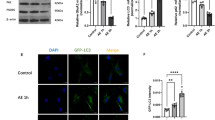
Abstract
PKM2 is a glycolytic pyruvate kinase isoenzyme, and its role in neurological diseases has been published. However, the role and mechanism of PKM2 in the process of status epilepticus have not been reported. The purpose of this study is to explore the role and mechanism of PKM2 in epilepsy. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and western blotting were used to explore the expression of PKM2 in cells. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits were used to evaluate the level of inflammatory factors. An epilepsy model was established by intraperitoneal injection of lithium chloride in rats. Various behavioural assays were conducted to explore the learning ability and cognitive level of rats. PKM2 expression was upregulated in Mg2+-induced hippocampal neurons. PKM2 inhibition ameliorated Mg2+-induced hippocampal neuronal inflammation and reduced neuronal apoptosis. In addition, PKM2 silencing inhibited the metabolic dysfunction of Mg2+-induced hippocampal neurons. Subsequent experiments showed that the Akt/mTOR pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome are involved in PKM2-mediated neuronal regulation. More importantly, PKM2 inhibition could alleviate status epilepticus in rats. PKM2 inhibition attenuates Mg2+-induced hippocampal neuronal inflammation, apoptosis and metabolic dysfunction and improves the cognitive ability of rats. Therefore, PKM2 may be an important target for epilepsy treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Rugg-Gunn F, Miserocchi A, McEvoy A (2020) Epilepsy surgery. Pract Neurol 20(1):4–14. https://doi.org/10.1136/practneurol-2019-002192
Husari KS, Dubey D (2019) Autoimmune Epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics: The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 16(3):685–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00750-3
Pack AM (2019) Epilepsy Overview and revised classification of seizures and epilepsies. Continuum (Minneapolis Minn) 25(2):306–321. https://doi.org/10.1212/con.0000000000000707
Perucca P, Bahlo M, Berkovic SF (2020) The Genetics of Epilepsy. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet 21:205–230. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-120219-074937
Zhang Z, Deng X, Liu Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Chen F (2019) PKM2, function and expression and regulation. Cell & Bioscience 9:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-019-0317-8
Yang W, Xia Y, Ji H, Zheng Y, Liang J, Huang W, Gao X, Aldape K, Lu Z (2011) Nuclear PKM2 regulates β-catenin transactivation upon EGFR activation. Nature 480(7375):118–122. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10598
Damasceno LEA, Prado DS, Veras FP, Fonseca MM, Toller-Kawahisa JE, Rosa MH, Públio GA, Martins TV, Ramalho FS, Waisman A, Cunha FQ, Cunha TM, Alves-Filho JC (2020) PKM2 promotes Th17 cell differentiation and autoimmune inflammation by fine-tuning STAT3 activation. J Exp Med 217(10). https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20190613
Dayton TL, Jacks T, Vander Heiden MG (2016) PKM2, cancer metabolism, and the road ahead. EMBO Rep 17(12):1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201643300
Wang B, Liu S, Fan B, Xu X, Chen Y, Lu R, Xu Z, Liu X (2018) PKM2 is involved in neuropathic pain by regulating ERK and STAT3 activation in rat spinal cord. J Headache Pain 19(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-018-0836-4
Dey P, Kundu A, Sachan R, Park JH, Ahn MY, Yoon K, Lee J, Kim ND, Kim IS, Lee BM, Kim HS (2019) PKM2 Knockdown induces autophagic cell death via AKT/mTOR pathway in human prostate Cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochemistry: Int J Experimental Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 52(6):1535–1552. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000107
Liu D, Xiao Y, Zhou B, Gao S, Li L, Zhao L, Chen W, Dai B, Li Q, Duan H, Zuo X, Luo H, Zhu H (2021) PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes skeletal muscle cell pyroptosis by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in dermatomyositis/polymyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60(5):2177–2189. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa473
Revathidevi S, Munirajan AK (2019) Akt in cancer: Mediator and more. Sem Cancer Biol 59:80–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.06.002
Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z, Lee MH (2019) AKT as a therapeutic target for Cancer. Cancer Res 79(6):1019–1031. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-2738
Murugan AK (2019) mTOR: role in cancer, metastasis and drug resistance. Sem Cancer Biol 59:92–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.003
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H, Wang J, Luo T, Jiang Y (2019) Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0754-1
Zhen Y, Zhang H (2019) NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol 10:276. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00276
Karasawa T, Takahashi M (2017) Role of NLRP3 inflammasomes in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 24(5):443–451. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV17001
Zhang H, Qu Y, Wang A (2018) Antagonist targeting microRNA-146a protects against lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in rats by nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep 17(4):5356–5361. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.8465
Beghi E, Giussani G, Sander JW (2015) The natural history and prognosis of epilepsy. Epileptic Disorders: International Epilepsy Journal with Videotape 17(3):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1684/epd.2015.0751
Thijs RD, Surges R, O’Brien TJ, Sander JW (2019) Epilepsy in adults. Lancet (London England) 393(10172):689–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32596-0
Li T, Han J, Jia L, Hu X, Chen L, Wang Y (2019) PKM2 coordinates glycolysis with mitochondrial fusion and oxidative phosphorylation. Protein Cell 10(8):583–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-019-0618-z
Magadum A, Singh N, Kurian AA, Munir I, Mehmood T, Brown K, Sharkar MTK, Chepurko E, Sassi Y, Oh JG, Lee P, Santos CXC, Gaziel-Sovran A, Zhang G, Cai CL, Kho C, Mayr M, Shah AM, Hajjar RJ, Zangi L (2020) Pkm2 regulates Cardiomyocyte Cell cycle and promotes Cardiac Regeneration. Circulation 141(15):1249–1265. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.119.043067
Li TE, Wang S, Shen XT, Zhang Z, Chen M, Wang H, Zhu Y, Xu D, Hu BY, Wei R, Zheng Y, Dong QZ, Qin LX (2020) PKM2 drives Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by inducing Immunosuppressive Microenvironment. Front Immunol 11:589997. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.589997
Xu D, Liang J, Lin J, Yu C (2019) PKM2: a potential Regulator of Rheumatoid Arthritis via Glycolytic and non-glycolytic pathways. Front Immunol 10:2919. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02919
Wei Y, Lu M, Mei M, Wang H, Han Z, Chen M, Yao H, Song N, Ding X, Ding J, Xiao M, Hu G (2020) Pyridoxine induces glutathione synthesis via PKM2-mediated Nrf2 transactivation and confers neuroprotection. Nat Commun 11(1):941. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14788-x
Xie M, Yu Y, Kang R, Zhu S, Yang L, Zeng L, Sun X, Yang M, Billiar TR, Wang H, Cao L, Jiang J, Tang D (2016) PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Nat Commun 7:13280. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13280
Narayanan A, Srinaath N, Rohini M, Selvamurugan N (2019) Regulation of Runx2 by MicroRNAs in osteoblast differentiation. Life Sci 232:116676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116676
Gao D, Tang T, Zhu J, Tang Y, Sun H, Li S (2019) CXCL12 has therapeutic value in facial nerve injury and promotes Schwann cells autophagy and migration via PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 124:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.212
Wang N, Wang M (2019) Dexmedetomidine suppresses sevoflurane anesthesia-induced neuroinflammation through activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. BMC Anesthesiol 19(1):134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-019-0808-5
Mangan MSJ, Olhava EJ, Roush WR, Seidel HM, Glick GD, Latz E (2018) Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 17(8):588–606. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.97
Shao BZ, Xu ZQ, Han BZ, Su DF, Liu C (2015) NLRP3 inflammasome and its inhibitors: a review. Front Pharmacol 6:262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00262
Lin S, Mei X (2020) Role of NLRP3 inflammasomes in Neuroinflammation Diseases. Eur Neurol 83(6):576–580. https://doi.org/10.1159/000509798
Rui W, Li S, Xiao H, Xiao M, Shi J (2020) Baicalein attenuates neuroinflammation by inhibiting NLRP3/caspase-1/GSDMD pathway in MPTP Induced mice Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 23(11):762–773. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyaa060
Aguiar CC, Almeida AB, Araújo PV, de Abreu RN, Chaves EM, do Vale OC, Macêdo DS, Woods DJ, Fonteles MM, Vasconcelos SM (2012) Oxidative stress and epilepsy: literature review. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2012(795259. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/795259
Geronzi U, Lotti F, Grosso S (2018) Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 18(5):427–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1465410
Waldbaum S, Patel M (2010) Mitochondria, oxidative stress, and temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 88(1):23–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.09.020
Xiong Y, Jin E, Yin Q, Che C, He S (2021) Boron attenuates heat Stress-Induced apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse granulosa cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 199(2):611–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02180-1
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiaoli Cui and Feng Jiang designed the experiments and wrote the paper; Ruihua Jia, Rui Zhao and Ni Ma carried out the experiments and performed the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Shaanxi Provincial People’s Hospital. The procedures of handling and caring animals conformed to the guidelines of the current international laws and policies (NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, The National Academies Press, 8th edition, 2011).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, X., Jia, R., Zhao, R. et al. Silencing PKM2 Attenuates Brain Injury Induced by Status Epilepticus by Inhibiting the AKT/mTOR Pathway and the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Neurochem Res 49, 212–221 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-04023-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-04023-6