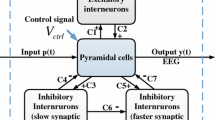
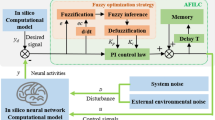
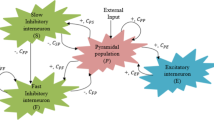
Abstract
A new closed-loop control method based on the fuzzy adaptive unscented Kalman filter (FAUKF) is proposed to suppress epileptiform spikes in a class of neural mass models with uncertain measurement noise. The FAUKF is used to estimate the nonlinear system states of the underlying models and amend measurement noise adaptively. The control law is constructed via the estimated states. Numerical simulations illustrate the efficiency of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wendling, F., Bellanger, J.J., Bartolomei, F., Chauvel, P.: Relevance of nonlinear lumped-parameter models in the analysis of depth-EEG epileptic signals. Biol. Cybern. 83, 367–378 (2000)
Gao, J.B., Hu, J., Tung, W.W.: Entropy measures for biological signal analyses. Nonlinear Dyn. 68, 431–444 (2012)
Ding, L., Hou, C.: Stabilizing control of Hopf bifurcation in the Hodgkin–Huxley model via washout filter with linear control term. Nonlinear Dyn. 60, 131–139 (2010)
Goodfellow, M., Schindler, K., Baier, G.: Intermittent spike-wave dynamics in a heterogeneous, spatially extended neural mass model. NeuroImage 55, 920–932 (2011)
Goodfellow, M., Schindler, K., Baier, G.: Self-organised transients in a neural mass model of epileptogenic tissue dynamics. NeuroImage 59, 2644–2660 (2012)
Nevado-Holgado, A.J., Marten, F., Richardson, M.P., Terry, J.R.: Characterising the dynamics of EEG waveforms as the path through parameter space of a neural mass model: application to epilepsy seizure evolution. NeuroImage 59, 2374–2392 (2012)
Krauss, G.L., Koubeissi, M.Z.: Cerebellar and thalamic stimulation treatment for epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 97, 347–356 (2007)
Pollo, C., Villemure, J.G.: Rationale, mechanisms of efficacy, anatomical targets and future prospects of electrical deep brain stimulation for epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 97, 311–320 (2007)
Benabid, A.L.: What the future holds for deep brain stimulation. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 4, 895–903 (2007)
Sunderam, S., Gluckman, B., Reato, D., Bikson, M.: Toward rational design of electrical stimulation strategies for epilepsy control. Epilepsy Behav. 17, 6–22 (2010)
Liu, X., Liu, H.J., Tang, Y.G., Gao, Q.: Fuzzy PID control of epileptiform spikes in a neural mass model. Nonlinear Dyn. 71, 13–23 (2013)
Kalman, R.E.: A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J. Basic Eng. 82, 35–45 (1960)
Wang, H., Han, Z.Z., Zhang, W., Xie, Q.Y.: Chaotic synchronization and secure communication based on descriptor observer. Nonlinear Dyn. 57, 69–73 (2009)
Choi, H.H., Jung, J.W.: Fuzzy speed control with an acceleration observer for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1717–1727 (2012)
Gholami, A., Markazi, A.H.D.: A new adaptive fuzzy sliding mode observer for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 70, 2095–2105 (2012)
Chong, M., Postoyan, R., Nesic, D., Kuhlmann, L., Varsavsky, A.: A robust circle criterion observer with application to neural mass models. Automatica 48, 2986–2989 (2012)
Mariani, S., Ghisi, A.: Unscented Kalman filtering for nonlinear structural dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 49, 131–150 (2007)
Ali, J., Mirza, M.R.U.B.: Performance comparison among some nonlinear filters for a low cost SINS/GPS integrated solution. Nonlinear Dyn. 61(3), 491–502 (2010)
Schiff, S.J., Sauer, T.: Kalman filter control of a model of spatiotemporal cortical dynamics. J. Neural Eng. 5, 1–8 (2008)
Liu, X., Gao, Q.: Parameter estimation and control for a neural mass model based on the unscented Kalman filter. Phys. Rev. E 88(4), 042905 (2013)
Liu, X., Gao, Q., Li, X.L.: Control of epileptiform spikes based on nonlinear unscented Kalman filter. Chin. Phys. B. 23, 010202 (2014)
Ren, H.W., Zhao, Y.D.: A kind of fuzzy adaptive Kalman filter and its application on INS/Doppler integrated navigation. Aerosp. Control 29, 3–6 (2011)
Xu, T.L., You, W.H., Cui, P.Y.: Research on INS/GPS integrated navigation system based on fuzzy adaptive Kalman filters. J. Astronaut. 26, 571–575 (2005)
Jwo, D.J., Yang, C.F., Chuang, C.H., Lee, T.Y.: Performance enhancement for ultra-tight GPS/INS integration using a fuzzy adaptive strong tracking unscented Kalman filter. Nonlinear Dyn. 73, 377–395 (2013)
Jansen, B.H., Rit, V.G.: Electroencephalogram and visual evoked potential generation in a mathematical model of coupled cortical columns. Biol. Cybern. 73, 357–366 (1995)
Ma, Z.X., Liu, Z.Y., Chen, M.: Application of adaptive Kalman filtering based on fuzzy logic to the integrated GPS/INS navigation. Inf. Control 35, 457–461 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61004050, 61273260, 61172095, 51207144), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20101333110006), and the Humanities and Social Sciences Fund, the Ministry of Education Foundation of China (12YJCZH021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Liu, HJ., Tang, YG. et al. Fuzzy adaptive unscented Kalman filter control of epileptiform spikes in a class of neural mass models. Nonlinear Dyn 76, 1291–1299 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1210-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1210-3