Abstract
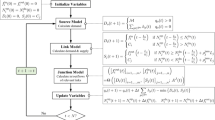
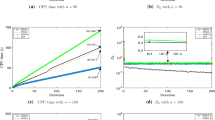
Although stochastic user equilibrium (SUE) problem has been studied extensively in the past decades, the solution convergence of SUE is generally quite slow because of the use of the method of successive averages (MSA), in which the auxiliary flow pattern generated at each iteration contributes equally to the final solution. Realizing that the auxiliary flow pattern is in fact approaching to the solution point when the iteration number is large, in this paper, we introduce the method of successive weighted averages (MSWA) that includes a new step size sequence giving higher weights to the auxiliary flow patterns from the later iterations. We further develop a self-regulated averaging method, in which the step sizes are varying, rather than fixed, depending on the distance between intermediate solution and auxiliary point. The proposed step size sequences in both MSWA and self-regulated averaging method satisfy the Blum theorem, which guarantees the convergence of SUE problem. Computational results demonstrate that convergence speeds of MSWA and self-regulated averaging method are much faster than those of MSA and the speedup factors are in a manner of magnitude for high accuracy solutions. Besides SUE problem, the proposed methods can also be applied to other fixed-point problems where MSA is applicable, which have wide-range applications in the area of transportation networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu T (1996) Cyclic flows, Markov process and stochastic traffic assignment. Transp Res Part B 30(5):369–386
Bar-Gera H, Boyce D (2006) Solving a non-convex combined travel forecasting model by the method of successive averages with constant step sizes. Transp Res Part B 40(5):351–367
Bell MGH (1995) Alternative to Dial’s logit assignment algorithm. Transp Res Part B 29(4):287–295
Blum JR (1954) Multidimensional stochastic approximation methods. Ann Math Stat 25(4):737–744
Bottom J, Ben-Akiva M, Bierlaire M, Chabini I, Koutsopoulos H, Yang Q (1999) Investigation of route guidance generation issues by simulation with DynaMIT. In: Ceder A (ed) Transportation and traffic theory. Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory, Pergamon, Amsterdam, pp 577–600
Bottom J, Chabini I (2001) Accelerated averaging methods for fixed point problems in transportation analysis and planning. Triennial Symposium on Transportation Analysis (TRISTAN IV). São, Miguel, Azores, Preprints 1, 69–74
Cascetta E, Postorino MN (2001) Fixed point approaches to the estimation of O/D matrices using traffic counts on congested networks. Transp Sci 35(2):134–147
Chen M, Alfa AS (1991) Algorithms for solving Fisk’s stochastic traffic assignment model. Transp Res Part B 25(6):405–412
Daganzo CF, Sheffi Y (1977) On stochastic models of traffic assignment. Transp Sci 11(3):253–274
Fisk C (1980) Some developments in equilibrium traffic assignment. Transp Res Part B 14(3):243–255
Frees E, Ruppert D (1990) Estimation following a sequentially designed experiment. J Am Stat Assoc 85:1123–1129
Magnanti TL, Perakis G (1997) Averaging schemes for variational inequalities and system of equations. Math Oper Res 22(3):568–587
Maher MJ (1998) Algorithms for logit-based stochastic user equilibrium assignment. Transp Res Part B 32(8):539–549
Maher MJ, Hughes PC (1998) Recent developments in stochastic assignment modeling. Traffic Eng Control 39(3):174–179
Nagurney A, Zhang D (1996) Projected dynamical systems and variational inequalities with applications. Kluwer, Boston, Massachusetts
Nocedal J, Wright SJ (1999) Numerical optimization. Springer, New York
Polyak BT (1990) New method of stochastic approximation type. Autom Remote Control 51(7):937–946
Robbins H, Monro S (1951) A stochastic approximation method. Ann Math Stat 22(3):400–407
Sheffi Y (1985) Urban transportation networks: equilibrium analysis with mathematical programming methods. Prentice-Hall, New York
Sheffi Y, Powell WB (1982) An algorithm for the equilibrium assignment problem with random link times. Networks 12(2):191–207
Wong SC (1999) On the convergence of Bell’s logit assignment formulation. Transp Res Part B 33(8):609–616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H.X., He, X. & He, B. Method of Successive Weighted Averages (MSWA) and Self-Regulated Averaging Schemes for Solving Stochastic User Equilibrium Problem. Netw Spat Econ 9, 485–503 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-007-9023-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11067-007-9023-x