Abstract
In this paper, the process by which geometrical and structural matrices of plate finite elements employing absolute nodal coordinate formulation (ANCF) are constructed is studied. The kinematic and topological properties of an arbitrary plate finite element are described using universal digital code dncm that provides systematic enumeration of finite elements. This code is formed using the element’s dimension d, the number of nodes it possesses n, the number of scalar coordinates per node c, and a multiplier describing the process of transforming a conventional finite element to an ANCF element m. The detailed generation of a new type of triangular plate finite element 2343 using numerical computation of shape functions is also discussed in the paper. The new triangular element employs position vectors and slope vectors up to second-order mixed-derivative slope vector. A detailed derivation of the equations of motion of the element is also provided and examples of its numerical simulation and validation presented.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
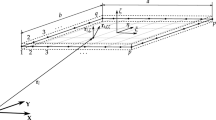
This problem can unambiguously be denoted by text line 0<{−l/2,−b/2:±b/2}[l×b×t,E×ν]{+l/2,±b/2}″(0,0,−P) for the further external references. This line contains all data mentioned above: geometry and material parameters of the plate are given in the square brackets […], application points (or intervals separated by a colon: symbol) for constraints and forces are given in the curly brackets {…} and are measured with respect to the plate’s center. The cantilever condition is denoted by combination 0< meaning attaching to the fixed reference frame indexed 0. The force vector is given in parenthesis ″(…). In the figure, the shortest notation is presented where the extreme points and intervals of the plate are shown just by signs −, +,: and ±, omitting numeric values l/2 and b/2.
A short text description of this problem, [1×2×0.01×1e3,1e5×0.3]{±,±}.g, contains two new elements: the dot symbol . denotes the spherical joints at the four edges denoted by {±,±}, while symbol g introduces the default uniform gravity force.
References
Shabana, A.A.: Definition of the slopes and the finite element absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 1(3), 339–348 (1997)
Berzeri, M., Shabana, A.A.: Development of simple models for the elastic forces in the absolute nodal co-ordinate formulation. J. Sound Vib. 235(4), 539–565 (2000)
Omar, M.A., Shabana, A.: A two-dimensional shear deformation beam for large rotation and deformation. J. Sound Vib. 243(3), 565–576 (2001)
Shabana, A.A., Yakoub, R.Y.: Three dimensional absolute nodal coordinate formulation for beam elements: theory. J. Mech. Des. 123(4), 606–613 (2001)
Von Dombrowski, S.: Analysis of large flexible body deformation in multibody systems using absolute coordinates. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 8(4), 409–432 (2002)
Gerstmayr, J., Matikainen, M.K., Mikkola, A.M.: A geometrically exact beam element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 20, 359–384 (2008)
Schwab, A.L., Meijaard, J.P.: Comparison of three-dimensional flexible beam elements for dynamic analysis: classical finite element formulation and absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 5(1), 10 (2010)
Nachbagauer, K., Gruber, P.G., Vetyukov, Yu., Gerstmayr, J.: A spatial thin beam finite element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation without singularities. In: Proc. of the ASME 2011 Int. Design Eng. Techn. Conf. & Computers and Information in Eng. Conf. IDETC/CIE 201, Washington, DC, USA, 28–31 August, 2011, pp. 28–31 (2011)
Omar, M.A., Shabana, A.A.: A two-dimensional shear deformable beam for large rotation and deformation problems. J. Sound Vib. 243(3), 565–576 (2001)
Sopanen, J.T., Mikkola, A.M.: Description of elastic forces in absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Nonlinear Dyn. 34(1), 53–74 (2003)
Garcia-Vallejo, D., Mikkola, A.M., Escalona, J.L.: A new locking-free shear deformable finite element based on absolute nodal coordinates. Nonlinear Dyn. 50(1–2), 249–264 (2007)
Nachbagauer, K., Pechstein, A., Irschik, H., Gerstmayr, J.: New locking-free formulation for planar, shear deformable, linear and quadratic beam finite elements based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 26(3), 245–263 (2011)
Mikkola, A.M., Shabana, A.A.: A non-incremental finite element procedure for the analysis of large deformation of plates and shells in mechanical system applications. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 9(3), 283–309 (2003)
Mikkola, A.M., Shabana, A.A.: A new plate element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. In: Proc. of ASME 2001 DETC, Pittsburgh (2001)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Pogorelov, D.Yu.: Generalization of plate finite elements for absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 10, 17–43 (2003)
Dufva, K., Shabana, A.: Analysis of thin plate structures using the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Proc., Part K, J. Multi-Body Dyn. 219, 345–355 (2005)
Mikkola, A.M., Matikainen, M.K.: Development of elastic forces for a large deformation plate element based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 1(2), 103–108 (2006)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Mikkola, A.M.: Two simple triangular plate elements based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 3(4), 041012 (2008)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Mikkola, A.M.: Shear correction for thin plate finite elements based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. In: Proc. of ASME 2009 IDETC/CIE 2009, San Diego, California, USA, 2009.08.30–02, pp. 1–9 (2009)
Kubler, L., Eberhard, P., Geisler, J.: Flexible multibody systems with large deformations and nonlinear structural damping using absolute nodal coordinates. Nonlinear Dyn. 34(1–2), 31–52 (2003)
Olshevskiy, A.A., Dmitrochenko, O.N.: Three-dimensional solid elements employing slopes in the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. In: Proc. of the 24th Nordic Seminar on Computational Mechanics, Helsinki, 2011.11.3–4, pp. 162–165 (2011)
Dufva, K., et al.: Nonlinear dynamics of three-dimensional belt drives using the finite-element method. Nonlinear Dyn. 48(4), 449–466 (2007)
Weed, D., Maqueda, L., Brown, M., Hussein, B., Shabana, A.: A new nonlinear multibody/finite element formulation for knee joint ligaments. Nonlinear Dyn. 60(4), 357–367 (2010)
Gantoi, F., Brown, M., Shabana, A.: ANCF finite element/multibody system formulation of the ligament/bone insertion site constraints. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 5(3), 9 (2010)
Wan, H., Dong, H., Ren, Y.: Study of strain energy in deformed insect wings dynamic. Behavior of materials. In: Conf. Proc. of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series, vol. 1, pp. 323–328. Springer, New York (2011)
Shabana, A.A., Hamed, A.M., Mohamed, A.-N.A.: Use of B-spline in the finite element analysis: comparison with ANCF geometry. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 7(1), 011008 (2012)
Sanborn, G., Choi, J., Choi, J.H.: Curve-induced distortion of polynomial space curves, flat-mapped extension modeling, and their impact on ANCF thin-plate finite elements. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 26, 191–211 (2011)
Dibold, M., Gerstmayr, J.: Comparison of planar structural elements for multibody systems with large deformations. Multibody Dyn. Comput. Methods Appl. Sci. 23, 87–105 (2011)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Mikkola, A.A.: A formal procedure and invariants of a transition from conventional finite elements to the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 22(4), 323–339 (2009)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Mikkola, A.A.: Extended digital nomenclature code dncm(dηςμ) for description of complex finite elements and generation of new elements. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 39(2), 229–252 (2011)
Dmitrochenko, O.N., Mikkola, A.A.: Digital nomenclature code for topology and kinematics of finite elements based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. J. Multi-Body Dyn. 225(1), 229–252 (2011)
Melosh, R.J.: Structural analysis of solids. J. Struct. Eng. 4, 205–223 (1963)
Specht, B.: Modified shape functions for the three node plate bending element passing the patch test. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 26, 705–715 (1988)
Bogner, F.K., Fox, R.L., Schmit, L.A.: The generation of interelement-compatible stiffness and mass matrices by the use of interpolation formulae. In: Proc. of 1st Conf. on Matrix Methods in Structural Mechanics, vol. AFFDITR-66-80, pp. 397–443 (1966)
Yoo, W.-S., Lee, J.-H., Park, S.-J., Sohn, J.-H., Pogorelov, D. Yu., Dmitrochenko, O.N.: Large deflection analysis of a thin plate: computer simulations and experiments. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 11(2), 185–208 (2004)
Craig, R., Kurdila, A.: Fundamentals of Structural Dynamics. Wiley, New York (2006)
Dunavant, D.: High degree efficient symmetrical Gaussian quadrature rules for the triangle. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 21(6), 1129–1148 (1985)
Zhang, L., Cui, T., Liu, H.: A set of symmetric quadrature rules on triangles and tetrahedra. J. Comput. Math. 27(l), 89–96 (2009)
Bathe, K.-J.: Finite Element Procedures. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1996)
Gere, J.M., Timoshenko, S.P.: Mechanics of Materials, 4th edn. PWS, Boston (1997)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (2012R1A2A2A04047240 and 2012R1A1A2008870), Russian Foundation for Basic Research (11-01-00500-A), and Defense Acquisition Program Administration and Agency for Defense Development under the contract UD120037CD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olshevskiy, A., Dmitrochenko, O., Lee, S. et al. A triangular plate element 2343 using second-order absolute-nodal-coordinate slopes: numerical computation of shape functions. Nonlinear Dyn 74, 769–781 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1004-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1004-7