
Argyris, A., Grivas, E., Bogris, A., Syvridis, D.: Transmission effects in wavelength division multiplexed chaotic optical communication systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 28, 3107–3114 (2010). doi:10.1109/JLT.2010.2073444
Zhang, J.Z., Wang, A.B., Wang, J.F., Wang, Y.C.: Wavelength division multiplexing of chaotic secure and fiber-optic communications. Opt. Express 17, 6357–6367 (2009). doi:10.1364/OE.17.006357
Jiang, N., Zhang, C.F., Qiu, K.: Secure passive optical network based on chaos synchronization. Opt. Lett. 37, 4501–4503 (2012). doi:10.1364/OL.37.004501
Ohtsubo, J.: Chaos synchronization and chaotic signal masking in semiconductor lasers with optical feedback. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 38, 1141–1154 (2002). doi:10.1109/JQE.2002.801883
Li, N.Q., Pan, W., Luo, B., Yan, L.S., Zou, X.H., Xiang, S.Y.: High bit rate fiber-optic transmission using a four-chaotic-semiconductor-laser scheme. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 24, 1072–1074 (2012). doi:10.1109/LPT.2012.2194482
Vicente, R., Perez, T., Mirasso, C.R.: Open- versus closed-loop performance of synchronized chaotic external-cavity semiconductor lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 38, 1197–1204 (2002). doi:10.1109/JQE.2002.802110
Yan, S.L.: Chaotic synchronization of two mutually coupled semiconductor lasers for optoelectronic logic gates. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer Simul. 17, 2896–2904 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.10.034
Jiang, N., Pan, W., Luo, B., Yan, L.S., Xiang, S.Y., Yang, L., Zheng, D., Li, N.: Properties of leader/laggard chaos synchronization in mutually coupled external-cavity semiconductor lasers. Phys. Rev. E 81, 066217 (2010). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.81.066217
Mengue, A.D., Essimbi, B.Z.: Secure communication using chaotic synchronization in mutually coupled semiconductor lasers. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 1241–1253 (2012). doi:10.1007/s11071-012-0528-6
Jiang, N., Pan, W., Yan, L.S., Luo, B., Zhang, W.L., Xiang, S.Y., Yang, L., Zheng, D.: Chaos synchronization and communication in mutually coupled semiconductor lasers driven by a third laser. J. Lightwave Technol. 28, 1978–1986 (2010). doi:10.1109/JLT.2010.2050858
Jiang, N., Pan, W., Luo, B., Yan, L.S., Xiang, S.Y., Yang, L.: Simultaneous unidirectional and bidirectional chaos-based optical communication using hybrid coupling semiconductor lasers. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 5, 012401 (2014). doi:10.1007/s11432-012-4721-5
Bogris, A., Argyris, A., Syvridis, D.: Encryption efficiency analysis of chaotic communication systems based on photonic integrated chaotic circuits. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 46, 1421–1429 (2010). doi:10.1109/JQE.2010.2049986
Kanakidis, D., Argyris, A., Bogris, A., Syvridis, D.: Influence of decoding process on the performance of chaos encrypted optical communication systems. J. Lightwave Technol. 24, 335–341 (2006). doi:10.1109/JLT.2005.859850
Jiang, N., Pan, W., Luo, B., Xiang, S.Y.: Synchronization properties of a cascaded system consisting of two external-cavity semiconductor lasers mutually coupled via an intermediate laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 19, 1500108 (2013). doi:10.1109/JSTQE.2012.2218220
Lang, R., Kobayashi, K.: External optical feedback effects on semiconductor injection laser properties. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 16, 347–355 (1980). doi:10.1109/JQE.1980.1070479
Buldu, J.M., Garcia-Ojalvo, J., Torrent, M.C.: Multimode synchronization and communication using unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 40, 640–650 (2004). doi:10.1109/JQE.2004.828230
Heil, T., Fischer, I., Elsasser, W., Mulet, J., Mirasso, C.R.: Chaos synchronization and spontaneous symmetry-breaking in symmetrically delay-coupled semiconductor lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 795–798 (2001). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.86.795
Wu, J.G., Wu, Z.M., Xia, G.Q., Deng, T., Lin, X.D., Tang, X., Feng, G.Y.: Isochronal synchronization between chaotic semiconductor lasers over 40-km fiber links. IEEE Photon Technol. Lett. 23, 1854–1856 (2011). doi:10.1109/LPT.2011.2170212
Lee, M.W., Shore, K.A.: Two-mode chaos synchronization using a multimode external-cavity laser diode and two single-mode laser diodes. J. Lightwave Technol. 23, 1068–1073 (2005). doi:10.1109/JLT.2004.839979
Bogris, A., Rizomiliotis, P., Chlouverakis, K.E., Argyris, A., Syvridis, D.: Feedback phase in optically generated chaos: a secret key for cryptographic applications. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 44, 119–124 (2008). doi:10.1109/JQE.2007.911687
Wu, J.G., Wu, Z.M., Liu, Y., Fan, L., Tang, X., Xia, G.Q.: Simulation of bidirectional long-distance chaos communication performance in a novel fiber-optic chaos synchronization system. J. Lightwave Technol. 31, 461–467 (2013). doi:10.1109/JLT.2012.2232283
Zhang, F., Chu, P.L.: Effect of transmission fiber on chaos communication system based on erbium-doped fiber ring laser. J. Lightwave Technol. 21, 3334–3343 (2003). doi:10.1109/JLT.2003.821721
Vicente, R., Mirasso, C.R., Fischer, I.: Simultaneous bidirectional message transmission in a chaos-based communication scheme. Opt. Lett. 32, 403–405 (2007). doi:10.1364/OL.32.000403
Acknowledgments
This Work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61301156, 61471087), and the Specialized Research Fund for Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China No. 20130185120007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, N., Xue, C., Lv, Y. et al. Physically enhanced secure wavelength division multiplexing chaos communication using multimode semiconductor lasers. Nonlinear Dyn 86, 1937–1949 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3006-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3006-8