Abstract
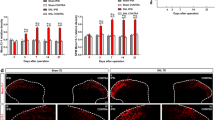
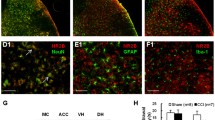
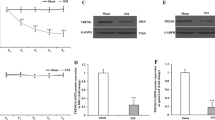
Previous studies suggested that postsynaptic neuroligin-2 may shift from inhibitory toward excitatory function under pathological pain conditions. We hypothesize that nerve injury may increase the expression of spinal MAM-domain GPI-anchored molecule 1 (MDGA1), which can bind to neuroligin-2 and thereby, alter its interactions with postsynaptic scaffolding proteins and increase spinal excitatory synaptic transmission, leading to neuropathic pain. Western blot, immunofluorescence staining, and co-immunoprecipitation studies were conducted to examine the critical role of MDGA1 in the lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn in rats after spinal nerve ligation (SNL). Small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs) targeting MDGA1 were used to examine the functional roles of MDGA1 in neuropathic pain. Protein levels of MDGA1 in the ipsilateral dorsal horn were significantly upregulated at day 7 post-SNL, as compared to that in naïve or sham rats. The increased levels of GluR1 in the synaptosomal membrane fraction of the ipsilateral dorsal horn tissues at day 7 post-SNL was normalized to near sham level by pretreatment with intrathecal MDGA1 siRNA2308, but not scrambled siRNA or vehicle. Notably, knocking down MDGA1 with siRNAs reduced the mechanical and thermal pain hypersensitivities, and inhibited the increased excitatory synaptic interaction between neuroligin-2 with PSD-95, and prevented the decreased inhibitory postsynaptic interactions between neuroligin-2 and Gephyrin. Our findings suggest that SNL upregulated MDGA1 expression in the dorsal horn, which contributes to the pain hypersensitivity through increasing the net excitatory interaction mediated by neuroligin-2 and surface delivery of GluR1 subunit in dorsal horn neurons.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Cathenaut L, Leonardon B, Kuster R et al (2022) Inhibitory interneurons with differential plasticities at their connections tune excitatory-inhibitory balance in the spinal nociceptive system. Pain 163(5):e675–e688
Huang Y, Chen SR, Pan HL (2022) Calcineurin regulates synaptic plasticity and nociceptive transmission at the spinal cord level. Neuroscientist 28(6):628–638
Li HL, Guo RJ, Guan Y et al (2022) Modulation of trans-synaptic neurexin-neuroligin interaction in pathological pain. Cells 11(12):1940
Prange O, Wong TP, Gerrow K et al (2004) A balance between excitatory and inhibitory synapses is controlled by PSD-95 and neuroligin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(38):13915–13920
Ali H, Marth L, Krueger-Burg D (2020) Neuroligin-2 as a central organizer of inhibitory synapses in health and disease. Sci Signal 13(663):eabd8379
Liu X, Hua F, Yang D et al (2022) Roles of neuroligins in central nervous system development: focus on glial neuroligins and neuron neuroligins. J Transl Med 20(1):418
Wu XB, Zhu Q, Gao YJ (2021) CCL2/CCR2 contributes to the altered excitatory-inhibitory synaptic balance in the nucleus accumbens shell following peripheral nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Neurosci Bull 37(7):921–933
Dolique T, Favereaux A, Roca-Lapirot O et al (2013) Unexpected association of the “inhibitory” neuroligin 2 with excitatory PSD95 in neuropathic pain. Pain 154(11):2529–2546
Guo RJ, Li HL, Li XY et al (2018) Increased neuroligin 2 levels in the postsynaptic membrane in spinal dorsal horn may contribute to postoperative pain. Neuroscience 382(2018):14–22
Connor SA, Elegheert J, Xie Y et al (2019) Pumping the brakes: suppression of synapse development by MDGA-neuroligin interactions. Curr Opin Neurobiol 57(2019):71–80
Kim JA, Kim D, Won SY et al (2017) Structural insights into modulation of neurexin-neuroligin trans-synaptic adhesion by MDGA1/neuroligin-2 complex. Neuron 94(6):1121–1131
Elegheert J, Cvetkovska V, Clayton AJ et al (2017) Structural mechanism for modulation of synaptic neuroligin-neurexin signaling by MDGA proteins. Neuron 95(4):896–913
Elegheert J, Cvetkovska V, Clayton AJ et al (2021) Structural mechanism for modulation of synaptic neuroligin-neurexin signaling by MDGA proteins. Neuron 109(1):189–190
Kim J, Kim S, Kim H et al (2022) MDGA1 negatively regulates amyloid precursor protein-mediated synapse inhibition in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119(4):e2115326119
Lee K, Kim Y, Lee SJ et al (2013) MDGAs interact selectively with neuroligin-2 but not other neuroligins to regulate inhibitory synapse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(1):336–341
Toledo A, Letellier M, Bimbi G et al (2022) (2022) MDGAs are fast-diffusing molecules that delay excitatory synapse development by altering neuroligin behavior. Elife 11:e75233
Ho KS, Mo CJ (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50(3):355–363
Guo RJ, Li HL, Shi R et al (2021) Intrathecal injection of GRIP-siRNA reduces postoperative synaptic abundance of kainate receptor GluK2 subunits in rat dorsal horns and pain hypersensitivity. Neurochem Res 46(7):1771–1780
Guo RJ, Li HL, Li XY et al (2018) (2018) Downregulation of neuroligin1 ameliorates postoperative pain through inhibiting neuroligin1/postsynaptic density 95-mediated synaptic targeting of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor GluA1 subunits in rat dorsal horns. Mol Pain 14:1744806918766745
Dunah AW, Standaert DG (2021) Dopamine D1 receptor dependent trafficking of striatal NMDA glutamate receptors to the postsynaptic membrane. J Neurosci 21(15):5546–5558
Guo RJ, Zhao YJ, Zhang MJ et al (2014) Down-regulation of stargazin inhibits the enhanced surface delivery of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor GluR1 subunit in rat dorsal horn and ameliorates postoperative pain. Anesthesiology 121(3):609–619
Litwack ED, Babey R, Buser R et al (2004) Identification and characterization of two novel brain-derived immunoglobulin superfamily members with a unique structural organization. Mol Cell Neurosci 25(2):263–274
Fujimura Y, Iwashita M, Matsuzaki F et al (2006) MDGA1, an IgSF molecule containing a MAM domain, heterophilically associates with axon- and muscle-associated binding partners through distinct structural domains. Brain Res 1101(1):12–19
Eisenach JC (1999) Muscarinic-mediated analgesia. Life Sci 64(6–7):549–554
Connor SA, Ammendrup-Johnsen I, Kishimoto Y et al (2017) Loss of synapse repressor MDGA1 enhances perisomatic inhibition, confers resistance to network excitation, and impairs cognitive function. Cell Rep 21(13):3637–3645
Pettem KL, Yokomaku D, Takahashi H et al (2013) Interaction between autism-linked MDGAs and neuroligins suppresses inhibitory synapse development. J Cell Biol 200(3):321–336
Hossain MR, Jamal M, Tanoue Y et al (2020) MDGA1-deficiency attenuates prepulse inhibition with alterations of dopamine and serotonin metabolism: An ex vivo HPLC-ECD analysis. Neurosci Lett 716:134677
Phelps CE, Navratilova E, Porreca F (2021) Cognition in the chronic pain experience: preclinical insights. Trends Cogn Sci 25(5):365–376
O’Gara BP, Gao L, Marcantonio ER et al (2021) Sleep, pain, and cognition: modifiable targets for optimal perioperative brain health. Anesthesiology 135(6):1132–1152
Chanda S, Hale WD, Zhang B et al (2017) Unique versus redundant functions of neuroligin genes in shaping excitatory and inhibitory synapse properties. J Neurosci 37(29):6816–6836
Hale WD, Südhof TC, Huganir RL (2023) Engineered adhesion molecules drive synapse organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 120(3):e2215905120
Halff EF, Hannan S, Kwanthongdee J et al (2022) Phosphorylation of neuroligin-2 by PKA regulates its cell surface abundance and synaptic stabilization. Sci Signal 15(739):eabg2505
Zhang W, Chen Y, Qin J et al (2022) Prolonged sevoflurane exposure causes abnormal synapse development and dysregulates beta-neurexin and neuroligins in the hippocampus in neonatal rats. J Affect Disord 312(2022):22–29
Halff EF, Szulc BR, Lesept F et al (2019) SNX27-mediated recycling of neuroligin-2 regulates inhibitory signaling. Cell Rep 29(9):2599–2607
Guo C (2021) Ma YY (2021) Calcium permeable-AMPA receptors and excitotoxicity in neurological disorders. Front Neural Circuits 15:711564
Miyagi Y, Fujiwara K, Hikishima K et al (2022) Altered calcium permeability of AMPA receptor drives NMDA receptor inhibition in the hippocampus of murine obesity models. Mol Neurobiol 59(8):4902–4925
Zhang W, Lei M, Wen QW et al (2022) Dopamine receptor D2 regulates GLUA1-containing AMPA receptor trafficking and central sensitization through the PI3K signaling pathway in a male rat model of chronic migraine. J Headache Pain 23(1):98
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171217, 81771181, 81571065), Beijing, China, and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7202053), Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL: Investigation, writing—original draft, methodology. RJ: Data curation, visualization, investigation. ZR and SH: Data curation, visualization. JF and YG: Conceptualization, methodology, and supervision. YW: Writing—review & editing, supervision, conceptualization.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, HL., Guo, RJ., Ai, ZR. et al. Upregulation of Spinal MDGA1 in Rats After Nerve Injury Alters Interactions Between Neuroligin-2 and Postsynaptic Scaffolding Proteins and Increases GluR1 Subunit Surface Delivery in the Spinal Cord Dorsal Horn. Neurochem Res 49, 507–518 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-04049-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-04049-w