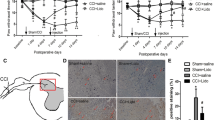
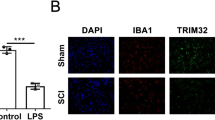
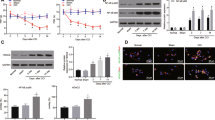
Abstract
E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Caritas B cell lymphoma (c-cbl) is associated with negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases, signal transduction of antigens and cytokine receptors, and immune response. However, the expression and function of c-cbl in the regulation of neuropathic pain after chronic constriction injury (CCI) are unknown. In rat CCI model, c-cbl inhibited the activation of spinal cord microglia and the release of pro-inflammatory factors including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), which alleviated mechanical and heat pain through down-regulating extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Additionally, exogenous TNF-α inhibited c-cbl protein level vice versa. In the primary microglia transfected with c-cbl siRNA, when treated with TNF-α or TNF-α inhibitor, the corresponding secretion of IL-1β and IL-6 did not change. In summary, CCI down-regulated c-cbl expression and induced the activation of microglia, then activated microglia released inflammatory factors via ERK signaling to cause pain. Our data might supply a novel molecular target for the therapy of CCI-induced neuropathic pain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gosselin RD, Suter MR, Ji RR, Decosterd I (2010) Glial cells and chronic pain. Neuroscientist 16:519
Zhang ZJ, Jiang BC, Gao YJ (2017) Chemokines in neuron–glial cell interaction and pathogenesis of neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:1–17
Carballovillalobos AI, Gonzáleztrujano ME, Alvaradovázquez N, Lópezmuñoz FJ (2017) Pro-inflammatory cytokines involvement in the hesperidin antihyperalgesic effects at peripheral and central levels in a neuropathic pain model. Inflammopharmacology 25:1–5
Zuo W, Huang F, Chiang YJ, Li M, Du J, Ding Y, Zhang T, Lee H, Jeong L, Chen Y (2013) c-Cbl-mediated neddylation antagonizes ubiquitination and degradation of the TGF-β type II receptor. Mol Cell 49:499
Caligiuri MA, Briesewitz R, Yu J, Wang L, Wei M, Arnoczky KJ, Marburger TB, Wen J, Perrotti D, Bloomfield CD (2007) Novel c-CBL and CBL-b ubiquitin ligase mutations in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 110:1022–1024
Mohapatra B, Ahmad G, Nadeau S, Zutshi N, An W, Scheffe S, Dong L, Feng D, Goetz B, Arya P, Bailey TA, Palermo N, Borgstahl GE, Natarajan A, Raja SM, Naramura M, Band V, Band H (2013) Protein tyrosine kinase regulation by ubiquitination: critical roles of Cbl-family ubiquitin ligases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:122–139
Bachmaier K, Krawczyk C (2000) Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature 403:211–216
Husnjak K, Dikic I (2012) Ubiquitin-binding proteins: decoders of ubiquitin-mediated cellular functions. Annu Rev Biochem 81:291–322
Qiao G, Zhao Y, Li Z, Tang PQ, Langdon WY, Yang T, Zhang J (2013) T cell activation threshold regulated by E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b determines fate of inducible regulatory T cells. J Immunol 191:632–639
Wallner S, Lutz-Nicoladoni C, Tripp CH, Gastl G, Baier G, Penninger JM, Stoitzner P, Wolf D (2013) The role of the e3 ligase cbl-B in murine dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 8:e65178
Dong L, Li YZ, An HT, Wang YL, Chen SH, Qian YJ, Wang K, Zhen JL, Fan Z, Gong XL (2016) The E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl inhibits microglia-mediated CNS inflammation by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 22:661
Schafer Dorothy P, Lehrman Emily K, Kautzman Amanda G, Koyama R, Mardinly Alan R, Yamasaki R, Ransohoff Richard M, Greenberg Michael E, Barres Ben A, Stevens B (2012) Microglia sculpt postnatal neural circuits in an activity and complement-dependent manner. Neuron 74:691–705
Wu Y, Dissing-Olesen L, MacVicar BA, Stevens B (2015) Microglia: dynamic mediators of synapse development and plasticity. Trends Immunol 36:605–613
Colonna M, Butovsky O (2017) Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol 35:441–468
Colton CA, Wilcock DM (2010) Assessing activation states in microglia. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9:174–191
Masuda T, Prinz M (2016) Microglia: a unique versatile cell in the central nervous system. ACS Chem Neurosci 7:428–434
Cunningham C (2013) Microglia and neurodegeneration: the role of systemic inflammation. Glia 61:71–90
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Hartung JE, Ciszek BP, Nackley AG (2014) beta2- and beta3-adrenergic receptors drive COMT-dependent pain by increasing production of nitric oxide and cytokines. Pain 155:1346–1355
Zhu X, Yao L, Guo A, Li A, Sun H, Wang N, Liu H, Duan Z, Cao J (2014) CAP1 was associated with actin and involved in Schwann cell differentiation and motility after sciatic nerve injury. J Mol Histol 45:337–348
Wallner FK, Hopkins MH, Lindvall T, Olofsson P, Tilevik A (2017) Cytokine correlation analysis based on drug perturbation. Cytokine 90:73–79
Kong H, Omran A, Ashhab MU, Gan N, Peng J, He F, Wu L, Deng X, Yin F (2014) Changes in microglial inflammation-related and brain-enriched microRNAs expressions in response to in vitro oxygen–glucose deprivation. Neurochem Res 39:233–243
Gioia R, Trégoat C, Dumas PY, Lagarde V, Prouzet-Mauléon V, Desplat V, Sirvent A, Praloran V, Lippert E, Villacreces A (2015) CBL controls a tyrosine kinase network involving AXL, SYK and LYN in nilotinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia. J Pathol 237:14–24
Sirvent A, Leroy C, Simon A, Roche V S (2008) The Src-like adaptor protein regulates PDGF-induced actin dorsal ruffles in a c-Cbl-dependent manner. Oncogene 27:3494
Li H, Li T, Fan J, Fan L, Wang S, Weng X, Han Q, Zhao RC (2015) miR-216a rescues dexamethasone suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Differ 22:1935–1945
Kline CL, Olson TL, Irby RB (2009) Src activity alters alpha3 integrin expression in colon tumor cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 26:77
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756
Schäfers M, Svensson CI, Sommer C, Sorkin LS (2003) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation by activation of p38 MAPK in primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci 23:2517–2521
Sommer C, Schäfers M, Marziniak M, Toyka KV (2001) Etanercept reduces hyperalgesia in experimental painful neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst 6:67
Xu JT, Xin WJ, Zang Y, Wu CY, Liu XG (2006) The role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the neuropathic pain induced by Lumbar 5 ventral root transection in rat. Pain 123:306–321
Constantin CE, Mair N, Sailer CA, Andratsch M, Xu ZZ, Blumer MJ, Scherbakov N, Davis JB, Bluethmann H, Ji RR, Kress M (2008) Endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha) requires TNF receptor type 2 to generate heat hyperalgesia in a mouse cancer model. J Neurosci 28:5072–5081
Pelletier C, Varin-Blank N, Rivera J, Iannascoli B, Marchand F, David B, Weyer A, Blank U Pelletier C et al (1998) FcRI-mediated induction of TNF- gene expression in the RBL-2H3 mast cell line: regulation by a novel NF-B-like nuclear binding complex. J Immunol 161:4768–4776
Ping D, Boekhoudt G, Zhang F, Morris A, Philipsen S, Warren ST, Boss JM (2000) Sp1 binding is critical for promoter assembly and activation of the MCP-1 gene by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem 275:1708
You M, Flick LM, Yu D, Feng GS (2001) Modulation of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway by Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase in mediating the induction of interleukin (IL)-6 by IL-1 or tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med 193:101–110
Costa B, Trovato AE, Colleoni M, Giagnoni G, Zarini E, Croci T (2005) Effect of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR141716, on nociceptive response and nerve demyelination in rodents with chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Pain 116:52–61
Komirishetty P, Areti A, Sistla R, Kumar A (2016) Morin mitigates chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress induced PARP over-activation and neuroinflammation. Neurochem Res 41:2029–2042
Gabay E, Tal M (2004) Pain behavior and nerve electrophysiology in the CCI model of neuropathic pain. Pain 110:354–360
Tatsumi E, Yamanaka H, Kobayashi K, Yagi H, Sakagami M, Noguchi K (2015) RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates p38 MAPK activation and morphological changes downstream of P2Y12/13 receptors in spinal microglia in neuropathic pain. Glia 63:216–228
Echeverry S, Shi XQ, Yang M, Huang H, Wu Y, Lorenzo LE, Perez-Sanchez J, Bonin RP, De Koninck Y, Zhang J (2017) Spinal microglia are required for long-term maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain 158:1792–1801
Martini AC, Berta T, Forner S, Chen G, Bento AF, Ji RR, Rae GA (2016) Lipoxin A4 inhibits microglial activation and reduces neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain after spinal cord hemisection. J Neuroinflammation 13:75
Liu X, Zhang Z, Cheng Z, Zhang J, Xu S, Liu H, Jia H, Jin Y (2016) Spinal heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) exerts antinociceptive effects against neuropathic pain in a mouse model of L5 spinal nerve ligation. Pain Med 17:220–229
Wang D, Xue Y, Chen Y, Ruan L, Hong Y (2016) Mas-related gene (Mrg) C receptors inhibit mechanical allodynia and spinal microglia activation in the early phase of neuropathic pain in rats. Neurosci Lett 618:115–121
Zhang T, Sun K, Shen W, Qi L, Yin W, Wang LW (2016) SOCS1 regulates neuropathic pain by inhibiting neuronal sensitization and glial activation in mouse spinal cord. Brain Res Bull 124:231–237
Carswell EA, Old LJ, Kassel RL, Green S, Fiore N, Williamson B (1975) An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3666–3670
Shubayev VI, Myers RR (2001) Axonal transport of TNF-alpha in painful neuropathy: distribution of ligand tracer and TNF receptors. J Neuroimmunol 114:48–56
Zhang H, Zhang H, Dougherty PM (2013) Dynamic effects of TNF-alpha on synaptic transmission in mice over time following sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury. J Neurophysiol 110:1663–1671
Jancalek R, Dubovy P, Svizenska I, Klusakova I (2010) Bilateral changes of TNF-alpha and IL-10 protein in the lumbar and cervical dorsal root ganglia following a unilateral chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. J Neuroinflammation 7:11
Li YY, Wei XH, Lu ZH, Chen JS, Huang QD, Gong QJ (2013) Src/p38 MAPK pathway in spinal microglia is involved in mechanical allodynia induced by peri-sciatic administration of recombinant rat TNF-alpha. Brain Res Bull 96:54–61
Liu YL, Zhou LJ, Hu NW, Xu JT, Wu CY, Zhang T, Li YY, Liu XG (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces long-term potentiation of C-fiber evoked field potentials in spinal dorsal horn in rats with nerve injury: the role of NF-kappa B, JNK and p38 MAPK. Neuropharmacology 52:708–715
Sommer C, Lindenlaub T, Teuteberg P, Schafers M, Hartung T, Toyka KV (2001) Anti-TNF-neutralizing antibodies reduce pain-related behavior in two different mouse models of painful mononeuropathy. Brain Res 913:86–89
Zanella JM, Burright EN, Hildebrand K, Hobot C, Cox M, Christoferson L, McKay WF (2008) Effect of etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor, on neuropathic pain in the rat chronic constriction injury model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 33:227–234
Kundu M, Pathak SK (2009) A TNF- and c-Cbl-dependent FLIP(S)-degradation pathway and its function in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced macrophage apoptosis. Nat Immunol 10:918
Manganaro D, Consonni A, Guidetti GF, Canobbio I, Visconte C, Kim S, Okigaki M, Falasca M, Hirsch E, Kunapuli SP, Torti M (2015) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase beta by the platelet collagen receptors integrin alpha2beta1 and GPVI: the role of Pyk2 and c-Cbl. Biochim Biophys Acta 1853:1879–1888
Dong L, Li YZ, An HT, Wang YL, Chen SH, Qian YJ, Wang K, Zhen JL, Fan Z, Gong XL, Zheng Y, Wang XM (2016) The E3 ubiquitin ligase c-Cbl inhibits microglia-mediated CNS inflammation by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther 22:661–669
Chen SP, Zhou YQ, Liu DQ, Zhang W, Manyande A, Guan XH, Tian YK, Ye DW, Omar DM (2017) PI3K/Akt pathway: a potential therapeutic target for chronic pain. Curr Pharm Des 23:1860–1868
Zhang L, Fu ZJ, Sun T, Zhao XL, Song WG, Jia MR, Wei GF (2010) [Expression of NF-kappaB and TNF-alpha in spinal dorsal horn in a rat model of neuropathic pain]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 90:1067–1071
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81501076, 81401365), the Science and Technology of construction and people’s livelihood Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BL2014061), Jiangsu Province Young Medical Key Talents Project of China (QNRC2016407), the Nantong Science and Technology Innovation Project (No. MS12015056); and the 14th Six Talents Peak Project of Jiangsu Province (No. SWYY-058), and National Natural Youth Science Fund (No. 81702216).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, P., Liu, X., Shen, Y. et al. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase c-cbl Inhibits Microglia Activation After Chronic Constriction Injury. Neurochem Res 43, 1631–1640 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2578-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2578-8