Abstract
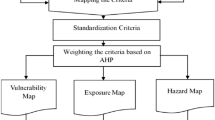
Flooding is a major and recurring natural disaster in Northeast Penang, Malaysia. The ability to effectively identify flood hazard areas represents an important part of flood risk analysis and management. There is a need for a structured study that incorporates stakeholders’ inputs such as the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) model to delineate flood-prone locations to support the management and mitigation measures of flooding in this area. Previous studies have compared the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and fuzzy AHP methods in flood hazard mapping. Therefore, this study proposes to test the predicting capability of three MCDM models in the determination of flood-prone areas: the AHP, triangular fuzzy AHP (TF-AHP), and trapezoidal fuzzy AHP (TZF-AHP) in this area. The methodology applies nine flood-causative factors (FCFs) which include drainage density, elevation, land use, slope, rainfall, flood depth, distance from rivers, lithology, and distance from inundation. The resulting flood hazard maps showed a closer similarity between the TF-AHP and TZ-AHP methods compared to the AHP method for flood hazard mapping. The sensitivity analysis indicated that the AHP was more accurate than the fuzzy AHP models based on the weight estimation. The validation results showed that 100%, 93%, and 93% of the actual flood events occurred in the ‘moderate’ to ‘very high’ flood hazard areas for the AHP, TF-AHP, and TZF-AHP, respectively. Overall results showed the accuracy of all three models in modeling flood hazard areas. Therefore, the findings can be adopted as a tool in making informed and accurate policies about flood management for effective climate mitigation decision making.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhafid EAEF, Alaa N, Bachnou A, Rachidi S (2018) Flood frequency analysis and generation of flood hazard indicator maps in a semi-arid environment, case of Ourika watershed (western High Atlas, Morocco). J African Earth Sci 141:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.02.004
Abdullah L, Najib L (2014) A new type-2 fuzzy set of linguistic variables for the fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. Expert Syst Appl 41:3297–3305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.11.028
Arabameri A, Rezaei K, Cerdà A, Conoscenti C, Kalantari Z (2019) A comparison of statistical methods and multi-criteria decision making to map flood hazard susceptibility in Northern Iran. Sci Total Environ 660:443–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.021
Buckley JJ (1985) Fuzzy hierarchical analysis. Fuzzy Sets Syst 17:233–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(85)90090-9
Bui DT, Khosravi K, Shahabi H, Daggupati P, Adamowski JF, Melesse AM, PhamPourghasemi BTHR, MahmoudiBahramiPradhanShirzadiChapiLee MSBAKS (2019) Flood spatial modeling in Northern Iran using remote sensing and GIS: a comparison between evidential belief functions and its ensemble with a multivariate logistic regression model. Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11131589
Cahyadi TA, Widodo LE, Syihab Z, Notosiswoyo S, Widijanto E (2017) Hydraulic conductivity modeling of fractured rock at grasberg surface mine. Papua-Indonesia J Eng Technol Sci 49:37–57. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2017.49.1.3
Chan HK, Sun X, Chung SH (2019) When should fuzzy analytic hierarchy process be used instead of analytic hierarchy process? Decis Support Syst 125:113114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2019.113114
Chen YR, Yeh CH, Yu B (2011) Integrated application of the analytic hierarchy process and the geographic information system for flood risk assessment and flood plain management in Taiwan. Nat Hazards 59:1261–1276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-9831-7
Chen-Tung C (2002) A decision model for information system project selection. IEEE Int Eng Manag Conf 2:585–589. https://doi.org/10.1109/iemc.2002.1038501
Chen-Tung C, Lin CT, Huang SF (2006) A fuzzy approach for supplier evaluation and selection in supply chain management. Int J Prod Econ 102:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2005.03.009
Costache R (2019) Flood susceptibility assessment by using bivariate statistics and machine learning models - a useful tool for flood risk management. Water Resour Manag 33:3239–3256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02301-z
Cozannet GL, Garcin M, Bulteau T, Mirgon C, Yates ML, Méndez M, Baills A, Idier D, Oliveros C (2013) An AHP-derived method for mapping the physical vulnerability of coastal areas at regional scales. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13:1209–1227. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-1209-2013
Crawford G, Williams C (1985) A note on the analysis of subjective judgment matrices. J Math Psychol 29:387–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2496(85)90002-1
Danumah JH, Odai SN, Saley BM, Szarzynski J, Thiel M, Kwaku A, Kouame FK, Akpa LY (2016) Flood risk assessment and mapping in Abidjan district using multi-criteria analysis (AHP) model and geoinformation techniques, (cote d’ivoire). Geoenviron Dis. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-016-0044-y
Darabi H, Choubin B, Rahmati O, Torabi Haghighi A, Pradhan B, Kløve B (2019) Urban flood risk mapping using the GARP and QUEST models: a comparative study of machine learning techniques. J Hydrol 569:142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.002
Demirel T, Demirel NÇ, Kahraman C (2008) Fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and its application. Springer Optim Its Appl 16:53–83. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315369884
Dermawan, A., 2017. New Strait Times 1–5.
Diakakis M (2011) A method for flood hazard mapping based on basin morphometry: application in two catchments in Greece. Nat Hazards 56:803–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9592-8
DID, 2018. Kajian Pelan Induk Sistem Saliran Mesra Alam Bagi Daerah Timur Laut, Pulau Pinang (Review of Eco-Friendly Drainage System Master Plan for Timur Laut area, Penang). Jabatan Pengairan dan Saliran Negeri Pulau Pinang- Department of Irrigation and Drainage, Penang.
Fernández DS, Lutz MA (2010) Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng Geol 111:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.12.006
Franci F, Bitelli G, Mandanici E, Hadjimitsis D, Agapiou A (2016) Satellite remote sensing and GIS-based multi-criteria analysis for flood hazard mapping. Nat Hazards 83:31–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2504-9
Ha H, Luu C, Bui QD, Pham DH, Hoang T, Nguyen VP, Vu MT, Pham BT (2021) Flash flood susceptibility prediction mapping for a road network using hybrid machine learning models. Nat Hazards 109:1247–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04877-5
Hategekimana Y, Yu L, Nie Y, Zhu J, Liu F, Guo F (2018) Integration of multi-parametric fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and GIS along the UNESCO World Heritage: a flood hazard index, Mombasa County. Kenya Nat Hazards 92:1137–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3244-9
Hawley RJ, Bledsoe BP (2011) How do flow peaks and durations change in suburbanizing semi-arid watersheds? A Southern California Case Study. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.05.011
Hollis GE (1975) The effect of urbanization on floods of different recurrence interval. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR011i003p00431
Hosseini FS, Choubin B, Mosavi A, Nabipour N, Shamshirband S, Darabi H, Haghighi AT (2019) Flash-flood hazard assessment using Ensembles and Bayesian-based machine learning models: application of the simulated annealing feature selection method. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135161
Huali C, Ito Y, Sawamukai M, Tokunaga T (2015) Flood hazard assessment in the kujukuri plain of Chiba prefecture, Japan, based on GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Nat Hazards 78:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1699-5
Huang HJ, Cheng SJ, Wen JC, Lee JH (2008) Effect of growing watershed imperviousness on hydrograph parameters and peak discharge. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6807
Ismail WR (2000) The hydrology and sediment yield of the Sungai Air Terjun catchment, Penang Hill. Malaysia Hydrol Sci J 45:897–909
Jenks G (1967) The Data Model Concept in Statistical Mapping. undefined
Jingyi W, Hu C, Ma B, Mu X (2020) Rapid urbanization impact on the hydrological processes in Zhengzhou. China Water (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/W12071870
Kanani-Sadat Y, Arabsheibani R, Karimipour F, Nasseri M (2019) A new approach to flood susceptibility assessment in data-scarce and ungauged regions based on GIS-based hybrid multi criteria decision-making method. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.034
Kazakis N, Kougias I, Patsialis T (2015) Assessment of flood hazard areas at a regional scale using an index-based approach and Analytical Hierarchy Process: application in Rhodope-Evros region. Greece Sci Total Environ 538:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.055
Kheir RB, Abdallah C, Khawlie M (2008) Assessing soil erosion in Mediterranean karst landscapes of Lebanon using remote sensing and GIS. Eng Geol 99:239–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.11.012
Khosravi K, Shahabi H, Pham BT, Adamowski J, Shirzadi A, Pradhan B, Dou J, Ly HB, Gróf G, Ho HL, Hong H, Chapi K, Prakash I (2019) A comparative assessment of flood susceptibility modeling using Multi-criteria decision-making analysis and machine learning methods. J Hydrol 573:311–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.03.073
Komi K, Neal J, Trigg MA, Diekkrüger B (2017) Modelling of flood hazard extent in data sparse areas: a case study of the Oti River basin West Africa. J Hydrol Reg Stud. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2017.03.001
Kordi M (2008) Comparison of fuzzy and crisp analytic hierarchy process ( AHP ) methods for spatial multicriteria decision analysis in GIS. Decis. Anal. pp. 1–55.
Kubota T, Ahmad S (2006) Wind environment evaluation of neighborhood areas in Major Towns of Malaysia. J Asian Archit Build Eng 5:199–206. https://doi.org/10.3130/jaabe.5.199
Laarhoven V, Pedrycz W (1983) A fuzzy extension of saaty’s priority theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst 11:229–241
Lappas I, Kallioras A (2019) Flood susceptibility assessment through GIS-based multi-criteria approach and analytical hierarchy process ( AHP ) in a River Basin in Central Greece. Int Res J Eng Technol 6:738–751
Lawal DU, Matori A, Hashim AM, Yusof KW, Chandio IA (2012) Detecting flood susceptible areas using GIS-based analytic hierarchy process vol. 28, pp. 4–8
Li Q, Zhou J, Cai J, Zhou J (2018) The environmental study on flash flood risk zonation based on trapezoidal fuzzy number and grey clustering. Ekoloji 27:2015–2025
Liu J, Xu Z, Chen F, Chen F, Zhang L (2019) Flood hazard mapping and assessment on the Angkor World Heritage Site. Cambodia Remote Sens 11:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010098
Lootsma FA (1980) Saaty’s priority theory and the nomination of a senior professor in operations research. Eur J Oper Res 4:380–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(80)90189-7
Luu C, Von Meding J, Kanjanabootra S (2018) Assessing flood hazard using flood marks and analytic hierarchy process approach: a case study for the 2013 flood event in Quang Nam. Vietnam Nat Hazards 90:1031–1050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3083-0
Madruga DBM, Evers M (2016) Multi-criteria decision-making for flood risk management: a survey of the current state of the art. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 16:1019–1033. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-16-1019-2016
Mahmoody VN, Jelokhani-Niaraki M (2019) The use of subjective–objective weights in GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis for flood hazard assessment: a case study in Mazandaran. Iran Geojournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-019-10075-5
Mahmoud SH, Gan TY (2018) Multi-criteria approach to develop flood susceptibility maps in arid regions of Middle East. J Clean Prod 196:216–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.047
Malczewski J (2000) On the use of weighted linear combination method in GIS: common and best practice approaches. Trans GIS 4:5–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9671.00035
Malczewski J (2007) GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: a survey of the literature. Int J Geogr Inf Sci ISSN 20:703–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810600661508
Malczewski J, Rinner C (2015) Multicriteria decision analysis in geographic information science, advances in geographic information science. Springer, New York Heidelberg, Dordrecht London
Mandeep JS, Hassan SIS, Tanaka K (2008) Rainfall measurements at Ku-band satellite link in Penang. Malaysia IET Microwaves Antennas Propag 2:147–151. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-map
Marco H, Mureau R, Glerum P, Slabbers S (2018) DRR-Team Mission Report
Mikhailov L (2003) Deriving priorities from fuzzy pairwise comparison judgements. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 134:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(02)00383-4
Moghadas M, Asadzadeh A, Vafeidis A, Fekete A, Kötter T (2019) A multi-criteria approach for assessing urban flood resilience in Tehran. Iran Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101069
Mohamed SA (2019) Application of satellite image processing and GIS-Spatial modeling for mapping urban areas prone to flash floods in Qena governorate. Egypt J African Earth Sci 158:103507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.05.015
Napolitano P, Fabbri AG (1996) Single parameter sensitivity analysis for aquifer vulnerability assessment using DRASTIC and SINTACS. In: Proceedings of the 2nd HydroGIS conference,. IAHS Publ. Appl. Geogr. Inf. Syst. Hydrol. Water Resour. Manag. (Proceedings Vienna Conf. April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, pp. 559–566
Noranis MAT, Maslina Z, Noraini CP (2019) Fuzzy AHP in a knowledge-based framework for early flood warning. Appl Mech Mater 892:143–149. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.892.143
Papaioannou G, Vasiliades L, Loukas A (2015) Multi-criteria analysis framework for potential flood prone areas mapping. Water Resour Manag 29:399–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0817-6
Parhizgar SM, Shahidi A, Pourreza-Bilondi M, Khashei-Siuki A (2017) Comparison of classic and fuzzy analytic hierarchy processes for mapping the flood hazard of Birjand plain. Water Harvest. Res. 2:43–56
Partington D, Brunner P, Simmons CT, Werner AD, Therrien R, Maier HR, Dandy GC (2012) Evaluation of outputs from automated baseflow separation methods against simulated baseflow from a physically based, surface water-groundwater flow model. J Hydrol 458–459:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.06.029
Pheng KS (2017) Understanding the causes of floods in Penang and seeking solutions.
Pirnazar M, Feizizadeh B, Eslamian S, Zand Karimi A, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Hasheminasab H, Ghorbanzadeh O, Hamedani MH (2017) assessing flood hazard using gis based multicriteria decision making approach; study area: East-Azerbaijan Province (Kaleybar Chay Basin). J. Flood Eng. 8:203–223
Pourghasemi HR, Gayen A, Panahi M, Rezaie F, Blaschke T (2019) Multi-hazard probability assessment and mapping in Iran. Sci Total Environ 692:556–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.203
Raj JK (2019) Lithologic map units and anticipated method of open excavation (<20 M High) in Peninsular Malaysia https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.26547.17446
Romdani RP, Tamamadin M, Susandi A, Pratama A, Wijaya AR (2018) Development of flash flood hazard map in bima City (NTB) using analytical hierarchy process. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/166/1/012035
Rosenfield GH, Fitzpatrick-Lins K (1986) A coefficient of agreement as a measure of thematic classification accuracy. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 52:223–227
Saaty T (1977) A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J Math Psychol 15:234–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2496(77)90033-5
Saaty T (1987) The analytical hierarchy process- what and why it is used. Math Model 9:161–176
Saaty T (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48:9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Saaty T (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0483(87)90016-8
Saaty T, Vargas LG (1980) Hierarchical analysis of behavior in competition: prediction in chess. Behav Sci 25:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1002/bs.3830250303
Saragih, D.F., 2020. Spatial Multi-Criteria Site Selection of Detention and Retention Ponds for Urban Stormwater Management at Medan City. Thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Submitted to the School of Civil Engineering, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Seejata K, Yodying A, Wongthadam T, Mahavik N, Tantanee S (2018) Assessment of flood hazard areas using analytical hierarchy process over the Lower Yom basin. Sukhothai Province Procedia Eng 212:340–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2018.01.044
Shaban AM, Hamzé MH (2017) Shared water resources of Lebanon. Shared Water Resour Lebanon. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48717-1
Shuster WD, Bonta J, Thurston H, Warnemuende E, Smith DR, Bonta J, Thurston H, Warnemuende E, Smith DR, Shuster WD, Bonta J, Thurston H, Warnemuende E, Smith DR (2007) Impacts of impervious surface on watershed hydrology : a review Impacts of impervious surface on watershed hydrology : a review. Urbam Water J. https://doi.org/10.1080/15730620500386529
Singh VP (1997) EFFECT OF SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIABILITY IN RAINFALL AND WATERSHED CHARACTERISTICS ON STREAM FLOW HYDROGRAPH, Ltd. Hydrol. Process. John Wiley & Sons.
Souissi D, Zouhri L, Hammami S, Msaddek MH, Zghibi A, Dlala M (2019) GIS-based MCDM–AHP modeling for flood susceptibility mapping of arid areas, southeastern Tunisia. Geocarto Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2019.1566405
Su HT, Tung YK (2014) Multi-criteria decision making under uncertainty for flood mitigation. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:1657–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-013-0818-7
Thirumurugan P, Krishnaveni M (2019) Flood hazard mapping using geospatial techniques and satellite images—a case study of coastal district of Tamil Nadu. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7327-1
Toosi AS, Calbimonte GH, Nouri H, Alaghmand S (2019) River basin-scale flood hazard assessment using a modified multi-criteria decision analysis approach: a case study. J Hydrol 574:660–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.072
Viera AJ, Garrett JM (2005) Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med 37:360–363
Vojtek M, Vojteková J (2019) Flood susceptibility mapping on a national scale in Slovakia using the analytical hierarchy process. Water (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020364
Vojtek M, Vojteková J, Vojtekov J (2016) Flood hazard and flood risk assessment at the local spatial scale: a case study. Nat Hazards and Risk. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2016.1166874
Wang Y, Hong H, Chen W, Li S, Pamučar D, Gigović L, Drobnjak S, Bui DT, Duan H (2019) A hybrid GIS multi-criteria decision-making method for flood susceptibility mapping at Shangyou. China Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11010062
Xiao Y, Yi S, Tang Z (2017) Integrated flood hazard assessment based on spatial ordered weighted averaging method considering spatial heterogeneity of risk preference. Sci Total Environ 599–600:1034–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.218
Yang X, ling D, hua J, Hou H (2013) Application of a triangular fuzzy AHP approach for flood risk evaluation and response measures analysis. Nat Hazards 68:657–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0642-x
Zhang C, Ma CB, Xu JD (2006) A new fuzzy MCDM method based on trapezoidal fuzzy AHP and hierarchical fuzzy integral. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. (including Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinformatics) 3614 LNAI, 466–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/11540007_57
Zheng G, Zhu N, Tian Z, Chen Y, Sun B (2012) Application of a trapezoidal fuzzy AHP method for work safety evaluation and early warning rating of hot and humid environments. Saf Sci 50:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2011.08.042
Zhou F, Xu Y, Chen Y, Xu CY, Gao Y, Du J (2013) Hydrological response to urbanization at different spatio-temporal scales simulated by coupling of CLUE-S and the SWAT model in the Yangtze River Delta region. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.040
Acknowledgements
This article is financially supported by the Tertiary Institutions Education Fund (TETFund), Nigeria.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby declare no conflicting interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mudashiru, R.B., Sabtu, N., Abdullah, R. et al. A comparison of three multi-criteria decision-making models in mapping flood hazard areas of Northeast Penang, Malaysia. Nat Hazards 112, 1903–1939 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05250-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-022-05250-w