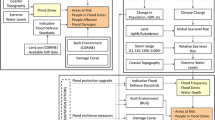
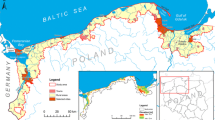
Abstract
This paper presents a methodology for estimating coastal flood and inundation risk using passive modeling in four coastal urban areas in India. The methodology has been developed by identifying the latest and publicly available datasets, open-source software, and easily adaptable methodology to estimate coastal flood risk: Mumbai, Chennai, Kochi, and Thiruvananthapuram. The highest projections of combined SLR, tide and surge levels from the GTSMip dataset was used for each of the study areas to model the flood risk for the period 2023–2027. The method has been successful in generating subsidence forecasts for regions where GNSS measurements are not available, resulting in better modeling of coastal flooding risk. Further, including land use as a dampening effect for flood water reduced the risk of overestimation while using bathtub models. The analysis showed that Mumbai had a significantly higher percentage of vulnerable regions than the other three cities. The method can be considered a first step in realistically estimating the coastal flood risks and providing valuable insights for policymakers.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airbus (2020) Copernicus DEM product handbook. https://spacedata.copernicus.eu/documents/20126/0/GEO1988-CopernicusDEM-SPE-002_ProductHandbook_I3.0.pdf
Anderson TR, Fletcher CH, Barbee MM, Romine BM, Lemmo S, Delevaux JMSMS (2018) Modeling multiple sea level rise stresses reveals up to twice the land at risk compared to strictly passive flooding methods. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32658-x
Bhardwaj A (2022) Accuracy assessment of FABDEM on the different types of topographic regions in india using differential GPS data
Bilbao RAF, Gregory JM, Bouttes N (2015) Analysis of the regional pattern of sea level change due to ocean dynamics and density change for 1993–2099 in observations and CMIP5 AOGCMs. Clim Dyn 45(9):2647–2666. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2499-z
Chen Y, He Y, Zhang L, Chen Y, Pu H, Chen B, Gao L (2021) Prediction of InSAR deformation time-series using a long short-term memory neural network. Int J Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2021.1947540
Christensen JH, Hewitson B, Busuioc A, Chen A, Gao X, Held I, Jones R, Kolli RK, Kwon W-T, Laprise R, Rueda VM, Mearns L, Menéndez CG, Räisänen J, Rinke A, Sarr A, P Whetton (2007) Regional climate projections. In: Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1080/07341510601092191
Ciro Aucelli PP, Di Paola G, Incontri P, Rizzo A, Vilardo G, Benassai G, Buonocore B, Pappone G (2017) Coastal inundation risk assessment due to subsidence and sea level rise in a Mediterranean alluvial plain (Volturno coastal plain—southern Italy). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.06.017
Colberg F, McInnes KL (2012) The impact of future changes in weather patterns on extreme sea levels over southern Australia. J Geophys Res Oceans 117(8):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JC007919
Cook A, Merwade V (2009) Effect of topographic data, geometric configuration and modeling approach on flood inundation mapping. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.015
Coveney S, Fotheringham AS (2011) The impact of DEM data source on prediction of flooding and erosion risk due to sea-level rise. Int J Geogr Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2010.545064
Cui L, Ge Z, Yuan L, Zhang L (2015) Vulnerability assessment of the coastal wetlands in the Yangtze Estuary, China to sea-level rise. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2014.06.015
Dahl K, Spanger-Siegfried E, Caldas A, Udvardy S (2017) Effective inundation of continental United States communities with 21st century sea level rise. Elem Sci Anth 5:37. https://doi.org/10.1525/elementa.234
Dalaison M, Jolivet R (2020) A Kalman filter time series analysis method for InSAR. J Geophys Res Solid Earth. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JB019150
Deng Z, Ke Y, Gong H, Li X, Li Z (2017) Land subsidence prediction in Beijing based on PS-InSAR technique and improved Grey-Markov model. Gisci Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1080/15481603.2017.1331511
Deshpande M, Singh VK, Ganadhi MK, Roxy MK, Emmanuel R, Kumar U (2021) Changing status of tropical cyclones over the north Indian Ocean. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05880-z
Dube SK, Rao AD, Sinha PC, Murty TS, Bahulayan N (1997) Storm surge in the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea: the problem and its prediction. MAUSAM. https://doi.org/10.54302/mausam.v48i2.4012
Dullaart JCM, Muis S, Bloemendaal N, Aerts JCJH (2020) Advancing global storm surge modelling using the new ERA5 climate reanalysis. Clim Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-019-05044-0
Fang Y, Yin J, Wu B (2016) Flooding risk assessment of coastal tourist attractions affected by sea level rise and storm surge: a case study in Zhejiang Province. China Nat Hazards 84(1):611–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2444-4
Farr TG, Rosen PA, Caro E, Crippen R, Duren R, Hensley S, Kobrick M, Paller M, Rodriguez E, Roth L, Seal D, Shaffer S, Shimada J, Umland J, Werner M, Oskin M, Burbank D, Alsdorf DE (2007) The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005RG000183
Fattahi H, Amelung F, Chaussard E, Wdowinski S (2015) Coseismic and postseismic deformation due to the 2007 M5.5 Ghazaband fault earthquake, Balochistan, Pakistan. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL063686
Fitchett JM, Grant B, Hoogendoorn G (2016) Climate change threats to two low-lying South African coastal towns: risks and perceptions. South Afr J Sci. https://doi.org/10.17159/SAJS.2016/20150262
Fraile-Jurado P, Álvarez-Francoso JI, Guisado-Pintado E, Sánchez-Carnero N, Ojeda-Zújar J, Leatherman SP (2017) Mapping inundation probability due to increasing sea level rise along El Puerto de Santa María (SW Spain). Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2782-x
Gesch DB (2018) Best practices for elevation-based assessments of sea-level rise and coastal flooding exposure. Front Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2018.00230
Gourmelen N, Amelung F, Casu F, Manzo M, Lanari R (2007) Mining-related ground deformation in Crescent Valley, Nevada: implications for sparse GPS networks. Geophys Res Lett 6:66. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL029427
Hawker L, Uhe P, Paulo L, Sosa J, Savage J, Sampson C, Neal J (2022) A 30 m global map of elevation with forests and buildings removed. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac4d4f
Hinkel J, Feyen L, Hemer M, Le Cozannet G, Lincke D, Marcos M, Mentaschi L, Merkens JL, de Moel H, Muis S, Nicholls RJ, Vafeidis AT, van de Wal RSW, Vousdoukas MI, Wahl T, Ward PJ, Wolff C (2021) Uncertainty and bias in global to regional scale assessments of current and future coastal flood risk. Earth’s Future. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020EF001882
Hogenson K, Kristenson H, Kennedy J, Johnston A, Rine J, Logan T, Zhu J, Williams F, Herrmann J, Smale J, Meyer F (2020) Hybrid pluggable processing pipeline (HyP3): a cloud-native infrastructure for generic processing of SAR data. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4646138
Hooijer A, Vernimmen R (2021) Global LiDAR land elevation data reveal greatest sea-level rise vulnerability in the tropics. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23810-9
Hooper A, Bekaert D, Spaans K, Arikan M (2012) Recent advances in SAR interferometry time series analysis for measuring crustal deformation. In Tectonophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2011.10.013
Jayanthi M, Thirumurthy S, Samynathan M, Duraisamy M, Muralidhar M, Ashokkumar J, Vijayan KK (2018) Shoreline change and potential sea level rise impacts in a climate hazardous location in southeast coast of India. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6426-0
Jennath A, Paul S (2022) Migration as a response to climate disasters in coastal areas: insights from Kerala, India. In: OCEANS 2022—Chennai, pp 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1109/OCEANSChennai45887.2022.9775396
Kirezci E, Young IR, Ranasinghe R, Muis S, Nicholls RJ, Lincke D, Hinkel J (2020) Projections of global-scale extreme sea levels and resulting episodic coastal flooding over the 21st Century. Sci Rep 10(1):11629. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67736-6
Kulp SA, Strauss BH (2019) New elevation data triple estimates of global vulnerability to sea-level rise and coastal flooding. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12808-z
Kulp S, Strauss BH (2021) A high-accuracy and high-resolution global coastal elevation model trained on ICESat-2satellite lidar
Le Roy S, Stepanian A, Pedreros R, Bulteau T, Nicolae-Lerma A, Balouin Y (2016) Assessing coastal flooding hazard in urban areas: the case of estuarian villages in the city of Hyères-les-Palmiers. In: E3S web of conferences. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20160701010
Li X, Grady CJ, Peterson AT (2014) Delineating sea level rise inundation using a graph traversal algorithm. Mar Geodesy. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490419.2014.902884
Malik A, Abdalla R (2016) Geospatial modeling of the impact of sea level rise on coastal communities: application of Richmond, British Columbia, Canada. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0199-2
Mani Murali R, Dinesh Kumar PK (2015) Implications of sea level rise scenarios on land use/land cover classes of the coastal zones of Cochin, India. J Environ Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2014.06.010
Marfai MA, King L (2008) Potential vulnerability implications of coastal inundation due to sea level rise for the coastal zone of Semarang city, Indonesia. Environ Geol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0906-4
Mcinnes KL, Macadam I, Hubbert G, O’Grady J (2013) An assessment of current and future vulnerability to coastal inundation due to sea-level extremes in Victoria, southeast Australia. Int J Climatol 33(1):33–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3405
Measham TG, Preston BL, Smith TF, Brooke C, Gorddard R, Withycombe G, Morrison C (2011) Adapting to climate change through local municipal planning: Barriers and challenges. Mitig Adapt Strat Glob Change. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-011-9301-2
Mohanty A, Wadhawan S (2021) Mapping India’s climate vulnerability: a district-level assessment
Muis S, Verlaan M, Winsemius HC, Aerts JCJH, Ward PJ (2016) A global reanalysis of storm surges and extreme sea levels. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11969
Muis S, Apecechea MI, Dullaart J, de Lima Rego J, Madsen KS, Su J, Yan K, Verlaan M (2020) A high-resolution global dataset of extreme sea levels, tides, and storm surges, including future projections. Front Marine Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00263
Muis S, Apecechea MI, Álvarez JA, Verlaan M, Yan K, Dullaart J, Aerts J, Duong T, Ranasinghe R, Erikson L, O’Neill A, le Bars D, Haarsma R, Roberts M (2022) Global sea level change time series from 1950 to 2050 derived from reanalysis and high resolution CMIP6 climate projections. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). https://cds-dev.copernicus-climate.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/sis-water-level-change-timeseries-cmip6?tab=overview
Mukherjee P, Ramakrishnan B (2022) On the understanding of very severe cyclone storm Ockhi with the WRF-ARW model. Environ Res Clim. https://doi.org/10.1088/2752-5295/ac6adb
Mulet S, Rio MH, Etienne H, Artana C, Cancet M, Dibarboure G, Feng H, Husson R, Picot N, Provost C, Strub PT (2021) The new CNES-CLS18 global mean dynamic topography. Ocean Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/os-17-789-2021
Murali RM, Riyas MJ, Reshma KN, Kumar SS (2020) Climate change impact and vulnerability assessment of Mumbai city, India. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-019-03766-2
Nicholls RJ, Lincke D, Hinkel J, Brown S, Vafeidis AT, Meyssignac B, Hanson SE, Merkens JL, Fang J (2021) A global analysis of subsidence, relative sea-level change and coastal flood exposure. Nat Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-021-00993-z
Ojha C, Werth S, Shirzaei M (2019) Groundwater loss and aquifer system compaction in San Joaquin Valley during 2012–2015 Drought. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 124(3):3127–3143. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JB016083
Oppenheimer M, Bruce G (2017) Chapter 4: sea level rise and implications for low lying islands, coasts and communities coordinating. In: IPCC SR ocean and cyrosphere
Perini L, Calabrese L, Salerno G, Ciavola P, Armaroli C (2016) Evaluation of coastal vulnerability to flooding: Comparison of two different methodologies adopted by the Emilia-Romagna region (Italy). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-16-181-2016
Pramanik MK, Dash P, Behal D (2021) Improving outcomes for socioeconomic variables with coastal vulnerability index under significant sea-level rise: an approach from Mumbai coasts. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01239-w
Ramakrishnan R, Remya PG, Mandal A, Mohanty P, Arayakandy P, Mahendra RS, Nair TMB (2022) Wave induced coastal flooding along the southwest coast of India during tropical cyclone Tauktae. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-24557-z
Ranger N, Hallegatte S, Bhattacharya S, Bachu M, Priya S, Dhore K, Rafique F, Mathur P, Naville N, Henriet F, Herweijer C, Pohit S, Corfee-Morlot J (2011) An assessment of the potential impact of climate change on flood risk in Mumbai. Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-010-9979-2
Rao AD, Upadhaya P, Ali H, Pandey S, Warrier V (2020) Coastal inundation due to tropical cyclones along the east coast of India: an influence of climate change impact. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-03861-9
Ravichandran P, Kripa V, Padua S, Mohamed K, Narayanakumar R, Prof PON (2021) Socio-economic impact of cyclone Ockhi on fishers along the Kerala and Tamil Nadu coasts, India. J Mar Biol Assoc India 63:90–96. https://doi.org/10.6024/jmbai.2021.63.1.2161-14
Schuerch M, Spencer T, Temmerman S, Kirwan ML, Wolff C, Lincke D, McOwen CJ, Pickering MD, Reef R, Vafeidis AT, Hinkel J, Nicholls RJ, Brown S (2018) Future response of global coastal wetlands to sea-level rise. Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0476-5
Simav Ö, Şeker DZ, Gazioǧlu C (2013) Coastal inundation due to sea level rise and extreme sea state and its potential impacts: Çukurova Delta case. Turk J Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.3906/yer-1205-3
Sobel AH, Lee CY, Camargo SJ, Mandli KT, Emanuel KA, Mukhopadhyay P, Mahakur M (2019) Tropical cyclone hazard to mumbai in the recent historical climate. Mon Weather Rev. https://doi.org/10.1175/MWR-D-18-0419.1
Spencer T, Schuerch M, Nicholls RJ, Hinkel J, Lincke D, Vafeidis AT, Reef R, McFadden L, Brown S (2016) Global coastal wetland change under sea-level rise and related stresses: the DIVA Wetland Change Model. Global Planet Change. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.12.018
Swathy Krishna PS, Aboobacker VM, Ramesh M, Sheela Nair L (2023) Remotely induced storm effects on the coastal flooding along the southwest coast of India. Oceanologia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceano.2023.03.003
Sweet WV, Park J (2014) From the extreme to the mean: acceleration and tipping points of coastal inundation from sea level rise. Earth’s Future. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014ef000272
Talchabhadel R, Nakagawa H, Kawaike K, Yamanoi K, Thapa BR (2021) Assessment of vertical accuracy of open source 30m resolution space-borne digital elevation models. Geomat Nat Haz Risk. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2021.1910575
Vernimmen R, Hooijer A (2023) New LiDAR-based elevation model shows greatest increase in global coastal exposure to flooding to be caused by early-stage sea-level rise. Earth’s Future. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022EF002880
Vousdoukas MI, Mentaschi L, Voukouvalas E, Verlaan M, Jevrejeva S, Jackson LP, Feyen L (2018) Global probabilistic projections of extreme sea levels show intensification of coastal flood hazard. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04692-w
Vousdoukas MI, Ranasinghe R, Mentaschi L, Plomaritis TA, Athanasiou P, Luijendijk A, Feyen L (2020) Sandy coastlines under threat of erosion. Nat Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-020-0697-0
Wang J, Gao W, Xu S, Yu L (2012) Evaluation of the combined risk of sea level rise, land subsidence, and storm surges on the coastal areas of Shanghai, China. Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-012-0468-7
Ward PJ, Marfai MA, Yulianto F, Hizbaron DR, Aerts JCJH (2011) Coastal inundation and damage exposure estimation: a case study for Jakarta. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9599-1
Williams LL, Lück-Vogel M (2020) Comparative assessment of the GIS based bathtub model and an enhanced bathtub model for coastal inundation. J Coast Conserv. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-020-00735-x
Woodruff JL, Dietrich JC, Wirasaet D, Kennedy AB, Bolster D, Silver Z, Medlin SD, Kolar RL (2021) Subgrid corrections in finite-element modeling of storm-driven coastal flooding. Ocean Model. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2021.101887
Wright MN, Ziegler A (2017) ranger: A Fast Implementation of Random Forests for High Dimensional Data in C++ and R. J Stat Softw 77(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v077.i01
Wu P-C, Wei M, D’Hondt S (2022) Subsidence in coastal cities throughout the world observed by InSAR. Geophys Res Lett 49(7): e2022GL098477. https://doi.org/10.1029/2022GL098477
Yan B, Li S, Wang J, Ge Z, Zhang L (2016a) Socio-economic vulnerability of the megacity of Shanghai (China) to sea-level rise and associated storm surges. Reg Environ Change. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-015-0878-y
Yan B, Wang J, Li S, Cui L, Ge Z, Zhang L (2016b) Assessment of socio-economic vulnerability under sea level rise coupled with storm surge in the Chongming County, Shanghai. Acta Ecol Sin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2016.01.006
Zhang Z, Zhang S, Hu C, Zhang X, Yang S, Yan H, Zhang Z (2023) Hazard assessment model of ground subsidence coupling AHP, RS and GIS—a case study of Shanghai. Gondwana Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2023.01.014
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Athira Krishnan, Scientist at CSIR National Institute of Oceanography Goa, for her assistance during this study.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jennath, A., Paul, S. A multi-risk approach for projecting climate change-associated coastal flood, applied to India. Nat Hazards 120, 4581–4600 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06420-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06420-8