Abstract
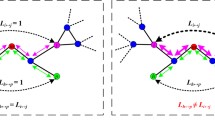
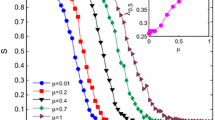
Considering the node weight and the effect of the neighboring nodes, we introduce a method to define the initial load of a node in a network and propose a cascading model. Our aim is to explore how to allocate the initial load and select some nodes to be protected so as to maximize the network robustness against cascading failures. According to the distribution of the node weight and the normalized effect of the neighboring nodes, we focus on investigating different roles of high-load and low-load nodes and the correlation between some parameters in our model and the strongest robust level of a network against cascading failures. We obtain by the numerical simulations the optimal values of the parameters in our model at which the network can reach the strongest robust level against cascading failures. In addition, we find that the effect of two attacks strongly depends on the parameters of the node weight and the normalized effect of the neighboring nodes, i.e., the network robustness of attacking the low-load nodes has a positive correlation with the parameter of the node weight, while has a negative correlation with the parameter of the normalized reaction of the neighboring nodes. While the result of attacking the high-load nodes is almost on the contrary. Finally, we verify the numerical results by the theoretical analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosato, V., Issacharoff, L., Tiriticco, F., Meloni, S., Porcellinis, S., Setola, R.: Modelling interdependent infrastructures using interacting dynamical models. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 4, 63C79 (2008)
Albert, R., Albert, I., Nakarado, G.L.: Structural vulnerability of the North American power grid. Phys. Rev. E 69, 025103(R) (2004)
Pastor-Satorras, R., Vázquez, A., Vespignani, A.: Dynamical and correlation properties of the Internet. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 258701 (2001)
Chang, L., Wu, Z.G.: Performance and reliability of electrical power grids under cascading failures. Int. J. Electr. Power 33(8), 1410–1419 (2011)
Wang, J.W., Rong, L.L.: Cascade-based attack vulnerability on the US power grid. Saf. Sci. 47(10), 1332–1336 (2009)
Leonardo, D.-O., Srivishnu, M.V.: Cascading failures in complex infrastructure systems. Struct. Saf. 31, 157–167 (2009)
Ricard, V.S., Martí, R.C., Bernat, C.M., Sergi, V.: Robustness of the European power grids under intentional attack. Phys. Rev. E 77, 026102 (2008)
Wang, J.W.: Robustness of complex networks with the local protection strategy against cascading failures. Saf. Sci. 53, 219–225 (2013)
Goh, K.I., Hahng, B., Kim, D.: Fluctuation-driven dynamics of the Internet topology. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88(10), 108701 (2002)
Zhang, G.D., Li, Z., Zhang, B., Halang, W.A.: Understanding the cascading failures in Indian power grids with complex networks theory. Phys. A 392, 3273–3280 (2013)
Wang, W.X., Lai, Y.C., Dieter, A.: Cascading failures and the emergence of cooperation in evolutionary-game based models of social and economical networks. Chaos 21(3), 033112 (2011)
Crucitti, P., Latora, V., Marchiori, M.: Model for cascading failures in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 69, 045104 (2004)
Mirzasoleiman, B., Babaei, M., Jalili, M., Safari, M.: Cascaded failures in weighted networks. Phys. Rev. E 84, 046114 (2011)
Wang, J.W., Rong, L.L., Zhang, L., Zhang, Z.Z.: Attack vulnerability of scale-free networks due to cascading failures. Phys. A 387(26), 6671–6678 (2008)
Vespignani, A.: The fragility of interdependency. Nature 464, 984–985 (2010)
Buldyrev, S.V., Parshani, R., Paul, G., Stanley, H.E., Havlin, S.: Catastrophic cascade of failures in interdependent networks. Nature 464, 1025–1028 (2010)
Gao, J., Buldyrev, S.V., Stanley, H.E., Havlin, S.: Networks formed from interdependent networks. Nat. Phys. 8, 40–48 (2012)
Gao, J., Buldyrev, S.V., Havlin, S., Stanley, H.E.: Robustness of a network of networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(19), 195701 (2011)
Brummitt, C.D., D’souza, R.M., Leicht, E.A.: Suppressing cascades of load in interdependent networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109(12), E680–E689 (2012)
Shao, J., Buldyrev, S.V., Havlin, S., Stanley, H.E.: Cascade of failures in coupled network systems with multiple support-dependence relations. Phys. Rev. E 83(3), 036116 (2011)
Qiu, Y.Z.: Cascading dynamics with local weighted flow redistribution in interdependent networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 86, 329 (2013)
Parshani, R., Buldyrev, S.V., Havlin, S.: Interdependent networks: reducing the coupling strength leads to a change from a first to second order percolation transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105(4), 048701 (2010)
Huang, X.Q., Gao, J.X., Buldyrev, S.V., havlin, S., Stanley, H.E.: Robustness of interdependent networks under targeted attack. Phys. Rev. E 83(6), 065101(R) (2011)
Schäfer, M., Scholz, J., Greiner, M.: Proactive Robustness Control of Heterogeneously Loaded Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96(10), 108701 (2006)
Simonsen, I., Buzna, L., Peters, K., Bornholdt, S., Helbing, D.: Transient dynamics increasing network vulnerability to cascading failures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100(21), 218701 (2008)
Ash, A., Newth, D.: Optimizing complex networks for resilience against cascading failure. Phys. A 380, 673–683 (2007)
Wang, B., Kim, B.J.: A high-robustness and low-cost model for cascading failures. Europhys. Lett. 78(4), 48001 (2007)
Cao, X.B., Hong, C., Du, W.B., Zhang, J.: Improving the network robustness against cascading failures by adding links. Chaos Soliton Fract. 57, 35–40 (2013)
Wang, J.W.: Mitigation of cascading failures on complex networks [J]. Nonlinear Dyn. 70(3), 1959–1967 (2012)
Yang, R., Wang, W.X., Lai, Y.C., Chen, G.R.: Optimal weighting scheme for suppressing cascades and traffic congestion in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 79(2), 026112 (2009)
Pahwa, S., Youssef, M., Schumm, P., Scoglio, C., Schulz, N.: Optimal intentional islanding to enhance the robustness of power grid networks. Phys. A 392, 3741–3754 (2013)
Buzna, L., Peters, K., Ammoser, H., Kühnert, C., Helbing, D.: Efficient response to cascading disaster spreading. Phys. Rev. E 75(5), 056107 (2007)
Wang, W.X., Chen, G.R.: Universal robustness characteristic of weighted networks against cascading failure. Phys. Rev. E 77, 026101 (2008)
Wu, Z.X., Peng, G., Wang, W.X., Chan, S., Wong, E.E.M.: Cascading failure spreading on weighted heterogeneous networks. J. Stat. Mech. 2008, P05013 (2008)
Wang, S.L., Hong, L., Ouyang, M., Zhang, J.H., Chen, X.G.: Vulnerability analysis of interdependent infrastructure systems under edge attack strategies. Saf. Sci. 51, 328–337 (2013)
Zhao, L., Park, K., Lai, Y.C.: Attack vulnerability of scale-free networks due to cascading breakdown. Phys. Rev. E 70(3), 035101(R) (2004)
Zhao, L., Park, K., Lai, Y.C., Ye, N.: Tolerance of scale-free networks against attack-induced cascades. Phys. Rev. E 72(2), 025104 (2005)
Moreira, A.A., Andrade Jr, J.S., Herrmann, H.J., Indekeu, J.O.: How to Make a Fragile Network Robust and Vice Versa. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102(1), 018701 (2009)
Li, S.D., Li, L.X., Yang, Y.X., Luo, Q.: Revealing the process of edge-based-attack cascading failures. Nonlinear Dyn. 69, 837–845 (2012)
Wang, J.W., Rong, L.L.: Edge-based-attack induced cascading failures on scale-free networks. Phys. A 388(8), 1731–1737 (2009)
Wang, J.W., Rong, L.L.: Robustness of the western United States power grid under edge attack strategies due to cascading failures. Saf. Sci. 49(6), 807–812 (2011)
Barabási, A.-L., Albert, R.: Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 286(5439), 509–512 (1999)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 71101022 and 71102119, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. N110406003, and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University under Grant no. NCET-12-0100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, C., Huang, Y. et al. Attack robustness of cascading model with node weight. Nonlinear Dyn 78, 37–48 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1420-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-014-1420-3