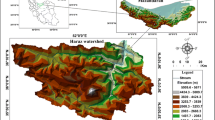
Abstract
Two landscape evaluation approaches, an integrated model and an ecological analysis method, based on landscape elements and environmental quality, respectively, were used to describe land desertification in the Heihe River Basin of northwestern China, by evaluating the current state of the local ecosystems and environment. Based on national water-quality criteria and fuzzy cluster analysis methods, surface water quality was divided into 5 grades with corresponding evaluation scores (evaluation rating threshold of water pollution), while groundwater quality was divided into 5 grades based on salinity and solute chemistry. For grassland ecosystems, grass yield (biomass) and types were the main indicators used. The soil component was described according to factors including its nutrient content, thickness, texture and degree of desertification, for a total of 11 evaluation indicators. Total vegetation cover is one of the 5 indicators chosen to describe the plant ecosystem. Based on conditions currently prevailing in the study region, evaluation factors such as total output value of agricultural, industrial, forestry and animal husbandry activities, the ratio of irrigation area to farmland area, the mean output return per unit area farmland, the level of education and per capital income were selected among others to characterize the social and economic situation. In total, 32 typical environment evaluation factors were selected, classifying land desertification in the region into four zones.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai WQ, Zhao SD (2001) An analysis of systems driving land use changes. Resour Sci 23(3):39–41
Cao SX, Feng Q (2012) Asian medicine: exploitation of plant. Sciences 335(6073):1168–1169
Chen L, Qu Y (1992) Rational development and utilization on water and soil resources in Hexi region. Science Press, Beijing
Del Valle H, Elissalde N, Gagliardini D, Milovich J (1998) Status of desertification in the Patagonian Region: assessment and mapping from satellite imagery. Arid Soil Res Rehab 12:95–122
Ding HW, Cui ZQ (2001) The reason of decay of spring water resources and trend analyses in the middle reaches of Heihe trunk stream area. Acta Geol Gansu 10(1):69–74
Ding HW, Gao YZ (2001) Reason of runoff reducing through Zheng Yixia Gorge on Heihe river and countermeasures. J Desert Res 21(1):62–66
Dong GR (1990) Climatic changes since the Late Pleistocene in deserts of northern China. Quat Sci 3:213–222
Dyer JS (1990) Remarks on the analytic hierarchy process. Manag Sci 36(3):249–258
Fortlage CA (1990) Environmental assessment: a practical guide. Gower Publishing Company, Limited, Hants
Gao QZ, Li FX (1991) Case study of relational development and utilization of water resources in the Heihe river basin. Gansu Sciences and Technology Press, Lanzhou, p 228
Gong JD, Cheng GD, Zhang XY (2002) Environmental changes of Ejin region in the lower reaches of Heihe River. Adv Earth Sci 17(4):491–496
He CY, Chen J, Chen YH (2001) Land use cover change based on hybrid method. J Nat Res 55(2):255–262
He CY, Zhou HL, Yu ZT, Zhang QT (2002) Regional land use/cover information processing. Resour Sci 24(2):64–70
Howarth PJ, Wickware GM (1981) Procedures for change detection using Landsat digital data. Int J Remote Sens 2:277–291
Jiao Y, Ma M, Xiao D (2003) Research on the landscape pattern of Zhangye oasis in the middle reaches of Heihe River. J Glaciol Geocryol 25:94–99
Lu L, Li X, Cheng G (2003) Landscape evolution in the middle Heihe River Basin of north-west China during the last decade. J Arid Environ 53:395–408
Luo F, Qi S, Xiao H (2005) Landscape change and sandy desertification in arid areas: a case study in the Zhangye Region of Gansu Province, China. Environ Geol 49:90–97
Ma Y, Zhen XM, Cao XQ, Kunihiko ED (1998) Environmental changes recorded by lacustrine sediment from Lake Swan, lower reaches of Heihe River during recent 200 years. J Lake Sci 10(2):45–51
Meng J, Wu X, Li Z (2003) Landuse/landcover changes in Zhangye oasis of Hexi Corridor. J Geogr Sci 3:71–75
Picketl TA, Cadanasso ML (1995) Landscape ecology, spatial heterogeneity in ecological systems. Science 269(21):331–334
Qi SZ, Cai YM (2007) Mapping and assessment of degraded land in the Heihe River Basin, Arid Northwestern China. Sensors 7:2565–2578
Qi S, Luo F (2005) Water environmental degradation of the Heihe River Basin in arid northwestern China. Environ Monit Assess 108:205–215
Qin D, Ding Y, Wang S, Wang S, Dong G, Lin E, Liu C, She Z, Sun H, Wang S, Wu G (2002) Ecological and environmental change in west China and its response strategy. J Adv Earth Sci 17(3):314–319
Sun HX (2000) Study on technology of diversiform-leveled poplar forest regeneration and restoration in Ejin oasis. J Arid Land Resour Environ 14(5):70–73
Tischendorf L (2001) Can landscape indices predict ecological processes consistently? Landsc Ecol 16:235–254
Turner BL II (1997) Socializing the pixel in LUCC. LUCC Newsl 1:10–11
Wang GX, Cheng GD (1998) Changes of hydrology and ecological environment during 50 years in Heihe River Basin. J Desert Res 18(3):233–238
Wang GX, Cheng GD (1999) The spatial pattern analysis of landscape in arid inland river basin A case study of the middle reaches of Heihe River. J Lanzhou Univ Nat Sci 35(1):211–217
Wang LF, Xu SB (1989) Theory and methods of AHP. Chinese People′ s University Press, Beijing, pp 42–131
Wang YL, Zhao YB, Han D (1999) The spatial structure of landscape ecosystems: concept, index and case studies. Adv Earth Sci 14(3):235–241
Wang GX, Qian J, Cheng GD (2001) The method of regions eco-environmental assessment and its usage in the case of Heihe River Basin. J Lanzhou Univ Nat Sci 37(2):131–141
Wang T, Wu W, Xuan X (2003) Spatial-temporal changes of sandy desertified land during last 5 decades in Northern China. J Desert Res 23(3):230–235
William ER, William B, Mand Turner BL II (1994) Modeling land use and land cover as part of global environmental change. Clim Chang 28:45–64
Xiao H (1999) Compiling the land use map of the Heihe River Basin. Lanzhou Institute of Desert Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 91025002; 41071052; 30970492; 31270482), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (GK201101002), the Key Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-04-05) and National Key Technology R & D Program (No. 2007BAD46B01). The authors would like to express deep gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, F., Wei, L. & Haiyang, X. Comprehensive evaluation and indicator system of land desertification in the Heihe River Basin. Nat Hazards 65, 1573–1588 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0429-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0429-5