Abstract
Objective
Reports of smell loss following traumatic brain injury (TBI) are a well-documented but understudied phenomenon. Given the broad consequences of olfactory loss, we characterized psychophysical olfactory dysfunction in individuals with moderate to severe TBI using systematic review and meta-analytic methods.
Methods
Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol, five databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Scopus) were reviewed for studies investigating olfactory dysfunction in persons with moderate to severe TBI. Of the 5,223 studies reviewed, 19 met our inclusion criteria for the systematic review and 11 met inclusion criteria for meta-analysis. We calculated effect sizes (Hedges’ g) to characterize the degree of olfactory dysfunction between patients with moderate to severe TBI and controls.
Results
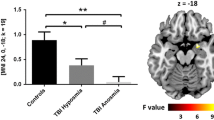
A total of 951 moderate-severe TBI patients from 19 studies were included in the systematic review, which largely demonstrated poorer olfactory psychophysical performances in this patient population. Meta-analysis demonstrated a large effect size for olfactory dysfunction in moderate-severe TBI relative to healthy controls (g=-2.43, 95%CI: -3.16 < δ<-1.69). The magnitude of the effect was moderated by age and patient sex, with larger effect sizes associated with older age (following exclusion of a pediatric population) and larger compositions of women in the patient group.
Conclusion
Moderate to severe TBI is associated with prominent olfactory dysfunction. Significant research gaps remain regarding the mechanism, recovery and natural history of olfactory dysfunction following moderate to severe TBI, which has significant clinical implications for the identification and treatment for those with post-traumatic olfactory dysfunction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, D. R., Wroblewski, K. E., Kern, D. W., Kozloski, M. J., Dale, W., McClintock, M. K., & Pinto, J. M. (2017). Factors associated with inaccurate self-reporting of olfactory dysfunction in older us adults. Chemical Senses, 42(3), 223–231. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjw108
Ahmedy, F., Mazlan, M., Danaee, M., & Abu Bakar, M. Z. (2020). Post-traumatic brain injury olfactory dysfunction: Factors influencing quality of life. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 277(5), 1343–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-020-05823-0
Begg, C. B., & Mazumdar, M. (1994). Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics, 50(4), 1088–1101
Bernstein, I. A., Roxbury, C. R., Lin, S. Y., & Rowan, N. R. (2021). The association of frailty with olfactory and gustatory dysfunction in older adults: A nationally representative sample. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, 11(5), 866–876. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22718
Biegon, A. (2021). Considering biological sex in traumatic brain injury. Frontiers in Neurology, 12, 576366. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.576366
Bratt, M., Skandsen, T., Hummel, T., Moen, K. G., Vik, A., Nordgard, S., & Helvik, A. S. (2018). Frequency and prognostic factors of olfactory dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 32(8), 1021–1027. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2018.1469043
Charland-Verville, V., Lassonde, M., & Frasnelli, J. (2012). Olfaction in athletes with concussion. American Journal Of Rhinology & Allergy, 26(3), 222–226. https://doi.org/10.2500/ajra.2012.26.3769
Chen, J. X., Lindeborg, M., Herman, S. D., Ishai, R., Knoll, R. M., Remenschneider, A., & Kozin, E. D. (2018). Systematic review of hearing loss after traumatic brain injury without associated temporal bone fracture. American Journal of Otolaryngology, 39(3), 338–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.01.018
Choi, J. S., Jang, S. S., Kim, J., Hur, K., Ference, E., & Wrobel, B. (2021). Association between olfactory dysfunction and mortality in US adults. JAMA Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, 147(1), 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3502
de Kruijk, J. R., Leffers, P., Menheere, P. P., Meerhoff, S., Rutten, J., & Twijnstra, A. (2003). Olfactory function after mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 17(1), 73–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269905021000010221
Deems, D. A., & Doty, R. L. (1987). Age-related changes in the phenyl ethyl alcohol odor detection threshold. Transactions - Pennsylvania Academy of Ophthalmology and Otolaryngology, 39(1), 646–650
Doty, R. L. (2006). Olfactory dysfunction and its measurement in the clinic and workplace. International Archives Of Occupational And Environmental Health, 79(4), 268–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-005-0055-6
Doty, R. L. (2015). Olfactory dysfunction and its measurement in the clinic. World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 1(1), 28–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wjorl.2015.09.007
Doty, R. L., Deems, D. A., & Stellar, S. (1988). Olfactory dysfunction in parkinsonism: A general deficit unrelated to neurologic signs, disease stage, or disease duration. Neurology, 38(8), 1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.38.8.1237
Doty, R. L., Marcus, A., & Lee, W. W. (1996). Development of the 12-item cross-cultural smell identification test (CC-SIT). The Laryngoscope, 106(3 Pt 1), 353–356. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199603000-00021
Doty, R. L., Shaman, P., Kimmelman, C. P., & Dann, M. S. (1984). University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test: A rapid quantitative olfactory function test for the clinic. The Laryngoscope, 94(2 Pt 1), 176–178. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-198402000-00004
Doty, R. L., Yousem, D. M., Pham, L. T., Kreshak, A. A., Geckle, R., & Lee, W. W. (1997). Olfactory dysfunction in patients with head trauma. Archives of Neurology, 54(9), 1131–1140. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.1997.00550210061014
Egger, M., Davey Smith, G., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ, 315(7109), 629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Ekstrom, I., Sjolund, S., Nordin, S., Nordin Adolfsson, A., Adolfsson, R., Nilsson, L. G., & Olofsson, J. K. (2017). Smell loss predicts mortality risk regardless of dementia conversion. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 65(6), 1238–1243. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14770
Fortin, A., Lefebvre, M. B., & Ptito, M. (2010). Traumatic brain injury and olfactory deficits: The tale of two smell tests!. Brain Injury, 24(1), 27–33. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699050903446815
Foster, E., Bayley, M., Langer, L., Saverino, C., Chandra, T., Barnard, C., & Comper, P. (2022). The Toronto Concussion Study: Sense of smell is not associated with concussion severity or recovery. Brain Injury, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2022.2037713
Fujiwara, E., Schwartz, M. L., Gao, F., Black, S. E., & Levine, B. (2008). Ventral frontal cortex functions and quantified MRI in traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychologia, 46(2), 461–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.08.027
Ghanizadeh, A. (2009). Loss of taste and smell during treatment with topiramate. Eating And Weight Disorders, 14(2–3), https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03327811. e137-138
Giguere, F. L., Frasnelli, A., De Guise, E., & Frasnelli, J. (2019). Olfactory, cognitive and affective dysfunction assessed 24 hours and one year after a mild traumatic brain injury (mtbi). Brain Injury, 33(9), 1184–1193. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2019.1631486
Green, P., & Iverson, G. L. (2001). Effects of injury severity and cognitive exaggeration on olfactory deficits in head injury compensation claims. Neurorehabilitation, 16(4), 237–243
Green, P., Rohling, M. L., Iverson, G. L., & Gervais, R. O. (2003). Relationships between olfactory discrimination and head injury severity. Brain Injury, 17(6), 479–496. https://doi.org/10.1080/0269905031000070242
Gupta, P. K., Sayed, N., Ding, K., Agostini, M. A., Van Ness, P. C., Yablon, S., & Diaz-Arrastia, R. (2014). Subtypes of post-traumatic epilepsy: Clinical, electrophysiological, and imaging features. Journal of Neurotrauma, 31(16), 1439–1443. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2013.3221
Gupte, R., Brooks, W., Vukas, R., Pierce, J., & Harris, J. (2019). Sex differences in traumatic brain injury: What we know and what we should know. Journal of Neurotrauma, 36(22), 3063–3091. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2018.6171
Han, P., Su, T., Qin, M., Chen, H., & Hummel, T. (2021). A systematic review of olfactory related questionnaires and scales. Rhinology, 59(2), 133–143. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhin20.291
Han, P., Winkler, N., Hummel, C., Hahner, A., Gerber, J., & Hummel, T. (2018a). Alterations of brain gray matter density and olfactory bulb volume in patients with olfactory loss after traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 35(22), 2632–2640. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2017.5393
Han, P., Winkler, N., Hummel, C., Hahner, A., Gerber, J., & Hummel, T. (2018b). Impaired brain response to odors in patients with varied severity of olfactory loss after traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurology, 265(10), 2322–2332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9003-8
Haxel, B. R., Grant, L., & Mackay-Sim, A. (2008). Olfactory dysfunction after head injury. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 23(6), 407–413. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.HTR.0000341437.59627.ec
Howell, J., Costanzo, R. M., & Reiter, E. R. (2018). Head trauma and olfactory function. World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery, 4(1), 39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wjorl.2018.02.001
Huang, T., Wei, Y., & Wu, D. (2021). Effects of olfactory training on posttraumatic olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, 11(7), 1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22758
Hura, N., Xie, D. X., Choby, G. W., Schlosser, R. J., Orlov, C. P., Seal, S. M., & Rowan, N. R. (2020). Treatment of post-viral olfactory dysfunction: An evidence-based review with recommendations. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, 10(9), 1065–1086. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.22624
Kim, D. H., Kim, S. W., Hwang, S. H., Kim, B. G., Kang, J. M., Cho, J. H., & Kim, S. W. (2017). Prognosis of olfactory dysfunction according to etiology and timing of treatment. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, 156(2), 371–377. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816679952
Kobal, G., & Hummel, T. (1998). Olfactory and intranasal trigeminal event-related potentials in anosmic patients. The Laryngoscope, 108(7), 1033–1035. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199807000-00015
Kobal, G., Hummel, T., Sekinger, B., Barz, S., Roscher, S., & Wolf, S. (1996). “Sniffin’ Sticks:“ Screening of olfactory performance. Rhinology, 34(4), 222–226
Kondo, H., Matsuda, T., Hashiba, M., & Baba, S. (1998). A study of the relationship between the T&T olfactometer and the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in a Japanese population. American Journal Of Rhinology, 12(5), 353–358. https://doi.org/10.2500/105065898780182390
Konstantinidis, I., Tsakiropoulou, E., Bekiaridou, P., Kazantzidou, C., & Constantinidis, J. (2013). Use of olfactory training in post-traumatic and postinfectious olfactory dysfunction. The Laryngoscope, 123(12), E85–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24390
Kraus, M. F., Little, D. M., Donnell, A. J., Reilly, J. L., Simonian, N., & Sweeney, J. A. (2007). Oculomotor function in chronic traumatic brain injury. Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, 20(3), 170–178. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNN.0b013e318142badb
Levin, H. S., High, W. M., & Eisenberg, H. M. (1985). Impairment of olfactory recognition after closed head injury. Brain, 108(3), 579–591. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/108.3.579
Liberati, A., Altman, D. G., Tetzlaff, J., Mulrow, C., Gotzsche, P. C., Ioannidis, J. P., & Moher, D. (2009). The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ, 339, b2700. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2700
Liu, G., Zong, G., Doty, R. L., & Sun, Q. (2016). Prevalence and risk factors of taste and smell impairment in a nationwide representative sample of the us population: A cross-sectional study. British Medical Journal Open, 6(11), e013246. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013246
Maas, A. I., Hukkelhoven, C. W., Marshall, L. F., & Steyerberg, E. W. (2005). Prediction of outcome in traumatic brain injury with computed tomographic characteristics: A comparison between the computed tomographic classification and combinations of computed tomographic predictors. Neurosurgery, 57(6), 1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000186013.63046.6b
McCrea, M. (2008). Mild traumatic brain injury and postconcussion syndrome: The new evidence base for diagnosis and treatment. Oxford University Press
Merezhinskaya, N., Mallia, R. K., Park, D., Bryden, D. W., Mathur, K., & Barker, F. M. 2nd (2019). Visual deficits and dysfunctions associated with traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Optometry and Vision Science, 96(8), 542–555. https://doi.org/10.1097/OPX.0000000000001407
Merkonidis, C., Grosse, F., Ninh, T., Hummel, C., Haehner, A., & Hummel, T. (2015). Characteristics of chemosensory disorders–results from a survey. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 272(6), 1403–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3210-4
Miao, X., Yang, L., Gu, H., Ren, Y., Chen, G., Liu, J., & Wei, Y. (2015). Evaluation of post-traumatic anosmia with MRI and chemosensory ERPs. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, 272(8), 1945–1953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-014-3278-x
Murphy, C., Schubert, C. R., Cruickshanks, K. J., Klein, B. E., Klein, R., & Nondahl, D. M. (2002). Prevalence of olfactory impairment in older adults. Journal of the American Medical Association, 288(18), 2307–2312. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.288.18.2307
Nelson, L. D., Temkin, N. R., Dikmen, S., Barber, J., Giacino, J. T., Yuh, E., & Zafonte, R. (2019). Recovery after mild traumatic brain injury in patients presenting to US Level I Trauma Centers: A transforming research and clinical knowledge in traumatic brain injury (track-tbi) study. JAMA Neurology, 76(9), 1049–1059. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1313
Neumann, D., Zupan, B., Babbage, D. R., Radnovich, A. J., Tomita, M., Hammond, F., & Willer, B. (2012). Affect recognition, empathy, and dysosmia after traumatic brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 93(8), 1414–1420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.03.009
Nordin, S., Monsch, A. U., & Murphy, C. (1995). Unawareness of smell loss in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Discrepancy between self-reported and diagnosed smell sensitivity. Journals of Gerontology Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 50(4), P187–192. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/50b.4.p187
Osborne-Crowley, K., & McDonald, S. (2016). Hyposmia, not emotion perception, is associated with psychosocial outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychology, 30(7), 820–829. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000293
Parma, V., Straulino, E., Zanatto, D., Cantagallo, A., Tirindelli, R., & Castiello, U. (2012). Implicit olfactory abilities in traumatic brain injured patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 34(9), 977–988. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803395.2012.711811
Peterson, A. B., Zhou, H., Thomas, K. E., & Daughertty, J. (2021). Surveillance report of traumatic brain injury-related hospitalizations and deaths by age group, sex, and mechanism of injury—United States, 2016 and 2017.
Proskynitopoulos, P. J., Stippler, M., & Kasper, E. M. (2016). Post-traumatic anosmia in patients with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI): A systematic and illustrated review. Surgical Neurology International, 7(Suppl 10), S263–275. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.181981
Rawal, S., Hoffman, H. J., Bainbridge, K. E., Huedo-Medina, T. B., & Duffy, V. B. (2016). Prevalence and risk factors of self-reported smell and taste alterations: Results from the 2011–2012 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Chemical Senses, 41(1), 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjv057
Sandford, A. A., Davidson, T. M., Herrera, N., Gilbert, P., Magit, A. E., Haug, K., & Murphy, C. (2006). Olfactory dysfunction: A sequela of pediatric blunt head trauma. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology, 70(6), 1015–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.10.013
Savage, R., Combs, D. R., Pinkston, J. B., Advokat, C., & Gouvier, W. D. (2002). The role of temporal lobe and orbitofrontal cortices in olfactory memory function. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 17(4), 305–318
Schafer, L., Schriever, V. A., & Croy, I. (2021). Human olfactory dysfunction: Causes and consequences. Cell and Tissue Research, 383(1), 569–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03381-9
Schofield, P. W., & Doty, R. L. (2019). The influence of head injury on olfactory and gustatory function. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 164, 409–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63855-7.00023-X
Schofield, P. W., Moore, T. M., & Gardner, A. (2014). Traumatic brain injury and olfaction: A systematic review. Frontiers in Neurology, 5, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2014.00005
Sigurdardottir, S., Andelic, N., Skandsen, T., Anke, A., Roe, C., Holthe, O. O., & Wehling, E. (2016). Olfactory identification and its relationship to executive functions, memory, and disability one year after severe traumatic brain injury. Neuropsychology, 30(1), 98–108. https://doi.org/10.1037/neu0000206
Sorokowski, P., Karwowski, M., Misiak, M., Marczak, M. K., Dziekan, M., Hummel, T., & Sorokowska, A. (2019). Sex differences in human olfaction: A meta-analysis. Frontiers In Psychology, 10, 242. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00242
St Ivany, A., & Schminkey, D. (2016). Intimate partner violence and traumatic brain injury: State of the science and next steps. Family and Community Health, 39(2), 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1097/FCH.0000000000000094
Summers, C. R., Ivins, B., & Schwab, K. A. (2009). Traumatic brain injury in the United States: An epidemiologic overview. Mount Sinai Journal Of Medicine, 76(2), 105–110. https://doi.org/10.1002/msj.20100
Sumner, D. (1964). Post-traumatic anosmia. Brain, 87, 107–120. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/87.1.107
Teasdale, G., & Jennett, B. (1974). Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet, 2(7872), 81–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91639-0
Temmel, A. F., Quint, C., Schickinger-Fischer, B., Klimek, L., Stoller, E., & Hummel, T. (2002). Characteristics of olfactory disorders in relation to major causes of olfactory loss. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 128(6), 635–641. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.128.6.635
Tobias, A. (1999). Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-analysis estimate. Stata Technical Bulletin, 8(47). https://ideas.repec.org/a/tsj/stbull/y1999v8i47sbe26.html
VA/DoD (2021). VA/DOD clinical practice guideline for the management of concussion-mild trauamtic brain injury
Wehling, E., Nordin, S., Espeseth, T., Reinvang, I., & Lundervold, A. J. (2011). Unawareness of olfactory dysfunction and its association with cognitive functioning in middle aged and old adults. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(3), 260–269. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acr019
Wells, G. A., Shea, B., O’Connell, D., Peterson, J., Welch, V., Losos, M., & Tugwell, P. (2013). The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Retrieved May 14, 2021, from http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp
Xydakis, M. S., Mulligan, L. P., Smith, A. B., Olsen, C. H., Lyon, D. M., & Belluscio, L. (2015). Olfactory impairment and traumatic brain injury in blast-injured combat troops: A cohort study. Neurology, 84(15), 1559–1567. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001475
Yamaki, T., Oka, N., Odaki, M., & Kobayashi, S. (2020). Usability of intravenous thiamine injection test compared with odor stick identification test for japanese patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Auris, Nasus, Larynx, 47(2), 233–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2019.07.004
Yousem, D. M., Geckle, R. J., Bilker, W. B., Kroger, H., & Doty, R. L. (1999). Posttraumatic smell loss: Relationship of psychophysical tests and volumes of the olfactory bulbs and tracts and the temporal lobes. Academic Radiology, 6(5), 264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1076-6332(99)80449-8
Yousem, D. M., Geckle, R. J., Bilker, W. B., McKeown, D. A., & Doty, R. L. (1996). Posttraumatic olfactory dysfunction: MR and clinical evaluation. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 17(6), 1171–1179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tai, K., Leland, E.M., Seal, S.M. et al. Olfactory Dysfunction Following Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 33, 717–732 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-022-09563-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-022-09563-2