Abstract
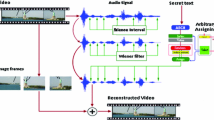
This paper presents a novel layering approach of steganography which implements deception theory by utilizing three types of multimedia, in order to hide the data in video file. In the proposed technique first, audio stream of video file is analyzed and two features are extracted, active zone and silence zone. These features define method numbers where each method number corresponds to one cipher technique which exists in the literature. After selecting the ciphering method, we apply it on the plaintext. In the second layer, first we convert the ciphered text into arbitrary characters and hide the data using chaotic map by generating logo image. In the third layer, we multiply that image with orthogonal matrix which is selected on the basis of silence zones. In the fourth layer, we hide that logo image using DWT with security key. The security key is generated locally by using logistic map, and its initial condition is set on the basis of selected method number. Lastly we hide resultant image into the audio signal using wavelet transform and regenerate the video file. The proposed system is implemented in MATLAB 7.0. Here, we analyzed the SNR values of the regenerated signal and other statistical results to prove that onion steganography works better than silence interval technique, LSB technique, echo hiding technique, magnitude technique and spectrum technique in many aspects.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kayarkar, H., Sanyal, S.: A survey on various data hiding techniques and their comparative analysis. In: arXiv preprint arXiv:1206.1957 (2012)
Gantz, J., Reinsel, D.: The digital universe in 2020: big data, bigger digital shadows, and biggest growth in the Far East. In: IDC iView: IDC Analyze the Future (2012). http://www.emcchannel.com/collateral/analyst-reports/idc-the-digital-universe-in-2020.pdf
Von Solms, R., Van Niekerk, J.: From information security to cyber security. Comput. Secur. 38, 97–102 (2013)
Djebbar, F., Ayad, B., Meraim, K.A., Hamam, H.: Comparative study of digital audio steganography techniques. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music Process. 2012(1), 1–16 (2012)
Bhattacharyya, D., Kim, T.H., Dutta, P.: A method of data hiding in audio signal. J. Chin. Instit. Eng. 35(5), 523–528 (2012)
Nosrati, M., Karimi, R., Hariri, M.: Audio steganography: a survey on recent approaches. World Appl. Program. 2(3), 202–205 (2012)
Hamid, N., Yahya, A., Ahmad, R.B., Al-Qershi, O.M.: Image steganography techniques: an overview. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Secur (IJCSS) 6(3), 68–187 (2012)
Stanescu, D., Stratulat, M., Ciubotaru, B., Chiciudean, D., Cioarga, R., Micea, M.V.: Embedding data in video stream using steganography. In: 4th IEEE International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, pp. 241–244 (2007)
Fridrich, J., & Long, M.: Steganalysis of LSB encoding in color images. In: Multimedia and Expo, ICME IEEE International Conference, pp. 1279–1282 (2000)
Fang, D.Y., Chang, L.W.: Data hiding for digital video with phase of motion vector. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 4–10 (2006)
Pradeep, M., Kamila, N.: Crypto steganography using linear algebraic equation. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Technol. 21(8), 106–112 (2011)
Nutzinger, M., Wurzer, J.: A novel phase coding technique for steganography in auditive media. In: IEEE Sixth International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, pp. 91–98 (2011)
Jamal, S.S., Shah, T., Hussain, I.: An efficient scheme for digital watermarking using chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(3), 1469–1474 (2013)
Pooyan, M., Delforouzi, A.: LSB-based audio steganography method based on lifting wavelet transform. In: IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, pp. 600–603 (2007)
Cvejic, N., Seppanen, T.: Increasing robustness of LSB audio steganography using a novel embedding method. In: IEEE International Conference on Information Technology: Coding and Computing, pp. 533–537 (2004)
Roy, R., Sarkar, A., Changder, S.: Chaos based edge adaptive image steganography. procedia Technol. 10(1), 138–146 (2013)
Malviya, S., Saxena, M., Khare, D.A.: Audio steganography by different methods. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2(7), 93–98 (2012)
Hussain, I., Azam, N.A., Shah, T.: Stego optical encryption based on chaotic S-box transformation. Opt. Laser Technol. 61, 50–56 (2014)
Sampat, V., Karmokar, S., Madia, J., Dave, K., Toprani, P.: Audio steganography using dynamic cover generation. In: IJCA Proceedings on National Conference on Advancement of Technologies, pp. 26–30 (2012)
Shirali-Shahreza, S., Shirali-Shahreza, M.: Steganography in silence intervals of speech. In: International Conference on Intelligent Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, pp. 605–607 (2008)
Hernandez-Castro, J.C., Blasco-Lopez, I., Estevez-Tapiador, J.M., Ribagorda-Garnacho, A.: Steganography in games: a general methodology and its application to the game of Go. Comput. Secur. 25(1), 64–71 (2006)
Nishu, G., Mrs, S.A.: Practical three layered approach of data hiding using audio steganography. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 3(7), 7505–7510 (2014)
Kamalpreet, K., Deepankar, V.: Multi-level steganographic algorithm for audio steganography using LSB, parity coding and phase coding technique. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. Softw. Eng. 4(1), 191–195 (2014)
Wiener, N.: Extrapolation, Interpolation, and Smoothing of Stationary Time Series. MIT Press, Cambridge (1949)
Paley, R.E.A.C., Wiener, N.: Fourier transforms in the complex domain. In: American Mathematical Society 19 (1934)
Doclo, S., Moonen, M.: On the output SNR of the speech distortion weighted multichannel Wiener filter. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 12(12), 809–811 (2005)
Proakis, J.G.: Digital signal processing: principles algorithms and applications. In: Pearson Education India (2001)
Mitra, S.K., Kuo, Y.: Digital Signal Processing: A Computer-Based Approach. McGraw-Hill, New York (2006)
Muhammad, K.F., Baig, F., Beg, S.: Steganography between silence intervals of audio in video content using chaotic maps. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(12), 3901–3919 (2014)
Podilchuk, C.I., Delp, E.J.: Digital watermarking: algorithms and applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 18(4), 33–46 (2001)
Sam, I.S., Devaraj, P., Bhuvaneswaran, R.S.: An intertwining chaotic maps based image encryption scheme. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 1995–2007 (2012)
Lai, H., Orgun, M.A., Xiao, J., Pieprzyk, J., Xue, L., Yang, Y.: Provably secure three-party key agreement protocol using Chebyshev chaotic maps in the standard model. Nonlinear Dyn. 77(4), 1427–1439 (2014)
Mandal, J.K., Das, D.: Steganography using adaptive pixel value differencing (APVD) of gray images through exclusion of overflow/underflow. In:arXivpreprint:1205.6775 (2012)
Toosizadeh, S., Farshchi, S.M.R.: A hybrid steganography algorithm based on chaos & BPCS. In: Proceedings of the World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing, pp. 1–5 (2012)
Adulkasem, K.C.J.P.S.: Image Steganography via Video Using Lifting Wavelet Transform, pp. 46–49 . Science & engineering research support society (SERC), Daegu (2013)
Ameen, S.Y., Al-Badrany, M.R.: Optimal image steganography content destruction techniques. In: International Conference on Systems, Control, Signal Processing and Informatics, pp. 453–457 (2013)
Wang, C.M., Wu, N.I., Tsai, C.S., Hwang, M.S.: A high quality steganographic method with pixel-value differencing and modulus function. J. Syst. Softw. 81(1), 150–158 (2008)
Hemalatha, S., Acharya, U.D., Renuka, A., Kamath, P.R.: A secure and high capacity image steganography technique. Signal Image Process. Int. J. 4(1), 83–89 (2013)
Tseng, H.W., Leng, H.S.: A steganographic method based on pixel-value differencing and the perfect square number. J. Appl. Math. Article ID 189706, 8 p. (2013). doi:10.1155/2013/189706
Douiri, S.M., Medeni, M.B.O., Elbernoussi, S., Souidi, E.M.: A new steganographic method for grayscale image using graph coloring problem. Appl. Math. 7(2), 521–527 (2013)
Ajeeshvali, N., Rajasekhar, B.: Steganography based on integer wavelet transform and bicubic interpolation. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 4(12), 26–33 (2012)
Nag, A., Biswas, S., Sarkar, D., Sarkar, P.P.: A novel technique for image steganography based on Block-DCT and Huffman Encoding. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2(3), 103–112 (2010)
Wu, D.C., Tsai, W.H.: A steganographic method for images by pixel-value differencing. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 24(9), 1613–1626 (2003)
Lin, S.L., Huang, C.F., Liou, M.H., Chen, C.Y.: Improving histogram-based reversible information hiding by an optimal weight-based prediction scheme. J. Inf. Hiding Multimed. Signal Process. 1(1), 19–33 (2013)
Weng, C.Y., Shiuh-Jeng, W.A.N.G., Liu, J., Goyal, D.: Prediction-based reversible data hiding using empirical histograms in images. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. (TIIS) 6(4), 1248–1266 (2012)
Ye, G.: Image scrambling encryption algorithm of pixel bit based on chaos map. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 31, 347–354 (2010)
Corrochano, E.B., Mao, Y., Chen, G.: Chaos-based image encryption. In: E. B. Corrochano (ed.) Handbook of Geometric Computing, pp. 231–265. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Menezes, A., Van Oorschot, P., Vanstone, S.: Handbook of Applied Cryptography. Chapman and Hall, London (1997)
Fournier-Prunaret, D., Lopez-Ruiz, R.: Basin bifurcations in a two-dimensional logistic map. In: e-print, arXiv:nlin/0304059 (2003)
Wang, X., Zhang, J.: An image scrambling encryption using chaos-controlled Poker shuffle operation. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biometrics and Security Technologies (ISBAST), pp. 1–6 (2008)
Patidar, V., Pareek, N.K., Sod, K.K.: A new substitution-diffusion based image cipher using chaotic standard and logistic maps. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14, 3056–3075 (2009)
Zhang, Y., Wang, X.: Analysis and improvement of a chaos-based symmetric image encryption scheme using a bit-level permutation. Int. J. Nonlinear Dyn. Chaos Eng. Syst. 77(3), 687–698 (2014)
Zhang, Y., Wang, X.: A symmetric image encryption algorithm based on mixed linear-nonlinear coupled map lattice. Inf. Sci. 273, 329–351 (2014)
Wang, X., Yang, L., Liu, R., Kadir, A.: A chaotic image encryption algorithm based on perceptron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 62, 615–621 (2010)
Zhang, Y., Li, C., Li, Q., Zhang, D., Shu, S.: Breaking a chaotic image encryption algorithm based on perceptron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 69, 1091–1096 (2012)
Li, C., Zhang, I., Ou, R., Wong, K., Shu, S.: Breaking a novel color image encryption algorithm based on chaos. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 2383–2388 (2012)
Sikarwar, N.S.: A model for performance enhancement of steganography through dynamic key cryptography. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Appl. 3(6), 1395–1401 (2012)
Bhatnagar, G., Wu, Q.J.: A novel chaos-based secure transmission of biometric data. Neurocomputing 147, 444–455 (2015)
Zhou, N.R., Hua, T.X., Gong, L.H., Pei, D.J., Liao, Q.H.: Quantum image encryption based on generalized Arnold transform and double random-phase encoding. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(4), 1193–1213 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baig, F., Khan, M.F., Beg, S. et al. Onion steganography: a novel layering approach. Nonlinear Dyn 84, 1431–1446 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2580-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2580-5