Abstract
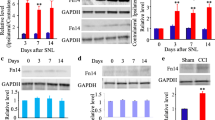
Neuropathic pain (NP) has complicated pathogenesis as it mainly involves a lesion or dysfunction of the somatosensory nervous system and its clinical treatment remains challenging. Chronic constriction injury (CCI) model is a widely used neuropathic pain model and involved in mechanisms including both nerve inflammatory and injury. Cytokines and their receptors play essential roles in the occurrence and persistence of neuropathic pain, but the underlying mechanisms have not well been understood. Therefore, Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) is chosen to explore the possible mechanisms of NP. In the present study, IRAK1 was found to persistently increase in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and spinal cord (SC) during CCI detected by western blot. The staining further confirmed that IRAK1 was mainly co-located in the DRG astrocytes or SC neurons, but less in the DRG microglia or SC astrocytes. Moreover, the region of increased IRAK1 expression was observed in superficial laminae of the spinal dorsal horn, which was the nociceptive neuronal expression domain, suggesting that IRAK1 may mediated CCI-induced pain by nociceptive primary afferent. In addition, intrathecal injection of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) inhibitor or IRAK1 siRNA decreased the expression of IRAK1 accompanied with the alleviation of CCI-induced neuropathic pain. The upregulation of p-NF-κB expression was reversed by IRAK1 siRNA in SC, and intrathecal injection of p-NF-κB inhibitor relieved neuropathic pain. Taking together, targeting IRAK1 may be a potential treatment for chronic neuropathic pain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ochoa JL (2009) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 72(14):1282–1283. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000346325.50431.5f
Zhu X, Cao S, Zhu MD, Liu JQ, Chen JJ, Gao YJ (2014) Contribution of chemokine CCL2/CCR2 signaling in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord to the maintenance of neuropathic pain in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation. J Pain 15(5):516–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2014.01.492
Nishimoto S, Okada K, Tanaka H, Okamoto M, Fujisawa H, Okada T, Naiki M, Murase T, Yoshikawa H (2016) Neurotropin attenuates local inflammatory response and inhibits demyelination induced by chronic constriction injury of the mouse sciatic nerve. Biologicals 44(4):206–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biologicals.2016.03.005
de Souza Grava AL, Ferrari LF, Defino HL (2012) Cytokine inhibition and time-related influence of inflammatory stimuli on the hyperalgesia induced by the nucleus pulposus. Eur Spine J 21(3):537–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2027-8
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Chemokines, neuronal-glial interactions, and central processing of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Ther 126(1):56–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.01.002
Hashizume H, DeLeo JA, Colburn RW, Weinstein JN (2000) Spinal glial activation and cytokine expression after lumbar root injury in the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25(10):1206–1217
Gwak YS, Hulsebosch CE, Leem JW (2017) Neuronal–glial interactions maintain chronic neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Neural Plast 2017:2480689. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2480689
Wang H, Hao P, Zhang H, Xu C, Zhao J (2018) MicroRNA-223 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by directly targeting Irak1 in the nucleus pulposus cells of intervertebral disc. IUBMB Life. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1747
Chou CK, Chi SY, Huang CH, Chou FF, Huang CC, Liu RT, Kang HY (2016) IRAK1, a target of miR-146b, reduces cell aggressiveness of human papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101(11):4357–4366. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2016-2276
Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X (1996) IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 271(5252):1128–1131
Janssens S, Beyaert R (2003) Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members. Mol Cell 11(2):293–302
Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M, Kurama T, Goeddel DV (1996) TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383(6599):443–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/383443a0
Wesche H, Henzel WJ, Shillinglaw W, Li S, Cao Z (1997) MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 7(6):837–847
Christianson CA, Dumlao DS, Stokes JA, Dennis EA, Svensson CI, Corr M, Yaksh TL (2011) Spinal TLR4 mediates the transition to a persistent mechanical hypersensitivity after the resolution of inflammation in serum-transferred arthritis. Pain 152(12):2881–2891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.09.020
Tanga FY, Nutile-McMenemy N, DeLeo JA (2005) The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(16):5856–5861. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0501634102
Li Y, Zhang H, Zhang H, Kosturakis AK, Jawad AB, Dougherty PM (2014) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling contributes to Paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Pain 15(7):712–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2014.04.001
Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H (2002) IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(8):5567–5572. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.082100399
Talreja J, Talwar H, Ahmad N, Rastogi R, Samavati L (2016) Dual inhibition of Rip2 and IRAK1/4 regulates IL-1beta and IL-6 in sarcoidosis alveolar macrophages and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol 197(4):1368–1378. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1600258
Li X, Commane M, Burns C, Vithalani K, Cao Z, Stark GR (1999) Mutant cells that do not respond to interleukin-1 (IL-1) reveal a novel role for IL-1 receptor-associated kinase. Mol Cell Biol 19(7):4643–4652
Adams AK, Bolanos LC, Dexheimer PJ, Karns RA, Aronow BJ, Komurov K, Jegga AG, Casper KA, Patil YJ, Wilson KM, Starczynowski DT, Wells SI (2015) IRAK1 is a novel DEK transcriptional target and is essential for head and neck cancer cell survival. Oncotarget 6(41):43395–43407. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6028
Kollewe C, Mackensen AC, Neumann D, Knop J, Cao P, Li S, Wesche H, Martin MU (2004) Sequential autophosphorylation steps in the interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 regulate its availability as an adapter in interleukin-1 signaling. J Biol Chem 279(7):5227–5236. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M309251200
Thomas JA, Allen JL, Tsen M, Dubnicoff T, Danao J, Liao XC, Cao Z, Wasserman SA (1999) Impaired cytokine signaling in mice lacking the IL-1 receptor-associated kinase. J Immunol 163(2):978–984
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16(2):109–110
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63
Belarbi K, Jopson T, Tweedie D, Arellano C, Luo W, Greig NH, Rosi S (2012) TNF-alpha protein synthesis inhibitor restores neuronal function and reverses cognitive deficits induced by chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflamm 9:23. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-23
Murakami Y, Mizoguchi F, Saito T, Miyasaka N, Kohsaka H (2012) p16(INK4a) exerts an anti-inflammatory effect through accelerated IRAK1 degradation in macrophages. J Immunol 189(10):5066–5072. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1103156
Gao Y, Xu X, Feng J, Ma Y, Zheng D, Meng Y, Shan F (2016) Effects of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 RNA interference in dendritic cells on inflammatory cytokine release and T-cell proliferation. Mol Med Rep 14(6):5685–5692. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5946
Zhang ZJ, Jiang BC, Gao YJ (2017) Chemokines in neuron-glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2513-1
Piao Y, Gwon DH, Kang DW, Hwang TW, Shin N, Kwon HH, Shin HJ, Yin Y, Kim JJ, Hong J, Kim HW, Kim Y, Kim SR, Oh SH, Kim DW (2018) TLR4-mediated autophagic impairment contributes to neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury mice. Mol Brain 11(1):11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-018-0354-y
Pan R, Di H, Zhang J, Huang Z, Sun Y, Yu W, Wu F (2015) Inducible lentivirus-mediated siRNA against TLR4 reduces nociception in a rat model of bone cancer pain. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/523896
Nong X, Lan Y (2018) Picroside II attenuates CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats by inhibiting spinal reactive astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation through the NF-kappaB pathway. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2518-7
Lu Y, Jiang BC, Cao DL, Zhang ZJ, Zhang X, Ji RR, Gao YJ (2014) TRAF6 upregulation in spinal astrocytes maintains neuropathic pain by integrating TNF-alpha and IL-1beta signaling. Pain 155(12):2618–2629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.09.027
Lv F, Huang Y, Lv W, Yang L, Li F, Fan J, Sun J (2017) MicroRNA-146a ameliorates inflammation via TRAF6/NF-kappaB pathway in intervertebral disc cells. Med Sci Monit 23:659–664
Su J, Richter K, Zhang C, Gu Q, Li L (2007) Differential regulation of interleukin-1 receptor associated kinase 1 (IRAK1) splice variants. Mol Immunol 44(5):900–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2006.03.021
Rao N, Nguyen S, Ngo K, Fung-Leung WP (2005) A novel splice variant of interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-associated kinase 1 plays a negative regulatory role in Toll/IL-1R-induced inflammatory signaling. Mol Cell Biol 25(15):6521–6532. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.15.6521-6532.2005
Yanagisawa K, Tago K, Hayakawa M, Ohki M, Iwahana H, Tominaga S (2003) A novel splice variant of mouse interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) activates nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Biochem J 370(Pt 1):159–166. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20021218
Shan SJ, Liu DZ, Wang L, Zhu YY, Zhang FM, Li T, An LG, Yang GW (2015) Identification and expression analysis of irak1 gene in common carp Cyprinus carpio L.: indications for a role of antibacterial and antiviral immunity. J Fish Biol 87(2):241–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.12714
Jensen LE, Whitehead AS (2001) IRAK1b, a novel alternative splice variant of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK), mediates interleukin-1 signaling and has prolonged stability. J Biol Chem 276(31):29037–29044. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M103815200
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
Kim JE, Kim SY, Lim SY, Kieff E, Song YJ (2014) Role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II-IRAK1 interaction in LMP1-induced NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 34(3):325–334. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00912-13
Wu J, Peng S, Xiao L, Cheng X, Kuang H, Zhu M, Zhang D, Jiang C, Liu T (2018) Cell-type specific distribution of T-type calcium currents in lamina II neurons of the rat spinal cord. Front Cell Neurosci 12:370. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00370
Huang SJ, Yan JQ, Luo H, Zhou LY, Luo JG (2018) IL-33/ST2 signaling contributes to radicular pain by modulating MAPK and NF-kappaB activation and inflammatory mediator expression in the spinal cord in rat models of noncompressive lumber disk herniation. J Neuroinflamm 15(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-1021-4
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (Nos. 81502053); Nantong science and technology project (MS22016008); Nantong science and technology project for Young Scientists (WQ2016085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nantong University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, D., Chen, Y., Li, Y. et al. Interleukin-1 Receptor Associated Kinase 1 Mediates the Maintenance of Neuropathic Pain after Chronic Constriction Injury in Rats. Neurochem Res 44, 1214–1227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02767-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02767-8