Abstract
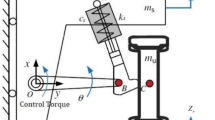
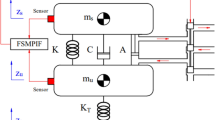
This paper presents a novel interval type-2 fuzzy-neural network indirect adaptive sliding mode control (SMC) approach (T2FNNAS) for a suspension system including actuator dynamics. It is equipped with a novel moving sliding surface in which the slope and intercept of sliding surface are simultaneity adjusted by adaptive interval T2FNN to improve controller robustness against system uncertainties and unknown disturbances. As a result, the drawbacks of the conventional SMC, such as chattering effect and a required priori knowledge of the bounds of uncertainties, are removed. Based on the Lyapunov synthesis approach, the free parameters of the adaptive FNN are tuned on-line. One advantage of the proposed approach is that, by incorporating the Lyapunov design approach and SMC method into the adaptive fuzzy-neural control scheme to derive the control law, the proposed approach not only assures closed-loop stability but also achieves a good performance for the overall system. Another advantage of the proposed method is that to relax the requirement for the bound of approximation error, and an estimation mechanism is also employed to observe the bound of it real time. Design of the control system consists of two interior loops. The inner loop is a force control of the hydraulic actuator, while the outer loop is position controller that use T2FNNAS. Finally, a comparison between the proposed approach and a robust model reference adaptive control approach is provided. Simulation results confirm that the proposed approach effectively improves both the passenger comfort and the ride quality of the car.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, H.-Y., Huang, S.-J.: A new model-free adaptive sliding controller for active suspension system. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 39(1), 57–69 (2008)
Chen, H., Guo, K.-H.: Constrained \(\text{ H }^\infty \) control of active suspensions: an LMI approach. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 13(3), 412–421 (2005)
Karnopp, D.: Theoretical limitations in active vehicle suspensions. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 15(1), 41–54 (1986)
Fateh, M.M., Zirkohi, M.M.: Adaptive impedance control of a hydraulic suspension system using particle swarm optimisation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 49(12), 1951–1965 (2011)
Lin, J.-S., Kanellakopoulos, I.: Nonlinear design of active suspensions. Control Syst. IEEE. 17(3), 45–59 (1997)
Shen, X., Peng, H., Abe M.: Analysis of active suspension systems with hydraulic actuators. In: The Dynamics of Vehicles on Roads and on Tracks Supplement to Vehicle System Dynamics: Proceedings Of The 18th Iavsd Symposium Held In Kanagawa, Japan August 24–30, 2003, CRC Press (2005)
Hrovat, D.: Survey of advanced suspension developments and related optimal control applications. Automatica 33(10), 1781–1817 (1997)
Lin, J.-S., Kanellakopoulos, I.: Nonlinear design of active suspensions. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 17, 45–49 (1995)
Corona, D., Giua, A., Seatzu, C.: Optimal control of hybrid automata: design of a semiactive suspension. Control Eng. Pract. 12(10), 1305–1318 (2004)
Sohn, H.-C., et al.: An adaptive LQG control for semi-active suspension systems. Int. J. Veh. Des. 34(4), 309–326 (2004)
Swevers, J., et al.: A model-free control structure for the on-line tuning of the semi-active suspension of a passenger car. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 21(3), 1422–1436 (2007)
Karnopp, D.: Theoretical limitations in active suspensions. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 15, 41–54 (1986)
Sharkawy, A.: Fuzzy and adaptive fuzzy control for the automobiles’ active suspension system. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 43(11), 795–806 (2005)
D’Amato, F.J., Viassolo, D.E.: Fuzzy control for active suspensions. Mechatronics 10(8), 897–920 (2000)
Wang, L.-X.: Stable adaptive fuzzy control of nonlinear systems. Fuzzy Syst. IEEE Trans. 1(2), 146–155 (1993)
Lin, T.-C.: Based on interval type-2 fuzzy-neural network direct adaptive sliding mode control for SISO nonlinear systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(12), 4084–4099 (2010)
Mendel, J.M., John, R.B.: Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. Fuzzy Syst. IEEE Trans. 10(2), 117–127 (2002)
Hagras, H.A.: A hierarchical type-2 fuzzy logic control architecture for autonomous mobile robots. Fuzzy Syst. IEEE Trans. 12(4), 524–539 (2004)
Yager, R.R.: Fuzzy subsets of type II in decisions. Cybern. Syst. 10(1–3), 137–159 (1980)
Lin, T.-C., Chen, M.-C., Roopaei, M.: Synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems based on adaptive type-2 fuzzy sliding mode control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 24(1), 39–49 (2011)
Majid, Moradi Zirkohi, Fateh, M.M., Shoorehdeli, M.A.: Type-2 fuzzy control for a flexible-joint robot using voltage control strategy. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 10(3), 242–255 (2013)
Hsiao, M.-Y., et al.: Design of interval type-2 fuzzy sliding-mode controller. Inf. Sci. 178(6), 1696–1716 (2008)
Pang, H.-P., Liu, C.-J., Zhang W: Sliding mode fuzzy control with application to electrical servo drive. In: Intelligent Systems Design and Applications, 2006. ISDA’06. Sixth International Conference on. 2006: IEEE
Kaynak, O., Erbatur, K., Ertugnrl, M.: The fusion of computationally intelligent methodologies and sliding-mode control—a survey. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. 48(1), 4–17 (2001)
Ha, Q.P., Rye, D.C., Durrant-Whyte, H.F.: Fuzzy moving sliding mode control with application to robotic manipulators. Automatica 35(4), 607–616 (1999)
Hung, J.Y., Gao, W., Hung, J.C.: Variable structure control: a survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 40(1), 2–22 (2003)
Slotine, J.J., Sastry, S.S.: Tracking control of non-linear systems using sliding surfaces, with application to robot manipulators\({^\dagger }\). Int. J. Control 38(2), 465–492 (1983)
Chantranuwathana, S., Peng H: Practical adaptive robust controllers for active suspensions. Digital Library 7 (2000)
Alleyne, A., Hedrick, J.K.: Nonlinear adaptive control of active suspensions. Control Syst. Technol. IEEE Trans. 3(1), 94–101 (1995)
Liang, Q., Mendel, J.M.: Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems: theory and design. Fuzzy Syst. IEEE Trans. 8(5), 535–550 (2000)
Karnik, N.N., Mendel, J.M.: Centroid of a type-2 fuzzy set. Inf. Sci. 132(1), 195–220 (2001)
Chen, P.-C., Huang, A.-C.: Adaptive sliding control of active suspension systems with uncertain hydraulic actuator dynamics. Veh. Syst. Dyns. 44(5), 357–368 (2006)
Choi, S.-B., Cheong, C.-C., Park, D.-W.: Moving switching surfaces for robust control of second-order variable structure systems. Int. J. Control 58(1), 229–245 (1993)
Park, D.-W., Choi, S.-B.: Moving sliding surfaces for high-order variable structure systems. Int. J. Control 72(11), 960–970 (1999)
Wai, R.-J., Lin, C.-M., Hsu, C.-F.: Adaptive fuzzy sliding-mode control for electrical servo drive. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 143(2), 295–310 (2004)
Slotine, J.-J.E., Li, W.: Applied Nonlinear Control, vol. 199. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Yagiz, N., Hacioglu, Y.: Robust control of a spatial robot using fuzzy sliding modes. Math. Comput. Model. 49(1), 114–127 (2009)
Maleki, N., Sedigh, A., Labibi B: Robust model reference adaptive control of active suspension system. In: Control and Automation, 2006. MED’06. 14th Mediterranean Conference on. 2006: IEEE
Acknowledgments
The first author gratefully appreciates the support of the Behbahan Khatam Alanbia University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zirkohi, M.M., Lin, TC. Interval type-2 fuzzy-neural network indirect adaptive sliding mode control for an active suspension system. Nonlinear Dyn 79, 513–526 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1683-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1683-8