Abstract
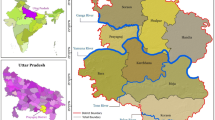
The present study attempts to identify the flood footprint of river Keleghai, a tributary of river Haldi, in West Bengal, India. Keleghai basin is known for recurrent flooding that causes severe damage to the socioeconomic infrastructure. So far, no attempt has been made for the identification of flood inundation footprints and flood risk zones in Keleghai river basin through remote sensing and multi-criteria decision-making process. Initially, a flood susceptibility or vulnerability map has been prepared, and secondly, flood footprints have been identified in the said river basin. For the preparation of flood vulnerability map with the help of the analytical hierarchy process (AHP), the elevation, slope, rainfall, normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI), land use and land cover (LULC) and distance from river and topographical wetness index (TWI) of the concerned river basin have been used. To prepare the flood footprints synthetic aperture radar (SAR), data have been processed on Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. The result shows that more than 50% of the basin area belongs to high risk zone, and the other 40% comes under the moderate risk category. The central, northern and eastern parts of the basin present the highest susceptibility to flood hazard. This area is characterised by moderate-to-low elevation, gentle slope, moderate rainfall and less vegetative cover. This outcome can effectively be utilised in hazard management purpose for Keleghai as well as other river basins. This study will help in identifying the most vulnerable zones of the basin in terms of flood hazard assessment. On the other hand, correlating the empirical model with the real world data will provide excellent opportunity to testify the applicability of the model in decision-making purpose that could lead to a way of resilience.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya N, Maiti S, Bandyopadhyay J (2010) Modeling flood of Pataspur-I block, in Purba Medinipur, West Bengal. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Nirupam-Acharyya/publication/325012699_MODELING_FLOOD_OF_PATASPUR-I_BLOCK_IN_PURBA_MEDINIPUR_WEST_BENGAL/links/5af17d6ea6fdcc24364b1531/MODELING-FLOOD-OF-PATASPUR-I-BLOCK-IN-PURBA-MEDINIPUR-WEST-BENGAL.pdf
Aksha SK, Resler LM, Juran L, Carstensen LW (2020) A geospatial analysis of multi-hazard risk in Dharan, Nepal. Geomat Nat Hazards Risk 11(1):88–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2019.1710580
Ali H, Mishra V (2018) Increase in subdaily precipitation extremes in India under 1.5 and 2.0 °C Warming Worlds. Geophys Res Lett 45(14):6972–6982. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078689
Aruldoss M, Lakshmi TM, Venkatesan VP (2013) A survey on multi criteria decision making methods and its applications. Am J Inf Syst. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajis-1-1-5
Bates B, Kundzewicz ZW, IPCC (eds) (2008) Climate change and water
Bathrellos GD, Gaki-Papanastassiou K, Skilodimou HD, Skianis GA, Chousianitis KG (2013) Assessment of rural community and agricultural development using geomorphological–geological factors and GIS in the Trikala prefecture (Central Greece). Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 27(2):573–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0602-0
Bathrellos GD, Karymbalis E, Skilodimou HD, Gaki-Papanastassiou K, Baltas EA (2016) Urban flood hazard assessment in the basin of Athens Metropolitan city. Greece Environ Earth Sci 75(4):319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5157-1
Bathrellos G, Skilodimou H, Soukis K, Koskeridou E (2018) Temporal and spatial analysis of flood occurrences in the drainage Basin of Pinios River (Thessaly, Central Greece). Land 7(3):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7030106
Beven KJ, Kirkby MJ (1979) A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology / Un modèle à base physique de zone d’appel variable de l’hydrologie du bassin versant. Hydrol Sci Bull 24(1):43–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667909491834
Brakenridge GR, Syvitski JPM, Overeem I, Higgins SA, Kettner AJ, Stewart-Moore JA, Westerhoff R (2013) Global mapping of storm surges and the assessment of coastal vulnerability. Nat Hazards 66(3):1295–1312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0317-z
Cerdà A (1998) Effect of climate on surface flow along a climatological gradient in Israel: a field rainfall simulation approach. J Arid Environ 38(2):145–159. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.1997.0342
Change, I. P. on C (2012) Managing the risks of extreme events and disasters to advance climate change adaptation: special report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press
Coumou D, Rahmstorf S (2012) A decade of weather extremes. Nat Clim Chang 2(7):491–496. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1452
Cutter SL, Emrich CT, Webb JJ, Morath D (2009) Social vulnerability to climate variability hazards: a review of the literature. Final Rep Oxfam Am 5:1–44
David CH, Frasson RPDM (2023) Blame the river not the rain. Nat Geosci 16(4):282–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-023-01163-w
Dwivedi RS, Sreenivas K (2002) The vegetation and waterlogging dynamics as derived from spaceborne multispectral and multitemporal data. Int J Remote Sens 23(14):2729–2740. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110076234
Fernández DS, Lutz MA (2010) Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol 111(1–4):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.12.006
Fowler HJ, Cooley D, Sain SR, Thurston M (2010) Detecting change in UK extreme precipitation using results from the climateprediction.net BBC climate change experiment. Extremes 13(2):241–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10687-010-0101-y
GIS & RS Solution (Director) (2022) Flood susceptibility mapping using GIS-AHP multi‐criteria analysis. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Lbbyi1YV2Hc
Hailin Z, Yi J, Xuesong Z, Gaoliao J, Yi Y, Baoyin H (2009) GIS-based risk assessment for regional flood disaster. In: 2009 International conference on environmental science and information application technology, 564–567. https://doi.org/10.1109/ESIAT.2009.279
Hammond MJ, Chen AS, Djordjević S, Butler D, Mark O (2015) Urban flood impact assessment: a state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J 12(1):14–29. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2013.857421
Huang D, Liu C, Fang H, Peng S (2008) Assessment of waterlogging risk in Lixiahe region of Jiangsu province based on AVHRR and MODIS image. Chin Geogra Sci 18(2):178–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-008-0178-2
Jackson RD, Huete AR (1991) Interpreting vegetation indices. Prev Vet Med 11(3–4):185–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-5877(05)80004-2
Kaiser MF, El Rayes A, Ghodeif K, Geriesh B (2013) GIS data integration to manage waterlogging problem on the eastern Nile delta of Egypt. Int J Geosci 04(04):680–687. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijg.2013.44063
Karymbalis E, Katsafados P, Chalkias C, Gaki-Papanastassiou K (2012) An integrated study for the evaluation of natural and anthropogenic causes of flooding in small catchments based on geomorphological and meteorological data and modeling techniques: The case of the Xerias torrent (Corinth, Greece). Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie Supplement 56:45–67. https://doi.org/10.1127/0372-8854/2012/S-00072
Kienberger S (2012) Spatial modelling of social and economic vulnerability to floods at the district level in Búzi. Mozambique Natural Hazards 64(3):2001–2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0174-9
Kundzewicz ZW, Kanae S, Seneviratne SI, Handmer J, Nicholls N, Peduzzi P, Mechler R, Bouwer LM, Arnell N, Mach K, Muir-Wood R, Brakenridge GR, Kron W, Benito G, Honda Y, Takahashi K, Sherstyukov B (2014) Flood risk and climate change: global and regional perspectives. Hydrol Sci J 59(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.857411
Masuya A (2014) Flood Vulnerability and Risk Assessment with Spatial Multi-criteria Evaluation. In Dewan A, Corner R (eds), Dhaka Megacity, pp 177–202. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-6735-5_10
Merwade V, Cook A, Coonrod J (2008) GIS techniques for creating river terrain models for hydrodynamic modeling and flood inundation mapping. Environ Model Softw 23(10–11):1300–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2008.03.005
Milly PCD, Wetherald RT, Dunne KA, Delworth TL (2002) Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature 415(6871):514–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/415514a
Mondal M, Haldar S, Biswas A, Mandal S, Bhattacharya S, Paul S (2021a) Modeling cyclone-induced multi-hazard risk assessment using analytical hierarchical processing and GIS for coastal West Bengal, India. Regional Stud Marine Sci 44:101779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101779
Mondal M, Haldar S, Biswas A, Mandal S, Bhattacharya S, Paul S (2021b) Modelling cyclone-induced multi-hazard risk assessment using analytical hierarchical processing and GIS for coastal West Bengal, India. Reg Stud Mar Sci 44:101779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2021.101779
Mukherjee S (1985) Floods in West Bengal: a spatial and temporal analysis. In Geographical mosaic pp 262–271. Modern Book Agency
NASA (2022) Data | NASA Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. https://gpm.nasa.gov/data
Pandey AC, Singh SK, Nathawat MS (2010) Waterlogging and flood hazards vulnerability and risk assessment in Indo Gangetic plain. Nat Hazards 55(2):273–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9525-6
Rentschller J, Salhab M, Jafino BA (2022) Flood risk already affects 1.81 billion people. Climate change and unplanned urbanization could worsen exposure. World Bank Blogs. https://blogs.worldbank.org/climatechange/flood-risk-already-affects-181-billion-people-climate-change-and-unplanned
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Saaty TL (2004) Decision making—the analytic hierarchy and network processes (AHP/ANP). J Syst Sci Syst Eng 13(1):1–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11518-006-0151-5
Sahu AS (2014) A study on Moyna basin water-logged areas (India) using remote sensing and GIS methods and their contemporary economic significance. Geography J 2014:401324. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/401324
Sar N, Chatterjee S, Das Adhikari M (2015) Integrated remote sensing and GIS based spatial modelling through analytical hierarchy process (AHP) for water logging hazard, vulnerability and risk assessment in Keleghai river basin, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 1(4):31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0039-9
Skilodimou HD, Bathrellos GD, Chousianitis K, Youssef AM, Pradhan B (2019) Multi-hazard assessment modeling via multi-criteria analysis and GIS: a case study. Environ Earth Sci 78(2):47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-8003-4
Skilodimou HD, Bathrellos GD, Alexakis DE (2021) Flood hazard assessment mapping in burned and urban areas. Sustainability 13(8):4455. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084455
Stefanidis S, Stathis D (2013) Assessment of flood hazard based on natural and anthropogenic factors using analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Nat Hazards 68(2):569–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0639-5
Suriya S, Mudgal BV (2012) Impact of urbanization on flooding: the Thirusoolam sub watershed—A case study. J Hydrol 412–413:210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.008
Tarasova L, Lun D, Merz R, Blöschl G, Basso S, Bertola M, Miniussi A, Rakovec O, Samaniego L, Thober S, Kumar R (2023) Shifts in flood generation processes exacerbate regional flood anomalies in Europe. Commun Earth Environ 4(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-023-00714-8
Tucker CJ (1979) Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens Environ 8(2):127–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(79)90013-0
United Nations (2015) Goal 13 | Department of Economic and Social Affairs. https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal13
USGS (2018) NDVI, the Foundation for Remote Sensing Phenology | U.S. Geological Survey. USGS Science for Changing World. https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/remote-sensing-phenology/science/ndvi-foundation-remote-sensing-phenology
Wang Y, Li Z, Tang Z, Zeng G (2011) A GIS-based spatial multi-criteria approach for flood risk assessment in the Dongting lake region, Hunan, Central China. Water Resour Manag 25(13):3465–3484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-011-9866-2
Whitaker R (2007) Validation examples of the analytic hierarchy process and analytic network process. Math Comput Model 46(7–8):840–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2007.03.018
Youssef AM, Abu-Abdullah MM, AlFadail EA, Skilodimou HD, Bathrellos GD (2021) The devastating flood in the arid region a consequence of rainfall and dam failure: case study, Al-Lith flood on 23th November 2018, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Z Geomorphol 63(1):115–136. https://doi.org/10.1127/zfg/2021/0672
Zhang H, Zhang J, Han J (2009) The assessment and regionalization of flood/waterlogging disaster risk in middle and lower reaches of Liao river of northeast China. 103–118. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=0ba55fe72b7a2d5c8fa732e47526169a4cdf341f
Τsolaki-Fiaka S, Bathrellos G, Skilodimou H (2018) Multi-criteria decision analysis for an abandoned quarry in the evros region (NE Greece). Land 7(2):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7020043
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, A., Dhar, S.B. Assessment of flood vulnerability and identification of flood footprint in Keleghai River basin in India: a geo-spatial approach. Nat Hazards 120, 4853–4874 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06411-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-024-06411-9