Abstract
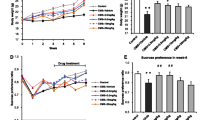
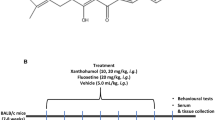
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the protective effect of Palmatine on LPS-induced depressive like behavior and explore its potential mechanism. The mice were intragastrically treated with Fluoxetine or Palmatine once daily for 1 week. After the last drug administration, the mice were intraperitoneally challenged with LPS and suffered for Sucrose preference test, Tail suspension test, Forced swimming test and Open field test. The pro-inflammatory biomarkers were measured by ELISA, qPCR, WB and immunofluorescence. As a result, the administration of Palmatine effectively lessened depressive-like behavior. Palmatine could decrease the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, the expressions of CD68, iNOS mRNA, as well as increase the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4, IL-10, the expressions of CD206, Arg1 mRNA, Ym1 mRNA both in LPS-induced mice and in LPS-induced BV2 cells. The beneficial effect of Palmatine might be attributed to the suppression of M1 microglia polarization and the promotion of M2 microglia polarization via PDE4B/KLF4 signaling. The similar results were observed in CUMS-induced depressive mice. The transfection with PDE4B SiRNA or KLF4 SiRNA indicated that PDE4B and KLF4 were both involved in the Palmatine-mediated microglia polarization. Molecular docking indicated that Palmatine could interact with PDE4B. In conclusion, this research demonstrated that Palmatine attenuated depressive like behavior by modulating microglia polarization via PDE4B/KLF4 signaling.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia B, Huang X, Sun G, Tao W (2021) Iridoids from Gardeniae fructus ameliorates depression by enhancing synaptic plasticity via AMPA receptor-mTOR signaling. J Ethnopharmacol 268:113665
Yirmiya R (1996) Endotoxin produces a depressive-like episode in rats. Brain Res 711:163–174
Hongxia L, Yuxiao T, Zhilei S, Yan S, Yicui Q, Jiamin S, Xin X, Jianxin Y, Fengfeng M, Hui S (2019) Zinc inhibited LPS-induced inflammatory responses by upregulating A20 expression in microglia BV2 cells. J Affect Disord 249:136–142
Chen T, Zheng M, Li Y, Liu S, He L (2020) The role of CCR5 in the protective effect of Esculin on lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive symptom in mice. J Affect Disord 277:755–764
Zheng M, Li K, Chen T, Liu S, He L (2021) Geniposide protects depression through BTK/JAK2/STAT1 signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive mice. Brain Res Bull 170:65–73
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Sasaki I, Yamashita T, Hosoi M, Kato TA, Tsuda M (2020) Involvement of exchange protein directly activated by cAMP and tumor progression locus 2 in IL-1β production in microglial cells following activation of β-adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Sci 143:133–140
Ramezani S, Vousooghi N, Ramezani Kapourchali F, Yousefzadeh-Chabok S, Reihanian Z, Alizadeh AM, Khodayari S, Khodayari H (2019) Rolipram optimizes therapeutic effect of bevacizumab by enhancing proapoptotic, antiproliferative signals in a glioblastoma heterotopic model. Life Sci 239:116880
Schreiber R, Hollands R, Blokland A (2020) A Mechanistic Rationale for PDE-4 Inhibitors to Treat Residual Cognitive Deficits in Acquired Brain Injury. Curr Neuropharmacol 18:188–201
Wang W, Zhang XY, Feng ZG, Wang DX, Zhang H, Sui B, Zhang YY, Zhao WX, Fu Q, Xu ZP, Mi WD (2017) Overexpression of phosphodiesterase-4 subtypes involved in surgery-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction in mice. Brain Res Bull 130:274–282
Guo J, Lin P, Zhao X, Zhang J, Wei X, Wang Q, Wang C (2014) Etazolate abrogates the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced downregulation of the cAMP/pCREB/BDNF signaling, neuroinflammatory response and depressive-like behavior in mice. Neuroscience 263:1–14
Rane MJ, Zhao Y, Cai L (2019) Krϋppel-like factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine 40:743–750
Wen M, Ye J, Han Y, Huang L, Yang H, Jiang W, Chen S, Zhong W, Zeng H, Li DY (2018) Hypertonic saline regulates microglial M2 polarization via miR-200b/KLF4 in cerebral edema treatment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499:345–353
Tarabasz D, Kukula-Koch W (2020) Palmatine: A review of pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res 34:33–50
Liu L, He L, Yin C, Huang R, Shen W, Ge H, Sun M, Li S, Gao Y, Xiong W (2020) Effects of palmatine on BDNF/TrkB-mediated trigeminal neuralgia. Sci Rep 10:4998
Dhingra D, Kumar V (2012) Memory-enhancing activity of palmatine in mice using elevated plus maze and morris water maze. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2012:357368
Dhingra D, Bhankher A (2014) Behavioral and biochemical evidences for antidepressant-like activity of palmatine in mice subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Pharmacol Rep 66:1–9
Du J, Yu Y, Qiu L, Qiu M, Zhu Q (2019) Palmatine plays a role in sedation and hypnosis by increasing 5-hydroxytryptamine. Cellular and molecular biology. France) 65:69–75(Noisy-le-Grand
Chen T, Liu S, Zheng M, Li Y, He L (2021) The effect of geniposide on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice through BTK/TLR4/NF-κB and BDNF/TrkB signaling pathways. Phytother Res 35:932–945
Zhang J, Yi S, Li Y, Xiao C, Liu C, Jiang W, Yang C, Zhou T (2020) The antidepressant effects of asperosaponin VI are mediated by the suppression of microglial activation and reduction of TLR4/NF-κB-induced IDO expression. Psychopharmacology 237:2531–2545
Coull JA, Beggs S, Boudreau D, Boivin D, Tsuda M, Inoue K, Gravel C, Salter MW, De Koninck Y (2005) BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature 438:1017–1021
Miao H, Li R, Han C, Lu X, Zhang H (2018) Minocycline promotes posthemorrhagic neurogenesis via M2 microglia polarization via upregulation of the TrkB/BDNF pathway in rats. J Neurophysiol 120:1307–1317
Liu B, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Liu M, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Song C (2021) ω-3 DPA Protected Neurons from Neuroinflammation by Balancing Microglia M1/M2 Polarizations through Inhibiting NF-κB/MAPK p38 Signaling and Activating Neuron-BDNF-PI3K/AKT Pathways. Marine drugs 19
Liao L, Zhang XD, Li J, Zhang ZW, Yang CC, Rao CL, Zhou CJ, Zeng L, Zhao LB, Fang L, Yang DY, Xie P (2017) Pioglitazone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behaviors, modulates NF-κB/IL-6/STAT3, CREB/BDNF pathways and central serotonergic neurotransmission in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 49:178–186
Li J, Wang H, Du C, Jin X, Geng Y, Han B, Ma Q, Li Q, Wang Q, Guo Y, Wang M, Yan B (2020) hUC-MSCs ameliorated CUMS-induced depression by modulating complement C3 signaling-mediated microglial polarization during astrocyte-microglia crosstalk. Brain Res Bull 163:109–119
Kaushik DK, Thounaojam MC, Kumawat KL, Gupta M, Basu A (2013) Interleukin-1β orchestrates underlying inflammatory responses in microglia via Krüppel-like factor 4. J Neurochem 127:233–244
Lin S, Wen Z, Li S, Chen Z, Li C, Ouyang Z, Lin C, Kuang M, Xue C, Ding Y (2022) LncRNA Neat1 promotes the macrophage inflammatory response and acts as a therapeutic target in titanium particle-induced osteolysis. Acta biomaterialia
Katz JP, Perreault N, Goldstein BG, Lee CS, Labosky PA, Yang VW, Kaestner KH (2002) The zinc-finger transcription factor Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon. Development 129:2619–2628
Kapoor N, Niu J, Saad Y, Kumar S, Sirakova T, Becerra E, Li X, Kolattukudy PE (2015) Transcription factors STAT6 and KLF4 implement macrophage polarization via the dual catalytic powers of MCPIP. J Immunol 194:6011–6023
Kaushik DK, Gupta M, Das S, Basu A (2010) Krüppel-like factor 4, a novel transcription factor regulates microglial activation and subsequent neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 7:68
Ji J, Wang J, Yang J, Wang XP, Huang JJ, Xue TF, Sun XL (2019) The Intra-nuclear SphK2-S1P Axis Facilitates M1-to-M2 Shift of Microglia via Suppressing HDAC1-Mediated KLF4 Deacetylation. Front Immunol 10:1241
Lorenz DR, Misra V, Gabuzda D (2019) Transcriptomic analysis of monocytes from HIV-positive men on antiretroviral therapy reveals effects of tobacco smoking on interferon and stress response systems associated with depressive symptoms. Hum Genomics 13:59
Hedde JR, Hanks AN, Schmidt CJ, Hughes ZA (2017) The isozyme selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, ABI-4, attenuates the effects of lipopolysaccharide in human cells and rodent models of peripheral and CNS inflammation. Brain Behav Immun 64:285–295
Rock RB, Hu S, Deshpande A, Munir S, May BJ, Baker CA, Peterson PK, Kapur V (2005) Transcriptional response of human microglial cells to interferon-gamma. Genes Immun 6:712–719
Jin SL, Conti M (2002) Induction of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase PDE4B is essential for LPS-activated TNF-alpha responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:7628–7633
Ernst O, Failayev H, Athamna M, He H, Tsfadia Y, Zor T (2020) A dual and conflicting role for imiquimod in inflammation: A TLR7 agonist and a cAMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Biochem Pharmacol 182:114206
Ghosh M, Garcia-Castillo D, Aguirre V, Golshani R, Atkins CM, Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD, Pearse DD (2012) Proinflammatory cytokine regulation of cyclic AMP-phosphodiesterase 4 signaling in microglia in vitro and following CNS injury. Glia 60:1839–1859
Avila DV, Myers SA, Zhang J, Kharebava G, McClain CJ, Kim HY, Whittemore SR, Gobejishvili L, Barve S (2017) Phosphodiesterase 4b expression plays a major role in alcohol-induced neuro-inflammation. Neuropharmacology 125:376–385
Li H, Fan C, Feng C, Wu Y, Lu H, He P, Yang X, Zhu F, Qi Q, Gao Y, Zuo J, Tang W (2019) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 attenuates murine ulcerative colitis through interference with mucosal immunity. Br J Pharmacol 176:2209–2226
Hedde JR, Hanks AN, Schmidt CJ, Hughes ZA (2017) The isozyme selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, ABI-4, attenuates the effects of lipopolysaccharide in human cells and rodent models of peripheral and CNS inflammation. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 64:285–295
Rutter AR, Poffe A, Cavallini P, Davis TG, Schneck J, Negri M, Vicentini E, Montanari D, Arban R, Gray FA, Davies CH, Wren PB (2014) GSK356278, a potent, selective, brain-penetrant phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that demonstrates anxiolytic and cognition-enhancing effects without inducing side effects in preclinical species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 350:153–163
You T, Cheng Y, Zhong J, Bi B, Zeng B, Zheng W, Wang H, Xu J (2017) Roflupram, a Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibitior, Suppresses Inflammasome Activation through Autophagy in Microglial Cells. ACS Chem Neurosci 8:2381–2392
Wang H, Zhang F-F, Xu Y, Fu H-R, Wang X-D, Wang L, Chen W, Xu X-Y, Gao Y-F, Zhang J-G, Zhang H-T (2020) The Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitor Roflumilast, a Potential Treatment for the Comorbidity of Memory Loss and Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preclinical Study in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 23:700–711
Choi H, Roh J (2020) LH-induced Transcriptional Regulation of Klf4 Expression in Granulosa Cells Occurs via the cAMP/PKA Pathway and Requires a Putative Sp1 Binding Site. Int J Mol Sci 21:7385
Wu HY, Tang XQ, Liu H, Mao XF, Wang YX (2018) Both classic Gs-cAMP/PKA/CREB and alternative Gs-cAMP/PKA/p38β/CREB signal pathways mediate exenatide-stimulated expression of M2 microglial markers. J Neuroimmunol 316:17–22
Bi C, Fu Y, Zhang Z, Li B (2020) Prostaglandin E2 confers protection against diabetic coronary atherosclerosis by stimulating M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the CREB/BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway. Faseb j 34:7360–7371
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by teaching and research project of Jiangsu Health Vocational College(JKA201815, JKC201939, JKA202003), Natural science fund for colleges and universities in Jiangsu Province(21KJB310011) and enterprise practice training project for young teachers in Higher Vocational Colleges of Jiangsu Province(2020QYSJPX115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Li, M., Zhu, C. et al. The protective effect of Palmatine on depressive like behavior by modulating microglia polarization in LPS-induced mice. Neurochem Res 47, 3178–3191 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03672-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03672-3