Abstract
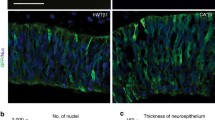
Integrins are heterodimeric cell surface receptors that mediate developmental events by binding extracellular matrix ligands. Several lines of evidence suggest a role for integrins, specifically the α 6 subunit, in neuronal migration, neurite outgrowth, and axon guidance during olfactory development. Therefore, we undertook an analysis of the expression of the α 6 subunit in the olfactory system of the embryonic and early postnatal mouse to understand the role it may play during neural development. In addition, as a functional assay we examined the developmental effects of the loss of this subunit on olfactory development by analyzing an α 6 knockout (α 6−/−). Immunohistochemical analyses and confocal microscopy were used to examine α 6 expression in the CD-1 embryonic and early postnatal olfactory system and also to examine the organization of the olfactory system in the α 6−/− mouse. In CD-1 mice from E13 to E17, α 6 localizes in radial patterns extending from the core of the olfactory bulb to the nerve layer and colocalizes with RC2, an antibody specific for radial glia. By the day of birth (P0; ∼E19), expression is limited to the external plexiform layer and the olfactory nerve layer, where it colocalizes with laminin and p75. In the α 6−/− mouse, areas of ectopic granule cells were observed in the mitral cell layer of the olfactory bulb. These ectopias coincided with areas of disorganization of the radial glial processes and breaks in the mitral cell layer. These observations suggest a role for α 6 integrin in neural migration during olfactory development, likely secondary to organization of the radial glial scaffold.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AGUIRRE, A. & GALLO, V. (2004) Postnatalneurogenesis and gliogenesis in the olfactory bulb from NG2-expressing progenitors of the subventricular zone. Journal of Neuroscience 24, 10530–10541.
ANTON, E. S., KREIDBERG, J. A. & RAKIC, P.(1999) Distinct functions of α3 and α(v) integrinreceptors in neuronal migration and laminar organization of thecerebral cortex. Neuron 22, 277–289.
AU, W. W., TRELOAR, H. B. & GREER, C. A.(2002) Sublaminar organization of the mouse olfactory bulb nervelayer. Journal of Comparative Neurology 446, 68–80.
BAYER, S. A. (1983) 3H-thymidine-radiographic studies ofneurogenesis in the rat olfactory bulb. Experimental Brain Research 50, 329–340.
BUCK, L. & AXEL R. (1991) A novel multigenefamily may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odorrecognition. Cell 65, 175–187.
CALOF, A. L., CAMPANERO, M. R., O'REAR, J. J. YURCHENCO, P.D. & LANDER, A. D. (1994) Domain-specific activationof neuronal migration and neurite outgrowth-promoting activitiesof laminin. Neuron 13, 117–130.
CALOF, A. L. & LANDER, A. D. (1991)Relationship between neuronal migration and cell-substratumadhesion: laminin and merosin promote olfactory neuronal migrationbut are anti-adhesive. Journal of Cell Biology 115, 779–794.
CHIU, K. & GREER, C. A. (1996)Immunocytochemical analyses of astrocyte development in theolfactory bulb. Developmental Brain Research 95, 28–37.
CHUAH, M. W. & WEST, A. K. (2002) Cellular andmolecular biology of ensheathing cells. Microscopy Research Techniques 58, 216–227.
CRANDALL, J. E., DIBBLE, C., BUTLER, D., PAYS, L., AHMAD,N., KOSTEK, C., PUSHCEL, A. W. & SCHWARTING, G. A. (2000) Patterning of olfactory sensory connections is mediated byextracellular matrix proteins in the nerve layer of the olfactorybulb. Journal of Neurobiology 45, 195–206.
DOETSCH, F., GARCIA-VERDUGO, J. M. & ALVAREZ-BUYLLA, A. (1997) Cellular composition andthree-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zonein the adult mammalian brain. Journal of Neuroscience 17, 5046–5061.
DULABON, K., OLASON, E. C., TAGLIENTI, M. G., EISENHUTH, S.,MCGRATH, B., WALSH, C. A., KREIDBERG, J. A. & ANTON, E.S. (2000) Reelin binds α6β1 integrin and inhibitsneuronal migration. Neuron 27, 33–44
EMSLEY, J. G. & HAGG, T. (2003) α6β1 integrin directs migration of neuronal precursors in adultmouse forebrain. Experimental Neurology 183, 273–285.
FEINSTEIN, P., BOZZA, T., RODRIGUEZ, I., VASSALLI, A. & MOMBAERTS, P. (2004) Axon guidance of mouse olfactorysensory neurons by odorant receptors and the beta2 adrenergicreceptor. Cell 117, 833–846.
FEINSTEIN, P. & MOMBAERTS, P. (2004) Acontextual model for axonal sorting into glomeruli in the mouseolfactory system. Cell 117, 817–831.
FORSTER, E., TIELSCH, A., SAUM, B., WEISS, K. H., JOHANSSEN, C., GRAUS-PORTA, D., MULLER, U. & FROTSCHER,M. (2002) Reelin, Disabled 1, and β1 integrins arerequired for the formation of the radial glial scaffold in thehippocampus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science U S A 99, 13178–13183.
GEORGES-LABOUESSE, E., MARK, M., MESSADDEQ, N. & GANSMULLER, A. (1998) Essential role of α6 integrins incortical and retinal lamination. Currents of Biology 8, 983–986.
GEORGES-LABOUSESSE, E., MESSADDEQ, N., YEHIA, G.,CADALBERT, L., DIERICH, A. & LE MEUR, M. (1996)Absence of integrin α6 leads to epidermolysis bullosa andneonatal death in mice. Nature Genetics 13, 370–373.
GONG, Q. & SHIPLEY, M. T. (1996) Expression ofextracellular matrix molecules and cell surface molecules in theolfactory nerve pathway during early development. Journalof Comparative Neurology 366, 1–14.
GRAUS-PORTA, D., BLAESS, S., SENFTEN, M., LITTLEWOOD-EVANS,A., DAMSKY, C., HUANG, Z., ORBAN, P., KLEIN, R., SCHITTNY, J. C. & MULLER, U. (2001) β1-class integrins regulatethe development of laminae and folia in the cerebral andcerebellar cortex. Neuron 31, 367–379.
21 HACK, I., BANCILA, M., LOULIER, K., CARROLL, P. & CREMER, H. (2002) Reelin is a detachment signal in tangentialchain-migration during postnatal neurogenesis. Nature Neuroscience 5, 939–945.
HARTFUSS, E., GALLI, R., HEINS, N. & GOTZ, M.(2001) Characterization of CNS precursor subtypes and radial glia. Developmental Biology 229, 15–30.
HIESBERGER, T., TROMMSDORFF, M., HOWELL, B. W., GOFFINET,A., MUMBY, M. C., COOPER, J. A. & HERZ, J. (1999)Direct binding of Reelin to VLDL receptor and Apo E receptor 2induces tyrosine phosphorylation of disabled-1 and modulates tauphosphorylation. Neuron 24, 481–489.
IVINS, J. K., PARRY, M. K. & LONG, D. A. (2004)A novel cAMP-dependent pathway activates neuronal integrinfunction in retinal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 24, 1212–1216.
IVINS, J. K., YURCHENCO, P. D. & LANDER, A. D. (2000) Regulation of neurite outgrowth by integrin activation. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 6551–6560.
JACQUES, T. S., RELVAS, J. B., NISHIMURA, S., PYTELA, R., EDWARDS, G. M., STREULI, C. H. & FFRENCH-CONSTANT, C.(1998) Neural precursor cell chain migration and division areregulated through different beta1 integrins. Development 125, 3167–3177.
KAFITZ, K. W. & GREER, C. A. (1997) Role oflaminin in axonal extension from olfactory receptor cells. Journal of Neurobiology 32, 298–310.
KASOWSKI, H. J., KIM, H. & GREER, C. A. (1999)Compartmental organization of the olfactory bulb glomerulus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 407, 261–274.
KEY, B. (1998) Molecular development of the olfactorynerve pathway. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 855, 76–82.
LLEDO, P. M., GHEUSI, G. & VINCENT, J. D. (2005)Information processing in the mammalian olfactory system. Physiology Review 85, 281–317.
LOIS, C. & ALVAREZ-BUYLLA, A. (1994)Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 264, 1145–1148.
LUSKIN, M. B. (1993) Restricted proliferation andmigration of postnatally generated neurons derived from theforebrain subventricular zone. Neuron 11, 173–189.
MOMBAERTS, P. (1999) Seven-transmembrane proteins asodorant and chemosensory receptors. Science 286, 707–711.
MOMBAERTS, P. (2001a) How smell develops. Nature Neuroscience 4 Suppl, 1192–1198.
MOMBAERTS, P. (2001b) The human repertoire of odorantreceptor genes and pseudogenes. Annual Review Genomics Human Genetics 2, 493–510.
MOMBAERTS, P., WANG, F. DULAC, C., CHAO, S. K., NEMES, A.,MENDELSOHN, M., EDMONDSON, J. & AXEL, R. (1996) Visualizing an olfactory sensory map. Cell 87, 675–686.
MORI, K. & YOSHIHARA, Y. (1995) Molecularrecognition and olfactory processing in the mammalian olfactorysystem. Progress in Neurobiology 45, 585–619.
MURASE, S. & HORWITZ, A. F. (2002) Deleted incolorectal carcinoma and differentially expressed integrinsmediate the directional migration of neural precursors in therostral migratory stream. Journal of Neuroscience 22, 3568–3579.
MURASE, S. & HORWITZ, A. F. (2004) Directionsin cell migration along the rostral migratory stream: the pathwayfor migration in the brain. Current Topics of Developmental Biology 61, 135–152.
OGAWA, M., MIYATA, T., NAKAJIMA, K., YAGYU, K., SEIKE, M.,IKENAKA, K., YAMAMOTO, H. & MIKOSHIBA, K. (1995) Thereeler gene-associated antigen on Cajal-Retzius neurons is acrucial molecule for laminar organization of cortical neurons. Neuron 14, 899–912.
PINCHING, A. J. & POWELL, T. P. (1971a) Theneuron types of the glomerular layer of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Cell Science 9, 305–345.
PINCHING, A. J. & POWELL, T. P. (1971b) Theneuropil of the glomeruli of the olfactory bulb. Journalof Cell Science 9, 347–377.
PINCHING, A. J. & POWELL, T. P. (1971c) Theneuropil of the periglomerular region of the olfactory bulb. Journal of Cell Science 9, 379–409.
PUCHE, A. C. & SHIPLEY, M. T. (2001) Radialglia development in the mouse olfactory bulb. Journal of Comparative Neurology 434, 1–12.
SAGHATELYAN, A., DE CHEVIGNY, A., SCHACHNER, M. & LLEDO, P. M. (2004) Tenascin-R mediates activity-dependentrecruitment of neuroblasts in the adult mouse forebrain. Nature Neuroscience 7, 347–356.
SCHMID, R. S. & ANTON, E. S. (2003) Role ofintegrins in the development of the cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex 13, 219–224.
SCHMID, R. S., SHELTON, S., STANCO, A., YOKOTA, Y., KREIDBERG, J. A. & ANTON E. S. (2004) alpha3beta1integrin modulates neuronal migration and placement during earlystages of cerebral cortical development. Development 131, 6023–6031.
SHEPHERD, G. M., CHEN, W. & GREER, C. A. (2004)The olfactory system. In Synaptic Organization of the Brain, 5thEdition(edited by SHEPHERD, G. M.), pp165–216. New York, NY, Oxford University Press.
SONNENBERG, A., LINDERS, C. J., MODDERMAN, P. W., DAMSKY,C. H., AUMAILLEY, M. & TIMPL, R. (1990) Integrinrecognition of different cell-binding fragments of laminin (P1,E3, E8) and evidence that α6β1 but not a 6β4functions as a major receptor for fragment E8. Journal of Cell Biology 110, 2145–2155.
SONNENBERG, A. MODDERMAN, P. W. & HOBERVORST, F. (1988) Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature 336, 487–489.
ST JOHN, J. A., TISAY, K. T., CARAS, I. W. & KEY B. (2000) Expression of Eph A5 during development of the olfactorynerve pathway in rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology 416, 540–550.
STROTMANN, J., LEVAI, O. FLEISCHER, J., SCHWARZENBACHER, K. & BREER, H. (2004) Olfactory receptor proteins inaxonal processes of chemosensory neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 24, 7754–7761.
TISAY, K. T. & KEY, B. (1999) The extracellularmatrix modulates olfactory neurite outgrowth on ensheathing cells. Journal of Neuroscience 19, 9890–9899.
TRELOAR, H. B., FEINSTEIN, P., MOMBAERTS, P. & GREER, C. A. (2002) Specificity of glomerular targeting byolfactory sensory axons. Journal of Neuroscience 22, 2469–2477.
TRELOAR, H. B., PURCELL, A. L. & GREER, C. A.(1999) Glomerular formation in the developing rat olfactory bulb. Journal Comparative Neurology 413, 289–304.
TROMMSDORFF, M., GOTTHARDT, M., HIESBERGER, T., SHELTON, J.,STOCKINGER, W., NIMPHF, J., HAMMER, R. E., RICHARDSON, J. A. & HERZ, J. (1999) Reeler/Disabled-like disruption ofneuronal migration in knockout mice lacking the VLDL receptor and Apo E receptor 2. Cell 97, 689–701.
ZHANG, X. & FIRESTEIN, S. (2002) The olfactoryreceptor gene superfamily of the mouse. Nature Neuroscience 5, 124–133.
ZHANG, Z. & GALILEO, D. S. (1998) Retroviraltransfer of antisense integrin a6 or α8 sequences resultsin laminar redistribution or clonal cell death in developingbrain. Journal of Neuroscience 18, 6928–6938.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitley, M., Treloar, H., De Arcangelis, A. et al. The α6 integrin subunit in the developing mouse olfactory bulb. J Neurocytol 34, 81–96 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-5049-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-005-5049-5