Abstract
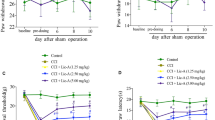
Reactive astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammatory responses in the spinal dorsal horn have been reported to play a pivotal role in pathological pain. Chronic constriction injury (CCI) enhances the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), which is involved in neuropathic pain (NP). Picroside II (PII), a major active component of Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora, has been investigated for its anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic activities. Here, we explored the analgesic effects of PII on a model of CCI-induced NP and investigated the levels of the GFAP protein and the mRNA and protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the spinal cord, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). CCI significantly induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. Intraperitoneal administration of PII remarkably reversed the CCI-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia and reduced the mRNA and protein levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the spinal cord. Additionally, according to the in vitro data, the PII treatment inhibited LPS-induced increases in the mRNA and protein levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α and suppressed the NF-κB pathway by inhibiting the phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 and the degradation of inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) in astrocytes without toxicity to astrocytes. Overall, the analgesic effect of PII correlated with the inhibition of spinal reactive astrocyte-mediated neuroinflammation through the NF-κB pathway in rats with NP.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen SP, Mao J (2014) Neuropathic pain: mechanisms and their clinical implications. BMJ 348:f7656. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f7656
Costigan M, Scholz J, Woolf CJ (2009) Neuropathic pain: a maladaptive response of the nervous system to damage. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135531
van Hecke O, Austin SK, Khan RA, Smith BH, Torrance N (2014) Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 155(4):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.013
Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpaa M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, Treede RD (2011) A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain 152(10):2204–2205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.06.017
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70(18):1630–1635. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
Schestatsky P, Vidor L, Winckler PB, Araujo TG, Caumo W (2014) Promising treatments for neuropathic pain. Arquivos de neuro-psiquiatria 72(11):881–888
Liu F, Yuan H (2014) Role of glia in neuropathic pain. Front Biosci (Landmark Edition) 19:798–807
Jha MK, Jeon S, Suk K (2012) Glia as a link between neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. Immune Netw 12(2):41–47. https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2012.12.2.41
Mika J, Zychowska M, Popiolek-Barczyk K, Rojewska E, Przewlocka B (2013) Importance of glial activation in neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 716(1–3):106–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.01.072
Inoue K, Tsuda M (2018) Microglia in neuropathic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Neurosci 19(3):138–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2018.2
Eto K, Kim SK, Takeda I, Nabekura J (2018) The roles of cortical astrocytes in chronic pain and other brain pathologies. Neurosci Res 126:3–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.08.009
Fattori V, Hohmann MSN (2017) Targeting IL-33/ST2 signaling: regulation of immune function and analgesia. Expert Opin Ther Targets 21(12):1141–1152. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2017.1398734
Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Verri WA Jr, Chiu IM (2017) Nociceptor sensory neuron-immune interactions in pain and inflammation. Trends Immunol 38(1):5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2016.10.001
Wang X, Yang L, Yang L, Xing F, Yang H, Qin L, Lan Y, Wu H, Zhang B, Shi H, Lu C, Huang F, Wu X, Wang Z (2017) Gypenoside IX suppresses p38 MAPK/Akt/NFkappaB signaling pathway activation and inflammatory responses in astrocytes stimulated by proinflammatory mediators. Inflammation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0654-x
Kronschlager MT, Drdla-Schutting R, Gassner M, Honsek SD, Teuchmann HL, Sandkuhler J (2016) Gliogenic LTP spreads widely in nociceptive pathways. Science 354(6316):1144–1148. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah5715
Sommer C, Leinders M, Uceyler N (2018) Inflammation in the pathophysiology of neuropathic pain. Pain 159(3):595–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001122
Ji RR, Berta T, Nedergaard M (2013) Glia and pain: is chronic pain a gliopathy? Pain 154(Suppl 1):S10–S28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.022
Clark AK, Old EA, Malcangio M (2013) Neuropathic pain and cytokines: current perspectives. J Pain Res 6:803–814. https://doi.org/10.2147/jpr.s53660
Guo CJ, Douglas SD, Gao Z, Wolf BA, Grinspan J, Lai JP, Riedel E, Ho WZ (2004) Interleukin-1beta upregulates functional expression of neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) via NF-kappaB in astrocytes. Glia 48(3):259–266. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20079
Shih RH, Wang CY, Yang CM (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8:77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077
Pan YD, Guo QL, Wang E, Ye Z, He ZH, Zou WY, Cheng ZG, Wang YJ (2010) Intrathecal infusion of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate for the prevention and reversal of neuropathic pain in rats using a sciatic chronic constriction injury model. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35(3):231–237. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181df245b
Negi AS, Kumar JK, Luqman S, Shanker K, Gupta MM, Khanuja SP (2008) Recent advances in plant hepatoprotectives: a chemical and biological profile of some important leads. Med Res Rev 28(5):746–772. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20115
Zhu J, Xue B, Ma B, Zhang Q, Liu M, Liu L, Yao D, Qi H, Wang Y, Ying H, Wu Z (2015) A pre-clinical pharmacokinetic study in rats of three naturally occurring iridoid glycosides, Picroside-I, II and III, using a validated simultaneous HPLC-MS/MS assay. Journal of chromatography B. Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 993–994:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.04.036
Zhao L, Guo Y, Ji X, Zhang M (2014) The neuroprotective effect of picroside II via regulating the expression of myelin basic protein after cerebral ischemia injury in rats. BMC Neurosci 15:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-15-25
Liu G, Zhao L, Wang T, Zhang M, Pei H (2014) Optimal therapeutic dose and time window of picroside II in cerebral ischemic injury. Neural Regen Res 9(15):1437–1445. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.139460
Li JZ, Xie MQ, Mo D, Zhao XF, Yu SY, Liu LJ, Wu C, Yang Y (2016) Picroside II protects myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury through inhibition of the inflammatory response. Experim Ther Med 12(6):3507–3514. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3841
Wang Y, Fang W, Wu L, Yao X, Wu S, Wang J, Xu Z, Tian F, He Z, Dong B (2016) Neuroprotective effect of picroside II in brain injury in mice. Am J Transl Res 8(12):5532–5544
Wang L, Liu XH, Chen H, Chen ZY, Weng XD, Qiu T, Liu L (2015) Picroside II protects rat kidney against ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and inflammation by the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Experim Ther Med 9(4):1253–1258. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2225
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33(1):87–107
Keyhanfar F, Shamsi Meymandi M, Sepehri G, Rastegaryanzadeh R, Heravi G (2013) Evaluation of antinociceptive effect of pregabalin in mice and its combination with tramadol using tail flick test. Iran J Pharm Res 12(3):483–493
Meymandi MS, Sepehri G, Mobasher M (2006) Gabapentin enhances the analgesic response to morphine in acute model of pain in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85(1):185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2006.07.037
Wang LX, Wang ZJ (2003) Animal and cellular models of chronic pain. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55(8):949–965
Guo Y, Xu X, Li Q, Li Z, Du F (2010) Anti-inflammation effects of picroside 2 in cerebral ischemic injury rats. Behav Brain Funct 6:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-9081-6-43
Wang L, Liu XH, Chen H, Chen ZY, Weng XD, Qiu T, Liu L (2014) Picroside II decreases the development of fibrosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail 36(9):1443–1448. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022x.2014.949766
Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, Bennett ML, Münch AE, Chung WS, Peterson TC, Wilton DK, Frouin A, Napier BA, Panicker N, Kumar M, Buckwalter MS, Rowitch DH, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Stevens B, Barres BA (2017) Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541(7638):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21029
Wang W, Mei XP, Wei YY, Zhang MM, Zhang T, Wang W, Xu LX, Wu SX, Li YQ (2011) Neuronal NR2B-containing NMDA receptor mediates spinal astrocytic c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Brain Behav Immun 25 (7):1355–1366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.04.002
Gao YJ, Ji RR (2010) Targeting astrocyte signaling for chronic pain. Neurotherapeutics 7(4):482–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2010.05.016
Zhang J, De Koninck Y (2006) Spatial and temporal relationship between monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression and spinal glial activation following peripheral nerve injury. J Neurochem 97(3):772–783. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03746.x
Zhuang ZY, Wen YR, Zhang DR, Borsello T, Bonny C, Strichartz GR, Decosterd I, Ji RR (2006) A peptide c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor blocks mechanical allodynia after spinal nerve ligation: respective roles of JNK activation in primary sensory neurons and spinal astrocytes for neuropathic pain development and maintenance. J Neurosci 26(13):3551–3560. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.5290-05.2006
Wang W, Wang W, Mei X, Huang J, Wei Y, Wang Y, Wu S, Li Y (2009) Crosstalk between spinal astrocytes and neurons in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. PloS ONE 4(9):e6973. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006973
Kiguchi N, Kobayashi Y, Kishioka S (2012) Chemokines and cytokines in neuroinflammation leading to neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12(1):55–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2011.10.007
Woolf CJ, Allchorne A, Safieh-Garabedian B, Poole S (1997) Cytokines, nerve growth factor and inflammatory hyperalgesia: the contribution of tumour necrosis factor alpha. Br J Pharmacol 121(3):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0701148
Sommer C, Kress M (2004) Recent findings on how proinflammatory cytokines cause pain: peripheral mechanisms in inflammatory and neuropathic hyperalgesia. Neurosci Lett 361(1–3):184–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.007
Zhang RX, Liu B, Li A, Wang L, Ren K, Qiao JT, Berman BM, Lao L (2008) Interleukin 1beta facilitates bone cancer pain in rats by enhancing NMDA receptor NR-1 subunit phosphorylation. Neuroscience 154(4):1533–1538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.072
Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, Ji RR (2008) Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 28(20):5189–5194. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.3338-07.2008
Shi ZM, Han YW, Han XH, Zhang K, Chang YN, Hu ZM, Qi HX, Ting C, Zhen Z, Hong W (2016) Upstream regulators and downstream effectors of NF-kappaB in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 366:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.05.022
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (No. 2011GXNSFA018222) and Medicine Health Science and Technology Program of Guangxi Province (No. S201414-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nong, X., Lan, Y. Picroside II Attenuates CCI-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats by Inhibiting Spinal Reactive Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Through the NF-κB Pathway. Neurochem Res 43, 1058–1066 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2518-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2518-7