Abstract
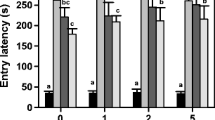
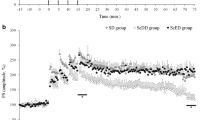
In this study, the effects of different doses of sulfite on learning, memory, and long term potentiation as well as the relationship of these effects with acetylcholine pathways, Arc and synapsin 1 levels were investigated. Sixty male Wistar albino rats were randomly divided into three groups as control, S100, and S260. Sodiummetabisulfite (S100;100 mg/kg/day, S260;260 mg/kg/day) was given by oral administration. Behavioral changes were evaluated. After long term potentiation recordings from the perforant pathway—dentate gyrus synapses, animals were sacrificed. Acetylcholinesterase activity, choline acetyltransferase activity, acetylcholine level as well as Arc and Synapsin 1 expressions were analyzed on the hippocampi. The total distance and average velocity values in the open field and Morris water maze tests increased in the sulfite groups, while the discrimination index in the novel object recognition test decreased compared to controls. Acetylcholine levels and choline acetyltransferase activity were also increased in the sulfite groups, while acetylcholinesterase activity was decreased compared to controls. Sulfite intake attenuated long term potentiation in the hippocampus. It has been observed that the excitatory postsynaptic potential slope and population spike amplitude of the field potentials obtained in sulfite groups decreased. This impairment was accompanied by a decrease in Arc and synapsin 1 expressions. In conclusion, it has been shown that sulfite intake in adults impairs learning and memory, possibly mediated by the cholinergic pathway. It is considered that the decrement in Arc and synapsin expressions may play a role in the mechanism underlying the impairment in long term potentiation caused by toxicity.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
We declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available.
References
Taylor SL, Higley NA, Bush RK (1986) Sulfites in foods: uses, analytical methods, residues, fate, exposure assessment, metabolism, toxicity, and hypersensitivity. Adv Food Res 30:1–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2628(08)60347-X
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization (FAO/WHO) (1994) Summary of Evaluations Performed by the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JEFCA). International Life Sciences Institute, Washington, DC
Cohen HJ, Fridovich I. (1971) Hepatic sulfite oxidase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 246:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)62499-8
Simon RA (1989) Sulfite challenge for the diagnosis of sensitivity. In: Allergy and asthma proceedings. OceanSide Publications. https://doi.org/10.2500/108854189778959858
Rencüzoǧullari E, İla HB, Kayraldiz A, Topaktaş M (2001) Chromosome aberrations and sister chromatid exchanges in cultured human lymphocytes treated with sodium metabisulfite, a food preservative. Mutat Res 490:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1383-5718(00)00142-X
Akdogan I, Kocamaz E, Kucukatay V, Yonguc NG, Ozdemir MB, Murk W (2011) Hippocampal neuron number loss in rats exposed to ingested sulfite. Toxicol Ind Health 27:771–778. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233710397418
Kencebay C, Derin N, Ozsoy O, Kipmen-Korgun D, Tanriover G, Ozturk N, Basaranlar G, Yargicoglu-Akkiraz P, Sozen B, Agar A (2013) Merit of quinacrine in the decrease of ingested sulfite-induced toxic action in rat brain. Food Chem Toxicol 52:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.015
Noorafshan A, Asadi-Golshan R, Karbalay-Doust S, Abdollahifar MA, Rashidiani-Rashidabadi A (2013) Curcumin, the main part of turmeric, prevents learning and memory changes induced by sodium metabisulfite, a preservative agent, in rats. Exp Neurobiol 22(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.5607/en.2013.22.1.23
Kandel E, Siegelbaum AS (2013) Cellular mechanisms of implicit memory storage and biological basis of individuality. In: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ (eds) Principles of neural science, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1462–1476
Hebb DO (1949) Summation and learning in perception. The organization of behavior: a neuropsychological theory, 1st edn. Chapman-Hall Companies, New York, pp 17–38
Matsuzaki M, Honkura N, Ellis-Davies GC, Kasai H (2004) Structural basis of long-term potentiation in single dendritic spines. Nature 429:761–766. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02617
Bliss TV, Cooke SF (2011) Long-term potentiation and long-term depression: a clinical perspective. Clinics 66:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1807-59322011001300002
Malenka RC, Nicoll RA (1999) Long-term potentiation—a decade of progress? Science 285(5435):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5435.1870
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 36:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/361031a0
Bramham CR, Messaoudi E (2005) BDNF function in adult synaptic plasticity: the synaptic consolidation hypothesis. Prog Neurobiol 76:99–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.06.003
Messaoudi E, Kanhema T, Soulé J, Tiron A, Dagyte G, da Silva B, Bramham CR (2007) Sustained Arc/Arg3. 1 synthesis controls long-term potentiation consolidation through regulation of local actin polymerization in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci 27:10445–10455. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2883-07.2007
Steward O, Worley PF (2001) Selective targeting of newly synthesized Arc mRNA to active synapses requires NMDA receptor activation. Neuron 30:227–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00275-6
Gil-Bea FJ, Solas M, Mateos L, Winblad B, Ramírez MJ, Cedazo-Mínguez A (2011) Cholinergic hypofunction impairs memory acquisition possibly through hippocampal Arc and BDNF downregulation. Hippocampus 21:999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20812
Greengard P, Valtorta F, Czernik AJ, Benfenati F (1993) Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science 259:780–785. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8430330
Llinas R, McGuinness T, Leonard C, Sugimori M, Greengard P (1985) Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci 82:3035–3039. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035
Nayak AS, Moore CI, Browning MD (1996) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II phosphorylation of the presynaptic protein synapsin I is persistently increased during long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:15451–15456. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.26.15451
Grothe M, Zaborszky L, Atienza M, Gil-Neciga E, Rodriguez-Romero R, Teipel SJ, Amunts K, Suarez-Gonzalez A, Cantero JL (2010) Reduction of basal forebrain cholinergic system parallels cognitive impairment in patients at high risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex 20:1685–1695. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp232
Teipel S, Heinsen H, Amaro E Jr., Grinberg LT, Krause B, Grothe M (2014) Cholinergic basal forebrain atrophy predicts amyloid burden in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 35:482–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.09.029
Bannerman DM, Sprengel R, Sanderson DJ, McHugh SB, Rawlins JN, Monyer H, Seeburg PH (2014) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nat Rev Neurosci 15:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3677
Gunnison AF, Palmes ED (1973) Persistence of plasma S-sulfonates following exposure of rabbits to sulfite and sulfur dioxide. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 24(2):266–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008x(73)90147-6
Scheff SW, Roberts KN (2016) Cognitive assessment of pycnogenol therapy following traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Lett 634:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.10.016
Navarro AAL, Sikoglu EM, Heinze CR, Rogan RC, Russell VA, King JA, Moore CM (2014) Effect of diet on brain metabolites and behavior in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Behav Brain Res 270:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.05.013
Roozendaal B, Hernandez A, Cabrera SM, Hagewoud R, Malvaez M, Stefanko DP, Haettig J, Wood MA (2010) Membrane-associated glucocorticoid activity is necessary for modulation of long-term memory via chromatin modification. J Neurosci 30:5037–5046. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5717-09.2010
Omidi G, Rezvani-Kamran A, Ganji A, Komaki S, Etaee F, Asadbegi M, Komaki A (2020) Effects of Hypericum scabrum extract on dentate gyrus synaptic plasticity in high fat diet-fed rats. J Physiol Sci 70:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12576-020-00747-0
Nazari M, Komaki A, Salehi I, Sarihi A, Shahidi S, Komaki H, Ganji A (2016) Interactive effects of AM251 and baclofen on synaptic plasticity in the rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res 1651:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.09.029
Süer C, Dolu N, Artis AS, Sahin L, Yilmaz A, Cetin A (2011) The effects of long-term sleep deprivation on the long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus and brain oxidation status in rats. Neurosci Res 70:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2011.01.008
Santos-Fandila A, Zafra-Gómez A, Barranco A, Navalon A, Rueda R, Ramirez M (2013) Quantitative determination of neurotransmitters, metabolites and derivates in microdialysates by UHPLC–tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 114:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.03.082
McGovern S, Maguire ME, Gurd RS, Mahler HR, Moore WJ (1973) Seperation of adrenergic and cholinergic synaptosomes from immature rat brain. FEBS Lett 32(2):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(73)80101-2
Vandevijvere S, Temme E, Andjelkovic M, De Wil M, Vinkx C, Goeyens L, Van Loco J (2010) Estimate of intake of sulfites in the Belgian adult population. Food Addit Contam 27:1072–1083. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440041003754506
Hui JY, Beery JT, Higley NA, Taylor SL (1989) Comparative subchronic oral toxicity of sulphite and acetaldehyde hydroxysulphonate in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 27(6):349–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(89)90140-3
Ozturk N, Yargicoglu P, Derin N, Akpinar D, Agar A, Aslan M (2011) Dose-dependent effect of nutritional sulfite intake on visual evoked potentials and lipid peroxidation. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33:244–254.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2010.09.002
Gunnison A (1981) Sulphite toxicity: a critical review of in vitro and in vivo data. Food Cosmet Toxicol 19:667–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/0015-6264(81)90519-8
Lester MR (1995) Sulfite sensitivity: significance in human health. J Am Coll Nutr 14:229–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1995.10718500
Til HP, Feron VJ, De Groot AP (1972) The toxicity of sulphite. I. Long-term feeding and multigeneration studies in rats. Food Cosmet Toxicol 10:291–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0015-6264(72)80250-5
Green LF (1976) Sulphur dioxide and food preservation-a review. Food Chem 1:103–124
Basaranlar G, Derin N, Kencebay-Manas C, Tanriover G, Aslan M (2019) The effects of sulfite on cPLA2, caspase-3, oxidative stress and locomotor activity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 123:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.11.021
Paredes D, Rada P, Bonilla E, Gonzalez LE, Parada M, Hernandez L (1999) Melatonin acts on the nucleus accumbens to increase acetylcholine release and modify the motor activity pattern of rats. Brain Res 850:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(99)01992-7
Day J, Damsma G, Fibiger HC (1991) Cholinergic activity in the rat hippocampus, cortex and striatum correlates with locomotor activity: an in vivo microdialysis study. Pharmacol Biochem and Behav. 38:723–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(91)90233-r
Kruk-Słomka M, Michalak A, Budzyńska B, Biała G (2014) A comparison of mecamylamine and bupropion effects on memory-related responses induced by nicotine and scopolamine in the novel object recognition test in mice. Pharmacol Rep 66:638–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.02.002
Sun J, Sakamoto T, Chung KF (1995) Effects of sodium metabisulphite on guinea pig contractile airway smooth muscle responses in vitro. Thorax 50:875–879. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.50.8.875
Bliss TV, Lømo T (1973) Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol 232:331–356. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273
Zuazaga C, Steinacker A, Castillo Jd (1984) The role of sulfhydryl and disulfide groups of membrane proteins in electrical conduction and chemical transmission. PR Health Sci J. 3:125–139
Sato K, Morimoto K, Suemaru S, Sato T, Yamada N (2000) Increased synapsin I immunoreactivity during long-term potentiation in rat hippocampus. Brain Res 872(1–2):219–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(00)02460-4
Orta-Salazar E, Cuellar-Lemus C, Díaz-Cintra S, Feria-Velasco A (2014) Cholinergic markers in the cortex and hippocampus of some animal species and their correlation to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurología (English Edition) 29:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrl.2012.10.007
Mineur YS, Picciotto MR (2021) The role of acetylcholine in negative encoding bias: Too much of a good thing? Eur J Neurosci 53(1):114–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.14641
Steinacker A (1982) Presynaptic effects of sodium bisulfite at the frog neuromuscular junction. Prog Neurobiol 7:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.490070309
Rojas L, Zuazaga C, Steinacker A (1991) Acetylcholine receptor channel gating and conductance involve extracellular disulfide bond (s). Brain Res 551:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(91)90906-C
Inoue H, Li YP, Wagner JA, Hersh LB (1995) Expression of the choline acetyltransferase gene depends on protein kinase A activity. J Neurochem 64:985–990. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.64030985.x
Guesmi F, Bellamine H, Landoulsi A (2018) Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress, acetylcholinesterase inhibition, and mediated brain injury attenuated by Thymus algeriensis. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43:1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2018-0107
Derin N, Yargiçoğlu P, Aslan M, Elmas O, Agar A, Alicigüzel Y (2006) The effect of sulfite and chronic restraint stress on brain lipid peroxidation and anti-oxidant enzyme activities. Toxicol Ind Health 22(6):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1191/0748233706th264oa
Shad MA, Zafar ZI, Nawaz H, Anwar F (2012) Effect of sorbic acid and some other food preservatives on human serum cholinesterase activity. Afr J Biotechnol 11:11280–11286. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.4037
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Foundation of Akdeniz University, Antalya, Turkey (Grant number [TDK-2018-3762]). Author Narin Derin has received research support from Akdeniz University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by BD, GA, DK, ÇGS and MA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by BD and supervision, project administration is ND. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant financial or non-financial interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Akdeniz University (Date 24.01.2018/No 24).”
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Danışman, B., Akçay, G., Gökçek-Saraç, Ç. et al. The Role of Acetylcholine on the Effects of Different Doses of Sulfite in Learning and Memory. Neurochem Res 47, 3331–3343 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03684-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03684-z