Abstract
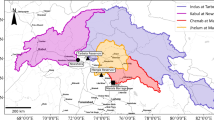
Runoff generation potential (RGP) on hillslopes is an important issue in the forest roads network monitoring process. In this study, an artificial neural network (ANN) was used to predict RGP in forest road hillslopes. We trained, optimized, and tested the ANN by using field plot data from the Shirghalaye watershed located in the southern part of the Caspian Sea in Iran. Field plots were used to evaluate the effective factors in runoff generation, 45 plots were installed to measure actual runoff volume (RFP) in different environmental conditions including land cover, slope gradient, soil texture, and soil moisture. A multi-layer perceptron (MLP) network was implemented. The runoff volume was the output variable and the ground cover, slope gradient, initial moisture of soil, soil texture (clay, silt and sand percentage) were the network inputs. The results showed that ANN can predict runoff volume within the values of an appropriate level in the training (R2 = 0.95, mean squared error (MSE) = 0.009) and test stages (R2 = 0.80, MSE = 0.01). Moreover, the tested network was used to predict the runoff volume on the forest road hillslopes in the study area. Finally, an RGP map was generated based on the results of the prediction of the ANNs and the geographic information system (GIS) capabilities. The results showed the RGP in the forest road hillslopes was better predicted when using both an ANN and a GIS. This study provides new insights into the potential use of ANN in hydrological simulations.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials as well as software application or custom code support our published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Abrahart RJ, Mount NJ, Shamseldin AY (2012) Neuroemulation: definition and key benefits for water resources research. Hydrol Sci J 57(407–423):10. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.658401
Afzaal H, Farooque AA, Abbas F, Acharya B, Esau T (2020) Groundwater estimation from major physical hydrology components using artificial neural networks and deep learning. Water 12:5. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010005
Akay AE, Erdas O, Reis M, Yuksel A (2008) Estimating sediment yield from a forest road network by using a sediment prediction model and GIS techniques. Build Environ 43:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2007.01.047
Al-Chokhachy R, Blac TA, Thomas C, Luce CH, Rieman B, Cissel R, Kershner JL (2016) Linkages between unpaved forest roads and streambed sediment: why context matters in directing road restoration. Restor Ecol 24:589–598. https://doi.org/10.1111/rec.12365
Aldrich GA, Tanaka JA, Adams RM, Buckhouse JC (2005) Economics of western juniper control in central Oregon. Rangel Ecol Manag 58:542–552. https://doi.org/10.2111/04-164R2.1
Brodowski R, Rejman J (2004) Effect of soil moisture content and surface conditions on runoff and wash on loamy sand. Acta Agroph 4:619–624
Cattan P, Ruy SM, Cabidoche YM, Findeling A, Desbois P, Charlier JB (2009) Effect on runoff of rainfall redistribution by the impluvium-shaped canopy of banana cultivated on an andosol with a high infiltration rate. J Hydrol 368:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.02.020
Choong CE, Ibrahim S, El-Shafie A (2020) Artificial neural network (ANN) model development for predicting just suspension speed in solid-liquid mixing system. Flow Meas Instrumen 71:101689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2019.101689
Dalir P, Naghdi R, Gholami V (2014) Modelling of forest road sediment in the northern forest of Iran (Lomir Watershed). J Forest Sci 60:109–114. https://doi.org/10.17221/91/2013-JFS
Dalir P, Naghdi R, Gholami V (2021) Assessing the rice straw effects on the soil erosion rate in forest road cut slope embankments. Casp J Environ Sci 19:325–339
De Ona J, Osorio F, Garcia PA (2009) Assessing the effects of using compost–sludge mixtures to reduce erosion in road embankments. J Hazard Mater 164:1257–1265
Dixon B (2004) Prediction of groundwater vulnerability using an integrated GIS-based neuro-fuzy techniques. J Spa Hydrol 14:1–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.11.010
Essig ET, Corradini C, Morbidelli R, Govindaraju RS (2009) Infiltration and deep flow over sloping surfaces: comparison of numerical and experimental results. J Hydrol 374(1–2):30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.05.017
Foster GR (2001) Keynote: soil erosion prediction technology for conservation planning. 847–51Stott DE, Mohtar RH, Steinhartdt GC (1999) Proceedings of the sustaining the global farm, selected papers from the 10th international soil conservation organization meeting. purdue university and the USDA-ARS national soil erosion research laboratory, 24–29.
Fotovatikhah F, Herrera M, Shamshirband S, Chau KW, Faizollahzadeh Ardabili S, Piran MJ (2018) Survey of computational intelligence as basis to big flood management: challenges, research directions and future work. Eng App Comput Flu Mec 12:411–437. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1448896
Fox DM, Bryan RB, Price AG (1997) The influence of slope angle on final infiltration rate for in Terrill conditions. Geoderma 80:181–194
Fu M, Fan T, Ding ZA, Salih SQ, Al-Ansari N, Yaseen ZM (2020) Deep learning data-intelligence model based on adjusted forecasting window scale: application in daily streamflow simulation. IEEE Access 24(8):32632–32651. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974406
Gholami G, Khaleghi MR (2013) The impact of vegetation on the bank erosion (case study: the Haraz river). J Soil Water Res 8:158–164. https://doi.org/10.17221/13/2012-SWR
Gholami V, Khaleghi MR, Sebghati MR (2016) A method of groundwater quality assessment based on fuzzy network-CANFIS and geographic information system (GIS). Appl Water Sci 7:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0508-y
Gholami V, Torkaman J, Dalir P (2019) Simulation of precipitation time series using tree-rings, earlywood vessel features, and artificial neural network. Theor Appl Climatol 137:1939–1948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2702-3
He Z, Wen X, Liu H, Du J (2014) A comparative study of artificial neural network, adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system and support vector machine for forecasting river flow in the semiarid mountain region. J Hydrol 509:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.054
Hu C, Wu Q, Li H, Jian S, Li N, Lou Z (2018) Deep learning with a long short-term memory networks approach for rainfall-runoff simulation. Water 10(11):1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111543
Iroumé A, Jones J, Bathurst JC (2021) Forest operations tree species composition and decline in rainfall explain runoff changes in the nacimiento experimental catchments south central chile. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14257
Isik S, Kalin L, Schoonover J, Srivastava P, Lockaby BG (2013) Modeling effects of changing land use/cover on daily stream flow: An artificial neural network and curve number based hybrid approach. J Hydrol 45:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.08.032
Jury WJ, Horton R (2004) Soil physics, 6th edn, ISBN: 978-0-471-05965-3.384
Kalra YP, Maynard DG (1991) Methods manual for forest soil and plant analysis Vol. 319.
Keim RF, Skaugset AE, Weiler M (2006) Storage of water on vegetation under simulated rainfall of varying intensity. Adv Water Resour 29:974–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.07.017
Kira C, Puntenney-Desmond Kevin D, Bladon US (2020) Runoff and sediment production from harvested hillslopes and the riparian area during high intensity rainfall events. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124452
Las Heras MM, Nicolau JM, Martín LM, Bradford P, Wilcox BW (2010) Plot-scale effects on runoff and erosion along a slope degradation gradient. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009WR007875
Li E, Mu X, Zhao G, Gao P, Sun W (2017) Effects of check dams on runoff and sediment load in a semi-arid river basin of the Yellow River. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 31:1791–1803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1333-4
Mao G, Wang M, Liu J, Wang Z, Wang K, Meng Y, Zhong R, Wang H, Li Y (2021) Comprehensive comparison of artificial neural networks and long short-term memory networks for rainfall-runoff simulation. Phys Chem Earth 123:103026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2021.103026
Martınez-Casasnovas JA (1998) Soil-landscape-erosion. Gully erosion in the Alt Penedes–Anoia (Catalonia, Spain). A spatial information technology approach: spatial databases, GIS and remote sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lleida, Lleida, 333p
Martínez-Zavala L, López AJ, Bellinfante N (2008) Seasonal variability of runoff and soil loss on forest road backslopes under simulated rainfall. CATENA 74:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2008.03.006
Meyer VD, Hefter J, Köhler P, Tiedemann R, Gersonde R, Wacker L, Mollenhauer G (2019) Permafrost-carbon mobilization in Beringia caused by deglacial meltwater runoff sea-level rise and warming. Environ Res Lett 14:085003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326
Mitra S, Nigam R (2021) An approach to utilize artificial neural network for runoff prediction: River perspective. Proc, Mater Today. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.198
Mosavi A, Ozturk P, Chau KW (2018) Flood prediction using machine learning models: literature review. Water 10:1536. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111536
Naghdi R, Dalir P, Gholami V, Pourghasemi HR (2017) Modeling of sediment generation from forest roads employing SEDMODL and its calibration for Hyrcanian forests in northern Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76(4):2–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6758-7
Nasiri M, Lotfalian M, Modarres A, Wu W (2017) Use of rice husk ash as a stabilizer to reduce soil loss and runoff rates on sub-base materials of forest roads from rainfall simulation tests. CATENA 150:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.010
Nayebi M, Khalili D, Amin S, Zand-Parsa SH (2006) Daily stream flow prediction capability of artificial neural networks as influenced by minimum air temperature data. Biosyst Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2006.08.012
Nilsson P, Uvo CB, Berndtsson R (2006) Monthly runoff simulation: Comparing and combining conceptual and neural network models. J Hydrol 321:344–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2005.08.007
Pastor M, Castro J (1995) Soil management systems and erosion. Olivae 59:64–74
Picchio R, Latterini F, Mederski PS, Venanzi R, Karaszewski Z, Bembenek M, Croce M (2019) Comparing accuracy of three methods based on the GIS environment for determining winching areas. Electronics 8:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8010053
Picchio R, Jourgholami M, Zenner EK (2021) Effects of forest harvesting on water and sediment yields: a review toward better mitigation and rehabilitation strategies. Curr Forestry Rep 7:214–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40725-021-00146-7
Pickup G, Marks A (2000) Identifying large-scale erosion and deposition processes fromairbone gamma radiometrics and digital elevation models in a weathered landscape. Earth Surf Proc Land 25:535–557
Pierson FB, Batees JD, Svejcar TJ, Hardegree SP (2007) Runoff and erosion after cutting western juniper. Rangeland Ecol Manage 60:285–292. https://doi.org/10.2111/1551-5028
Poesen JWA, Hooke JM (1997) Erosion, flooding and channel management in the Mediterranean environments of southern Europe. Prog Phys Geogr 21:157–199. https://doi.org/10.1177/030913339702100201
Puntenney-Desmond KC, Bladon KD, Silins U (2020) Runoff and sediment production from harvested hillslopes and the riparian area during high intensity rainfall events. J Hydrol 582:124452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124452
Riad S, Mania J, Bouchaou L, Najjar Y (2004) Rainfall-runoff model usingan artificial neural network approach. Math Comput Modell 40:839–846
Sahour H, Gholami V, Vazifedan M, Saeedi M (2021) Machine learning applications for water-induced soil erosion modeling and mapping. Soil Tillage Res 211:105032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105032
Sharafati A, Pezeshki E (2020) A strategy to assess the uncertainty of a climate change impact on extreme hydrological events in the semi-arid Dehbar catchment in Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 139:389–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-02979-6
Stieglitz M, Shaman J, McNamara J, Engel V, Shanley J, Kling GW (2003) An approach to understanding hydrologic connectivity on the hillslope and the implications for nutrient transport. Glob Biogeochem. Cycles 17:1105. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003GB002041
Sun J, Yu X, Li H, Yu Ch, Wang H, Tu Z, Liang H (2016) Simulated erosion using soils from vegetated slopes in the Jiufeng Mountains. China Catena 136(3):128–134. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13233453
Surfleet CG, Marks SJ (2021) Hydrologic and suspended sediment effects of forest roads using field and DHSVM modelling studies. For Ecol Manage 1(499):119632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119632
Taormina R, Chau KW (2015) ANN-based interval forecasting of streamflow discharges using the LUBE method and MOFIPS. Eng Appl Artif Intell 45:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2015.07.019
Tokar AS, Johnson PA (1999) Rainfall-runoff modeling using artificial neural networks. J Hydrol. Engng ASCE 4:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(1999)
Uson A (1998) Medidas de control de la erosion en suelos de vina de lascomarcasAnoia- AltPenedes(Barcelona): efectividad y viabilidad. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Lleida, Lleida
Wagenbrenner JW, Ebel BA, Bladon KD, Kinoshita AM (2021) Post-wildfire hydrologic recovery in Mediterranean climates: A systematic review and case study to identify current knowledge and opportunities. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126772
Wang B, Zheng F, Römkens MJ, Darboux F (2013) Soil erodibility for water erosion: a perspective and Chinese experiences. Geomorphology 187:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.01.018
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B, Huang Z, Wu D, Gui L (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area. China J Hydrol 335:247–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.11.016
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses: a guide to conservation planning Agric Handbook No 282. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC
Wu S M, Patil P, Gunaseelan S (2018) Comparison of different machine learning algorithms for multiple regression on black friday sales data. In: 2018 IEEE 9th international conference on software engineering and service science (ICSESS). IEEE, pp 16–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSESS.2018.8663760
Wischmeier WH, Smith D (1958) Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss. Trans-Am Geophys Union 39:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR039i002p00285
Wu CL, Chau KW (2011) Rainfall–runoff modeling using artificial neural network coupled with singular spectrum analysis. J Hydrol 399:394–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.01.017
Wu CL, Chau KW (2013) Prediction of rainfall time series using modular soft computingmethods. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26:997–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2012.05.023
Wu J, Zheng Y, Wen X, Lin Q, Chen X, Wu Z (2014) Silver nanoparticle/bacterial cellulose gel membranes for antibacterial wound dressing: investigation in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Mater 9:035005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/9/3/035005
Zhang Q, Wang X, Hou P, Wan W, Ren Y, Ouyang Z, Yang L (2013) The temporal changes in road stormwater runoff quality and the implications to first flush control in Chongqing, China. Environ Monit Assess 185:9763–9775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3289
Zhao Z, Chow TL, Rees HW, Yang Q, Xing Z, Meng FR (2009) Predict soil texture distributions using an artificial neural network model. Comput Electron Agri 65:36–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2008.07.008
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among authors.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors consent to participate in this manuscript.
Consent to publish
All authors consent to publish this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalir, P., Naghdi, R., Gholami, V. et al. Risk assessment of runoff generation using an artificial neural network and field plots in road and forest land areas. Nat Hazards 113, 1451–1469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05352-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05352-5